Website usability tests help businesses better understand user behavior and improve conversions. Testing also helps you understand on which page many users leave the website.
You should test the site’s usability before launching it on the Internet (that is, before opening permission to index the site in the robots.txt file) and throughout its entire life cycle. Testing is especially important before launching an advertising campaign in Google Ads. Otherwise, there is a risk of getting a very low conversion rate.
With usability testing methods, you can ensure that users find your website easy to use so they will not go to competitors. According to a study conducted by Acquia, 76% of customers leave websites if they have an unsuccessful UX. Let’s go over usability testing methods to guide you how to do it..
What is Usability Testing?
Usability testing is a method of evaluating a product or service by testing it with real users to see how they interact with it and identify areas for improvement. It’s a critical component of product design, helping organizations ensure their digital offerings meet the needs and expectations of their target audience.

With the rise of mobile technology, testing user behavior across different devices has become increasingly important. A staggering 62% of companies have seen a boost in sales after improving the usability of their mobile website design.
Usability testing is like a litmus test for websites and applications, revealing the good, the bad, and the ugly in user experience. It helps organizations understand why user behavior may deviate from expectations and pinpoint specific areas to improve the user experience.
At the end of a usability test, clients receive a comprehensive report, usually 20 to 100 pages, detailing the results and providing recommendations for optimization. These recommendations help increase conversion rates, boost average check values, and encourage repeat business – all critical components of a successful business strategy.
A client may see a conversion rate increase from 0.4% to 0.8% or even 1.3% in their niche, resulting from cross-selling and upselling efforts. Repeat business can also reduce the costs associated with acquiring new customers, contributing to the lifetime value of a client.
Usability testing is a no-brainer when it comes to ensuring the success of your digital product. By putting your product through its paces with real users, you can make sure it hits the right notes and satisfies user needs.
Who Needs Usability Testing?
Usability testing makes sense for projects with stable or increasing traffic.
Most internet marketers need usability tests. Usually, they seek the most effective ways of attracting potential clients with a further conversion improvement on all stages of sales funnels.
A website heatmap in dynamics in an online store:
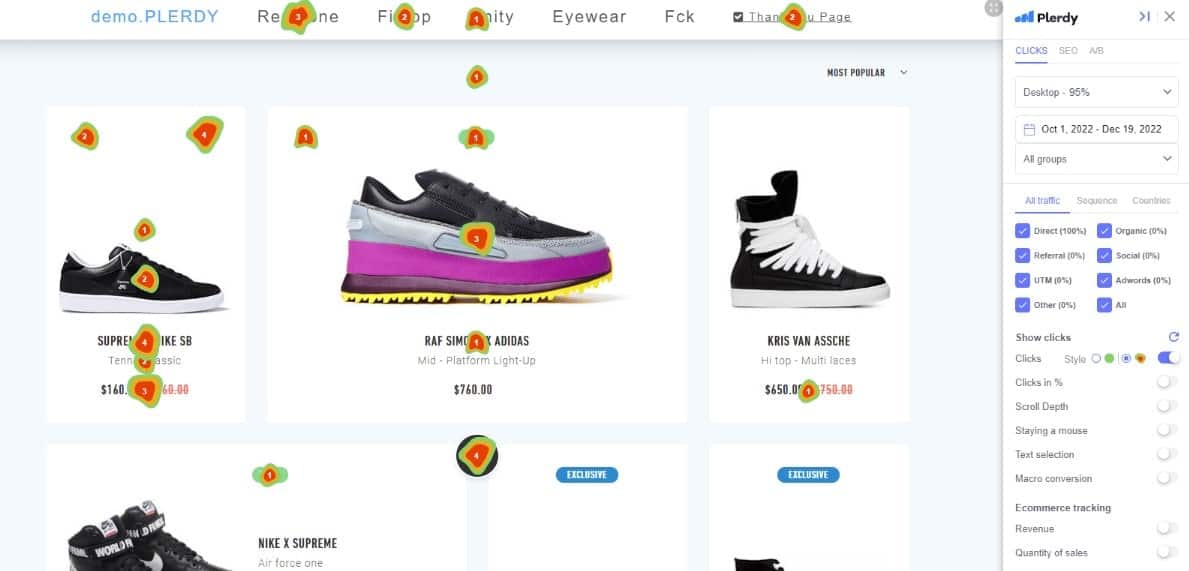
The more the competition grows, the more attention the usability test gets. 86% of marketers are do or plan to do usability testing to improve website conversion. Seems like this number will only grow.
What are the usability test methods?
