There are always more ideas for creating various products than opportunities to finance production and promotion. Product management helps to set correct priorities and find the optimal strategy for the company’s development. Product management involves planning all business activities and analyzing their ideal order. Equally important is the ability to stop creating irrelevant products – product management can help release the right product at the right time. Product management is also responsible for marketing activities that motivate potential customers to pay attention to the offer.
What Is Product Management?
Product management is a sequence of several global processes:
- Control and correction of product development.
- Bringing the finished product to market.
- Support and upgrade of solutions offered to customers.
The day-to-day responsibilities of product managers include:
- Researching the situation in the desired market segment, studying competitors and the characteristics of potential customers.
- Drawing up a strategy for developing and deploying the product based on the data obtained and the formulation of goals.
- Building a scheme for exchanging information between different company departments, coordinating the development, and laying out the necessary actions, taking into account customer feedback.
Tactical maneuvering tracking details and nuances are not the tasks of these specialists. Instead, they deal with larger issues and show attention to the consumer to determine the direction of product improvement. Why? The technology industry is brimming with innovations that are crowding out obsolete offerings. Therefore, understanding customer needs and striving to provide customized solutions is the main task of product management.
Why Is Product Management Important?
Quality product management allows the company to remain competitive in the face of ever-changing trends. First, newcomers break into a niche – it becomes more difficult to hold positions. Then global players try their hand at atypical segments for their brands. Finally, industries are losing their sharp lines of specialization – you need to test different marketing techniques to stay in the lead. Added to these questions is the complexity of determining optimal pricing and audience needs. Of course, with such various proposals, people are lost and cannot clearly state their desires.
Product managers are responsible for the order and absence of chaos in solving the described issues. They also solve the problems of comfortable interaction between product and sales departments. Their also competence includes processing feedback from consumers.
For the SaaS niche, there is another problem – the short-term relevance of the product. Product managers create roadmaps that provide an opportunity to analyze the future and invest in timely updates that follow trends.
Top 5 Product Manager Skills

Strategic Thinking
Strategic thinking, as a crucially important skill, shows what product management is and how it works. Pro must be able to create a company’s vision of a product and the way to its realization. It may include:
- building roadmaps;
- understanding the market;
- knowing the competitors;
- delegating jobs correctly;
- setting realistic goals.
A strategic thinking person should be a great forecaster and have a critical mindset to be efficient.
Communication Skills
When defining digital product management’s role, we should always remember incredible communication skills. Every working day managers spend hours and hours communicating.
They should have the right approach to motivate the team, get clients’ information, and set goals with team leads. Product management communication may include different forms, such as face-to-face meetings, online and phone conversations, and a lot of written dialogs. Can you make them all efficient?
Coding and Understanding Web Development
While product management services are highly popular in IT, specialists should understand coding and web dev quite well to be productive. It is a basic skill allowing them to build realistic roadmaps and set achievable goals.
Even if a product management role doesn’t require coding directly, this ability allows one to understand the web-development process. The most useful skill is the knowledge of SQL due to enabling powerful analytics.
Market Research Skills
Market research is necessary for efficient lifecycle product management service, especially at the start. When the product is in the idea stage, it is necessary to track its perspectives and your possible revenue from it.
A product manager can delegate tasks to marketing specialists but should understand the main steps. It involves exploring customer needs and staying very client-centric on the development path.
Problem Solving
We see that it is all about solving problems by finding out what product life cycle management is. You’ll have big tasks and deadlines and small daily difficulties appearing every hour. As a professional, you should provide solutions timely.
There might be bugs, database issues, communication problems, and many other obstacles. However, you should be able to keep all of them in mind and provide decisions that consume the least of time and resources, leading a team to economy and meeting deadlines.
Product Management Process
A great idea does not guarantee its transformation into a great product. Many good ideas at the startup stage require careful polishing – product management makes this possible. There is no one-size-fits-all recipe for product management, but the order in which tasks are performed is similar for most companies.
