Software quality assurance is a set of actions to test and create preventive measures to avoid errors at all stages of development. There are several approaches to organizing testing: in parallel with the development and before the launch of the finished product. The second option is less convenient and forces you to spend a lot of time fixing the identified bugs. Similar quality assurance involves the collaboration of developers and the QA department at each stage of the program life cycle.
Quality Assurance Software Tester

A quality assurance team typically consists of a test engineer, analyst, architect, manager, and supervisor. In this model, each specialist focuses on a separate work area: management, creating an optimal structure, testing, analysis of processes, and results.
A QA tester is an IT specialist who looks for problems and bugs in computer programs. He ensures that the final product meets quality standards and functional requirements. Together with logic and deduction, he uses manual or automated testing methods in his work.
Manual software testing is a product test without additional programs and scripts. All QA-testers carry out all processes manually. Step by step, they reproduce sets of user scenarios. In an automated approach, scripts are packaged into scripts. They do things like a manual method – compare results, create reports, etc. Depending on the structure of the QA team and the scale of development. Different specialists and the same person can perform both methods.
The QA Engineer is responsible for executing product test plans and is indirectly or directly associated with the development team. At the same time, he does not correct errors independently but only fixes and sends them for revision. For example, when testing a site, you need to:
- Compare the arrangement of elements on pages with the layout and correct display in browsers.
- Check the correct operation of buttons, sliders, pop-ups, and other interactive elements.
- Ensure that the links work and serve the correct content, including when switching to different site language versions.
- Check typography elements, etc.
This is a non-exhaustive list of tasks that a software quality tester performs manually or automatically.
Plerdy QA Testing Tools

Product verification continues after the official release. Regarding the website example, further testing improves performance, efficiency, and business metrics.
Plerdy has several tools for tracking user behavior for these tasks:
- Heatmaps: recreate the user’s path on a web page based on clicks and cursor movement.
- Session recording: reproduces the exact behavior of a web page visitor in video format.
These tools reveal design errors, broken links, lack of dynamic elements. That is, they provide information for analyzing user experience.
12 Quality Assurance Software Tester Skills
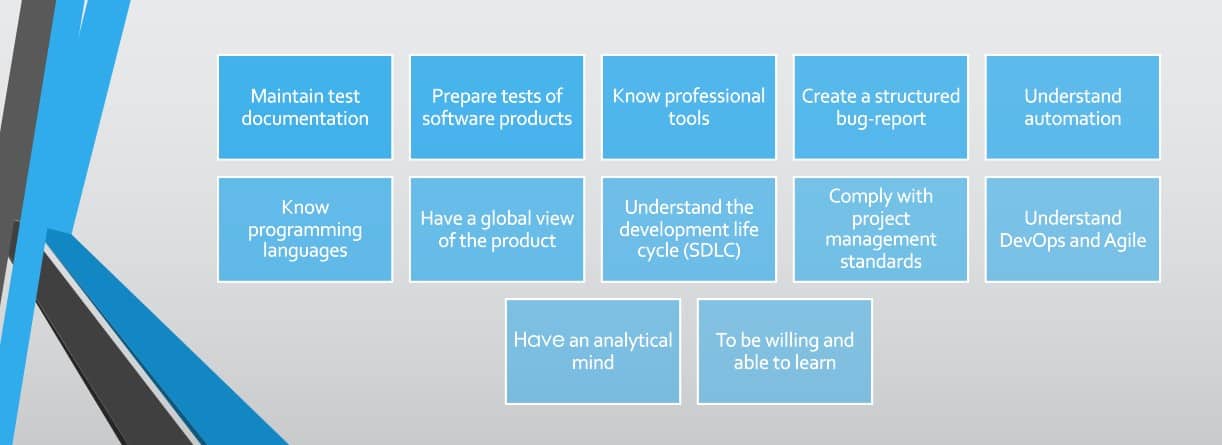
Requirements for a software quality tester vary in product type, test method, team structure, and other factors. Some companies prefer Full-stack specialists who do their testing and analytics. Or they know how to work with both manual and automated testing. But the basic list of skills is the same for all specialists.
Maintain test documentation
That is, draw up a test report and present your observations in a structured manner. Usually, companies already have an accepted reporting form, so you need to understand how to use the form and follow the rules.
Prepare tests of software products
Preparation for testing begins with selecting the type of test, drawing up a plan, developing scenarios and examples. This is where a good knowledge of theory comes in handy for a QA engineer, even if not all of it is needed in the early stages of a career.
Know professional tools
For example, bug tracking, security auditing, UI, CSS, and more. It is important to be proficient with the API and understand test automation software.
Create a structured bug-report
Bug reporting is a crucial test result that the rest of the QA team and developers work with. In addition to information about the bug, a basic bug report should describe its localization, circumstances of occurrence, the build version of the product, priority, and who identified the bug and who is responsible for fixing it.
Understand automation
The larger the software, the longer it takes to test it. Therefore, even if a QA engineer works manually, he must know where and when to use automation to improve efficiency.
Know programming languages
Basic knowledge will help you build communication with the development team more effectively and see the product’s operational side.
Have a global view of the product
To conduct tests efficiently and explain their results, the tester must understand the technical background of how the system works and its components. A tester must also understand the business component of the system to prioritize effectively.
Understand the development life cycle (SDLC)
Testing is only one stage in the software lifecycle. Knowing how a product is created, refined and what happens to it after release helps you prepare for future challenges and plan your activities for the future.
Comply with project management standards
Project management methodology is the key to their successful implementation. As an important team member, the QA engineer needs to know what strategy is used in the project and follow that strategy.
Understand DevOps and Agile
Agile management and communication methods between developers and IT professionals help you resolve business issues faster and more efficiently.
Have an analytical mind
Having an analytic mind can help one understand the software processes and see the cause-and-effect relationships of errors. A QA engineer needs to conclude – even if they do not need to be included in the final report.
To be willing and able to learn
Technology is constantly evolving. For professional growth, you need to stay abreast of trends and new techniques and adapt and apply them quickly in practice.
A quality tester must have the special technical knowledge and soft skills listed above, which are important for every development team member.
7 Best Quality Assurance Software Tester Courses
At the start of a career, paid or free courses will help put knowledge puzzles into one whole picture.
Introduction to Software Testing