The whole process has four steps. Each of them includes a group of tasks:
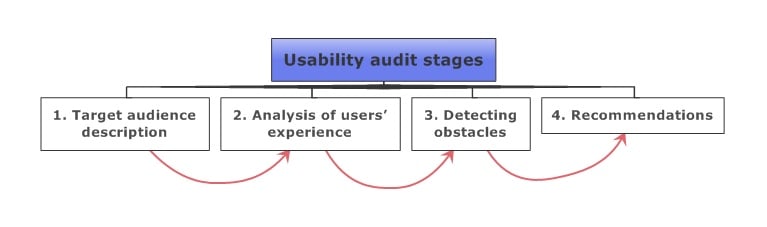
- Target audience description. The first method of a usability test is to determine the target audience. Marketers must understand customers’ habits and expectations.
- Analysis of users’ experience. Website heatmaps and scroll maps play an important part here. They allow us to detect the most problematic spots and user behavior patterns.
- Detecting obstacles. The third method is a search for obstacles that decrease conversion to detect problem areas in the design. For example, it can be improper contrast of colors, excessive objects, or unfunctional buttons.
- Recommendations. In the fourth method, recommendations regarding website improvements and optimization are prepared.
What do the usability test methods check?
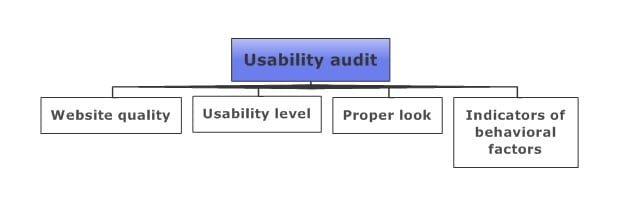
- Website quality. The look of a website and its technical implementation like speed or mistakes are analyzed. Quality is, first of all, connected to speed. Slow page loading can lead to an 80% bounce rate. Besides, 94% of users say that design is important for being trustworthy.
- Usability level. Every user relies on their previous experience, so a website must have a user-friendly interface and some hints and instructions.

- Proper look. A clear identity, content volume, and CTA location matter. Colors make a website 80% more recognizable.;
- Indicators of behavioral factors. Here you detect where users enter a website and where they leave it, explore ways of conversion, and study the most often clicked components.
What problems does a usability test solve?
The main problems that require a usability test:
- Unsatisfactory or decreasing sales;
- Use behavior anomalies;
- Too high price to bring a new client;
- High expenses on customer support;
- Short “lifetime cycle” of a client.
How much time does a usability test take?
The duration of a usability test depends on difficulty and methods. The minimum time required is 1 month.

List of Top 16 Usability Testing Methods
This list offers 16 methods suitable for testing website usability. Let’s consider each of them in more detail.
Session Recording
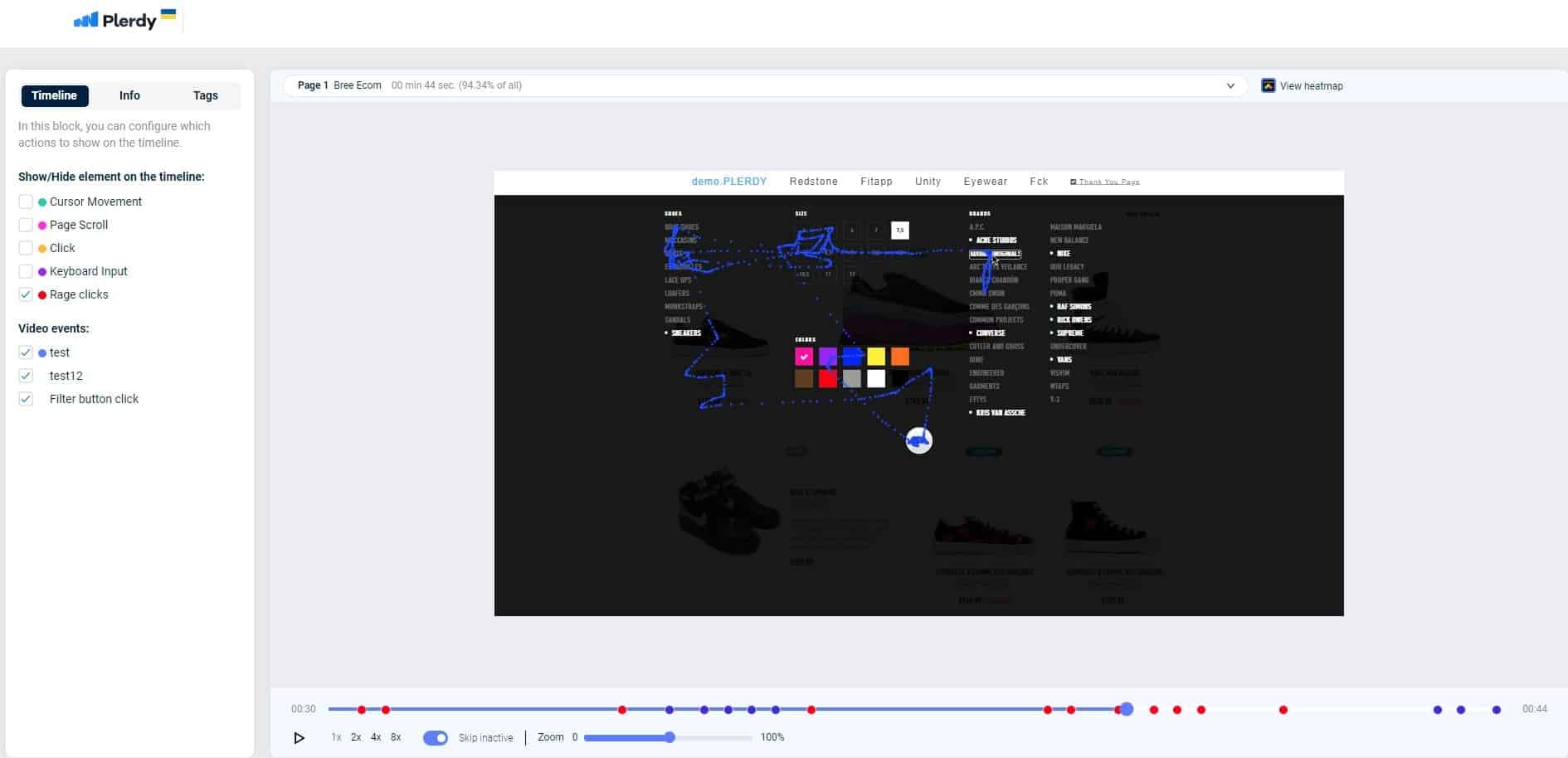
With Plerdy’s Session Replay tool, you can record sessions and observe the behavior of your website visitors. Using this method, you will see:
- Their actions on the page.
- Cursor movements.
- Scrolling depth.
- Mouse clicks.
- Hate clicks whnen users click many times on the same element.
- Custom actions, like adding items to cartor other events.
Session recordings are one of the most useful approaches on our web usability testing methods list. To better understand the user’s steps during the test, you should record their actions on the website.. In addition, you will have a visual understanding of which website parts are interesting and convenient for users and which are not.
This method works for both mobile and desktop website versions. By analyzing behavioral factors, you can push customers to perform the desired targeted actions, and as a result, increase conversion.