Defining the problem
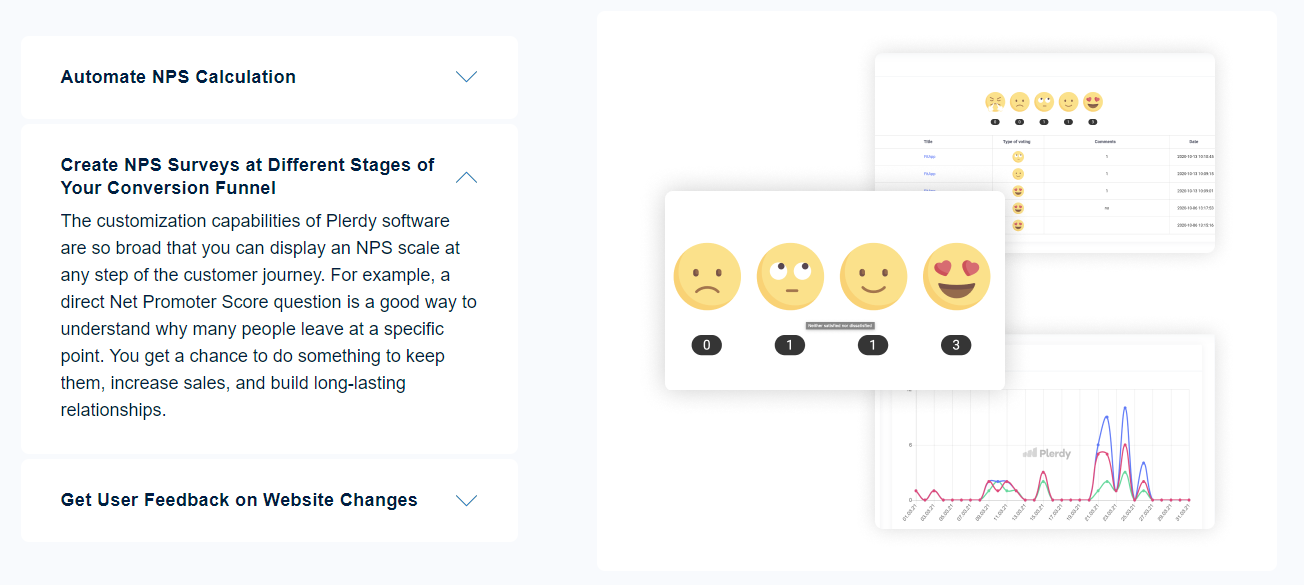
A product or service will have a chance of being successfully implemented if it solves a specific consumer problem or eliminates a pain point. Problems are identified quite easily – with the help of customer communication and analysis of competitors. Then, the product manager gathers information through algorithms to evaluate and prioritize problems. Systematization will allow you to track the status of each problem.
Quantifying the opportunity
Once a high-priority problem has been identified, analysis and opportunity assessment can begin. Here you have to carefully study the market to get acquainted with the activities of competitors. Identifying industry gaps and competing companies’ weaknesses will help you focus on what will be in demand. Clients’ interests (recorded earlier) are also considered at this stage.
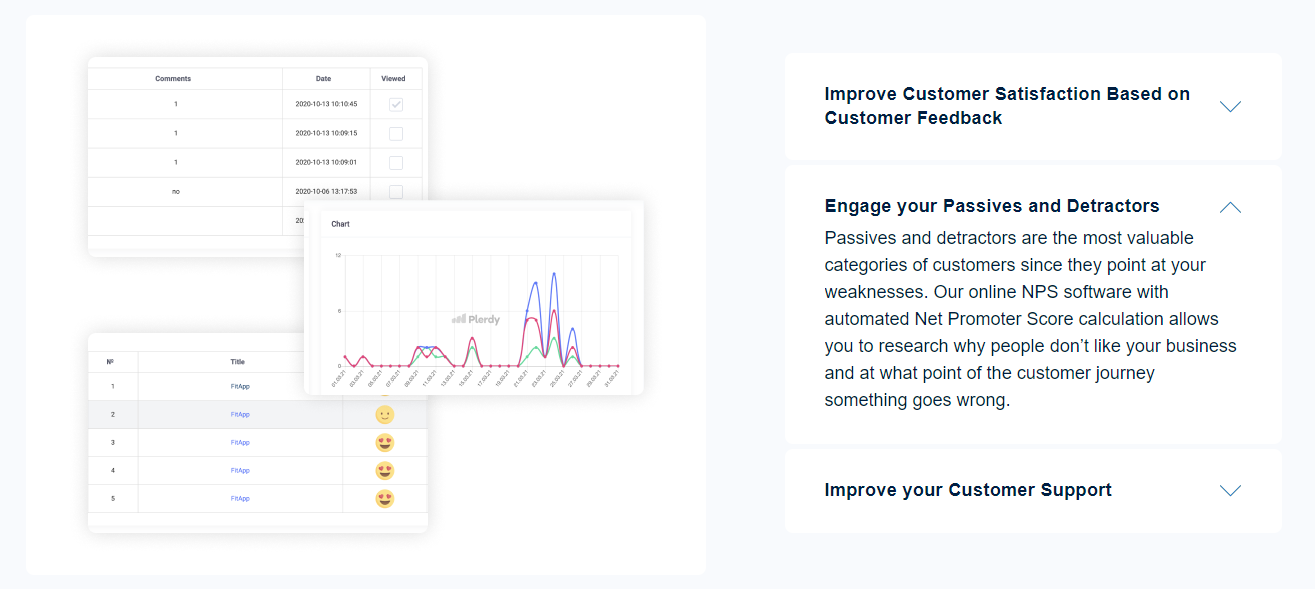
Researching potential solutions
Understanding the gaps in the market and the target audience’s needs makes it possible to find options for solving the problem. This could be generating a new product or adding to existing offerings. Sometimes, adding a new feature immediately takes the company to a higher level of profitability. Therefore, allocating resources wisely and building a clear roadmap is important.