University of Minnesota Beginner Course: Basic theoretical knowledge of test processes and methods, including practical exercises on error finding and statistical testing. Classes are taught by Sanjai Rayadurgam, Head of Software Development Center, and Kevin Wendt, Ph.D. Director.
Introduction to automated analysis

Another program of study at the University of Minnesota in the framework of the QA engineer specialization with a focus on automation offers theoretical and practical knowledge about analyzing, planning, and conducting tests using automated methods.
Kevin Wendt, Ph.D. Director of Software Engineering is leading the teaching process.
Complete course for QA testers

The course is taught by the founder of the most prominent blog for QA engineers, Swati Seela, who has been involved in testing since 2004. The program consists of 5 weeks of interactive training with practical assignments. In addition to basic professional skills, the course provides a general understanding of IT and helps prepare for an interview.
IT automation with Python

This is a full-fledged Google career certification of 6 courses using the Python programming language. Teachers will teach the theory and practice of task automation, software for version control, analysis, and scaling of solutions.
What is Data Science?

The course provides a general understanding of computer science, analytics, and skills that will help build a career in this field. Classes are taught by Rav Ahuja, head of the IBM Skills Network, and Alex Aklson, Ph.D. and data analyst.
Introduction to the principles and processes of user interaction

An introductory program on UI/UX will teach the future QA engineer to put himself in the user’s shoes, understand the principles of creating a user interface, and teach how to apply methods of determining needs and testing methods. The course is taught by Mark Newman, Associate Professor at the University of Michigan.
Rapid software development

Career specialization from University of Virginia faculty. It consists of four courses on the principles and methodologies of product development: Agile, Scrum, Kanban, etc. In the end, you need to create your project for the future portfolio.
Courses are an excellent way to comprehensively study the theory of QA testing and learn how to apply it in practice. You can also create a training program yourself: Google has enough information on the topic of software testing.
Quality Assurance Software Tester Salary
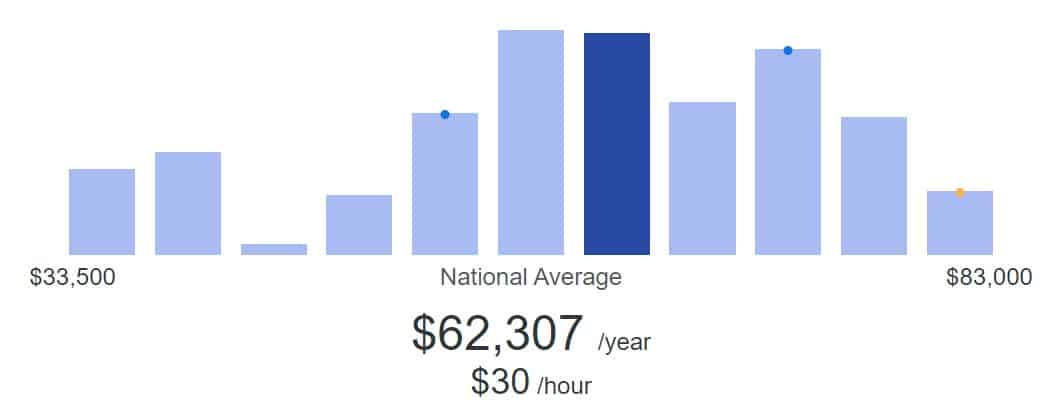
The salary of a QA engineer depends on experience, depth of skill, and (quite often) the type of product they work with. According to ziprecruiter.com, on average in the country, a tester earns $30 per hour, about $62,000 per year. By state, the average salary is the highest in California – $37/hour and almost $77,000 per annum, which generally raises the average wage in the field.
But this is not the limit. According to indeed.com, the company’s advanced professionals offer to pay more than double the average. At the same time, the lower bar for beginners is about $13-14 per hour.
This difference in salary suggests that there are many career opportunities in the QA profession. The higher the qualification level of a specialist, the more monetary compensation companies are ready to offer him.
Conclusion
A QA tester is responsible for the quality of the software. This profession is primarily suitable for diligent, meticulous, conscientious people who love and know how to evaluate everything practically. At the initial stages of a career, basic technical knowledge is enough, but you will need to be invested in learning new technologies in the future. Therefore, the main thing for a tester is self-education and steady growth because one’s product develops with oneself.