Heatmaps as a Method of Usability Testing

Heatmap is a set of online tools for tracking and analyzing user behavior on a website. With this method, you can record the sequence of mouseovers and clicks, scrolling, text selection, and other actions on a web page.
You can see examples of using heat maps on this web page with case studies.
Contextual inquiry
Contextual inquiry is a valuable method in UX research, as it combines observation and interview to uncover hidden insights about a user behaviors in their natural environment. This type of ethnographic study is especially useful for complex systems and in-depth processes, as well as expert user perspectives. By observing users in their context, researchers gain a rich understanding of the underlying thought processes and habits that influence UX. However, it’s not ideal for straightforward tasks like redesigning a website page.irect observation may be more appropriate in situations where users cannot be interrupted.
Quantitative vs. qualitative usability testing
Quantitative vs. qualitative usability testing are two complementary methods of evaluating user experience. Qualitative testing involves observing and collecting observational data from participants, while quantitative testing measures user performance through metrics such as task completion time and satisfaction ratings. Quantitative testing provides a basis for comparing a design to a reference or competitor, while qualitative testing offers direct insights into specific usability issues. Both methods have advantages, but qualitative testing is often necessary to supplement quantitative results and understand the reasons behind low user performance. Ultimately, both are essential in an iterative design cycle to inform design decisions and evaluate usability.
NPS
Net Promoter Score is a testing method in which customers answer questions like: “How likely are you to recommend our organization to a friend or colleague?”
After receiving the answers, the respondents are divided into three groups: supporters, neutrals, and critics. Then, using the formula “supporters minus critics,” the NPS level is calculated, measured from 1 to 10.
Survey
A website user survey is a good tool to get opinions on a specific issue, such as content quality, structure and navigation, visual design, functionality, etc.
As a rule, the survey has an online format. Respondents can choose the appropriate answer options.
Unmoderated usability testing
The method of unmoderated usability testing involves conducting tests that do not require moderators or other persons who will familiarize respondents with the questions. You can run it, for example, in the form of an online survey.
Unmoderated user testing is usually taken over by test software offering tasks for participants. You wait for the collected data and receive the test results within a very short time. The presence of a moderator is not required. In most cases, these services have a pool of respondents paid for the effort, so you do not have to recruit the appropriate target group. This option is one of the most widespread types of usability testing methods.