Building an MVP
A quick product launch will not bring returns, but small flaws are acceptable if a web project can change the logic of an entire industry. It is better to start with MVP, focusing on implementing the main options. Don’t waste your energy on non-essential things when building a beta. The landing page will provide an opportunity to see the reaction to the idea and understand where to place emphasis. It is also advisable to develop a mobile version. You can proceed to the next step if there is a minimum viable product.
Creating a feedback loop

Having an MVP allows the creation of a feedback collection system. This can be done in parallel with development processes. For example, when users have received the product, you need to check:
- Are they interacting correctly with the product?
- What improvements should be made?
At this stage, it is worth conducting interviews or surveying the audience. Clarifying questions will allow you to learn more about the nuances of consumer desires.
The collected opinions will be conveyed to the team. The ability to balance all parties’ wishes, requirements, and expectations is one of the key skills of a product manager.
Setting the strategy
After going through the five stages, you can concentrate on creating a promotion strategy and formulating a vision for the long-term development of the product. Previously obtained data allows you to create a realistic roadmap for the life cycle of a new product. It must be specific, set clear goals and describe how to achieve them.
Product Lifecycle Management
The product life cycle is a set of activities implemented when a need is identified in the market. Then, the idea is formulated to support the functionality of the finished product. Implementation, marketing, strategy adjustments and other mandatory components make PLM multifaceted and critical. Among the main advantages of the process, it is worth highlighting:
- Minimization of the development period.
- Optimization of production efforts.
- Understanding when to step up when demand rises or change focus during a decline in demand.
- Effective use of marketing opportunities.
- Constructive allocation of resources (financial, personnel and others).
The end of such a cycle means the end of release and support – the closure of the project. Initially, the term referred to manufacturing industries, but later it became actively used in software development. Let’s consider the components of managing the life cycle of a technological product.
Design

PLM allows combining design, modeling, manufacturing, and other processes. With the help of testing, you can determine the weaknesses of the project and make changes at the design stage. Corrections at the initial phase of work accelerate the pace of project formation and its launch to the market – accordingly, the company receives income earlier. In addition, lifecycle management simplifies the implementation of updates and allows you to respond to audience feedback promptly.
BOM Management
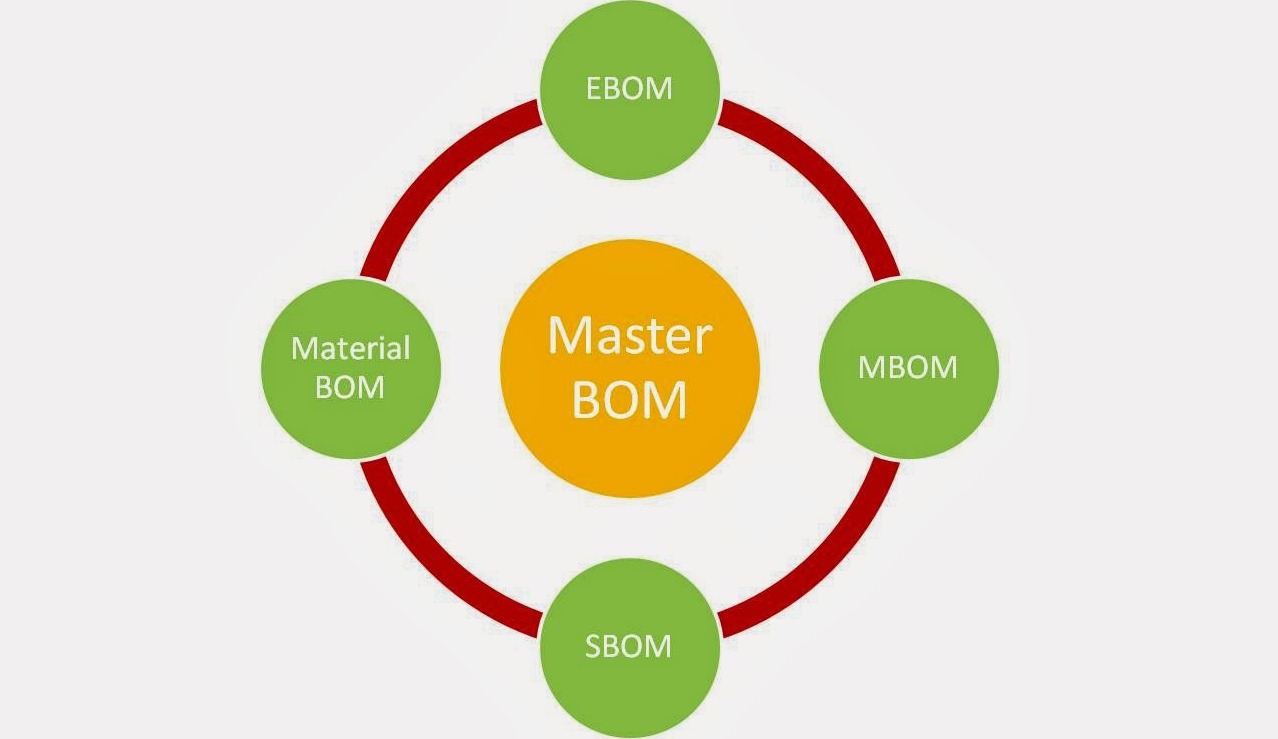
The bill of materials can be called the main component of PLM. The list of components of the project structure plays a crucial role in choosing the right strategy at different stages of work. It may include:
- Equipment.
- Soft.
- Documentation.
- Billing.
- Other options.
Specification management involves the cooperation of different departments and even companies during the design period, the choice of suppliers, and determining the best tactics for presenting the finished product. Using BOM in PLM allows you to synchronize the activities of engineers and other specialists, act more harmoniously and improve the quality of the finished product.
Engineer-to-Order
ETO is a unique approach that implies the maximum involvement of the target audience in the design. Receiving and quickly processing feedback, even at the early stages of creating and testing a product, allows you to bring the most helpful solution adapted to customer needs to the market. Developers, testers, sales managers, and vendors can use ETO to pre-determine which behaviors will help people positively perceive an offer and increase the frequency of its use.
Production
Important aspects of life cycle management are minimizing development costs and organizing production without unnecessary expenses. Also, product managers take care of accelerating the receipt of the product on sale. Following market changes, mistakes often need to be adjusted when designing and building products with frameworks certifications. After the start of sales, there are more such moments: a shift in the audience’s mood can force you to make changes to a product that recently seemed ideal. This area of activity is called change management.
Also, when developing products and supplies, it is necessary to track costs and manage the distribution of funds at each stage. The professionalism of suppliers can also be attributed to production. In addition, all actions during the product launch will have to be discussed to prevent missed deadlines and unpleasant surprises.
Distribution and Service
When the product is produced, it’s time to start promoting it. Make sure that the target audience receives reliable data about the new product. The management of such information (PIM) will allow more active product distribution through the planned channels (direct sales, distribution, and sales via the Internet). Engineers know everything about their projects, but PIM allows you to transform this knowledge into understandable information for customers.
Next, monitoring the audience’s satisfaction remains – the product’s lifespan depends on this factor. Finally, fixing bugs and adding the latest updates will help you gain trust and stay in a segment with any level of competition.
What is Agile Product Management?
Agile product management is an iterative technique that breaks each project phase into smaller tasks. The scheme allows you to check the correctness of the execution of actions and make changes on the go.
The main difference between flexible management and the standard methodology is the ability to change priorities and shift focus at any time. There is more feedback, which increases the likelihood of releasing a beneficial product.
Flexible product management requires management and subordinates to accept business dynamism and readiness for frequent changes. Well-coordinated and transparent work allows you to quickly meet demand and inform customers about the product’s value. The trio of high productivity, speed, and efficiency of the company is formed thanks to:
- Divide significant goals into small subtasks.
- Encourage the self-organization of small teams.
- Permission to meddle in “someone else’s” work.
- A combination of documented specifications and personal communication.
Planning and creating a product moves to a new level. Following traditional sequential approaches considerably slows down processes, so partial product management flexibility is necessary. By the way, the failures of large-scale projects with static controlled to this technique.
Accelerating and separating processes requires more careful tracking of nuances and timely changes to the roadmap. It should also be considered that small priorities should not counter global goals. Reasonable management flexibility is sure to accelerate the team’s progress toward success.
Conclusion
Effective product management consists of support at all stages – from the inception of an idea to the launch of a finished development. Particular emphasis is placed on the consumer’s functionality, convenience, and usefulness. Do you manage to beat your competitors and attract the target audience? Half of the tasks are completed. It remains only to keep the product relevant, release updates, respond wisely to feedback and follow the changes in the market.