Therefore, the choice of the most suitable procedure depends heavily on time, the available budget, and the product development phase.
For example, unmoderated testing is best for evaluating live websites and apps or highly functional prototypes. A moderated test would be used to investigate tasks requiring a lot of imagination or emotions from the tested persons.
In terms of time, it usually takes 20–30 minutes and includes testing 5–10 respondents. This method allows you to get more responses from more respondents than the moderated view, but it is unsuitable for testing sites.
Moderated Usability Testing
Moderated usability testing involves the participation of specialists who will acquaint respondents with the testing and its goals, issue tasks, and ask clarifying questions. This format is more expensive but provides more detailed results. It is one of the most popular UX usability testing methods.
Moderated testing is a core approach in our usability testing methods examples. In a moderated remote usability test, the tested person completes tasks in the presence of a moderator and observers. The moderator sets the tasks and accompanies the test person throughout the session. However, this person does not lead through the task. Otherwise, this would affect the test result. The moderator can ask additional questions and follow up with the tested person in case of unclear statements to gain valuable insights. If a product is in the concept phase or it’s a new product idea, it is advisable to carry out moderated tests. In the early stage of product development, you may lack knowledge about the users and their feedback.
Unlike a focus group, only one respondent participates at a time in the UX testing methodologies (rarely two or three). Users can either come to the lab in person or participate in usability testing at home, under the supervision of a UX analyst.
Typically, moderated usability testing is used to study user behavior in detail, while unmoderated usability testing provides answers to a specific question.
Guerilla Testing

In this method, you need to select random test participants in a public place where the target audience dwells. For example, if you test a mobile app for coffee shops, you may go to a coffee shop. That way, you can get a large number of results in a short time.
A guerrilla test takes approximately 10–15 minutes. The aim is to uncover a product’s or service’s weaknesses and identify the potential for improvement. For this purpose, test users check specific areas of an application. Low-fidelity prototypes in the development process with a low level of detail are sufficient for this. In this way, providers gain valuable insights into the usability of their products in the prototyping phase.
The task list for the user can look like this:
- Add an item to the shopping cart.
- Search for additional elements.
- Go to the checkout page.
- Login.
- Change the delivery address.
- Confirm the transaction details.
- Print out the payment confirmation.
- Find payment authorization in the email inbox.
It is one of the mobile usability testing methods that will help you understand a lot about your product.
You can use this type of testing to get an opinion on a specific issue in usability. The average time is 10-15 minutes, including a survey of 6-12 participants.
Lab Usability Testing
Lab usability testing involves gathering participants in usability testing labs and giving them tasks to perform on smartphones or computers. In addition to the respondents, a moderator participates in the test, asks questions, and studies their behavior.
A usability test in a laboratory is another method for measuring and improving usability. It is not the most popular among different user testing techniques, but it can be beneficial too.
A classic (scenario-based) user test, also called a laboratory test or usability test, is probably the best-known method to determine usability. Users from the specific target group test a prototype for vulnerabilities and possibilities for improvement (inductive test) or check an existing application to help achieve the necessary performance (deductive test).
In test sessions, which usually take place in a usability laboratory, people work on typical tasks that reflect the core functionalities of the application. , An experienced usability expert observes the tested people while they solve the tasks (participating observation). The participants are usually asked to describe their problems with the website, which helps clarify the reasons behind their behavior.
Lab testing allows you to get feedback on a product in early development stages. The average testing time for one user is 20-30 minutes, and the number of participants is 8-12 people.
Card Sorting
This test involves asking participants how they think the website navigation and layout should look. This way, you can determine if users’ expectations align with the website layout you design.
Card sorting tests are usually carried out at the beginning of the conceptual phase of a web project. The aim is to find out how to structure the planned content as user-friendly as possible on the website. For main sections, finding suitable names and logically assigning subcategories is important. The test persons receive cards with the respective subcategories and must first sort them into groups in terms of content. Inconclusions are immediately detected and can be corrected. It helps find suitable names for the main categories.
On average, such testing takes 20-30 minutes for 15 participants.
Tree Testing
Tree-based usability testing is similar to the card variant— respondents sort cards into specific categories. This method is often used to determine the usability of a navigation system.
The average test time is 15-20 minutes, and up to 50 people participate.
A/B Testing
A/B testing involves comparing two website pages that already have traffic. This way, you can determine which changes (for example, different versions of buttons or banners) give the best conversion. You can detect existing problems on a website, learn about user behavior, and reduce bounce rates through testing.
In A/B testing, you present users with one of two versions of a design – an A version or a B version – and compare the respective conversion rates to determine which version performs better. Such tests (sometimes called split testing) are the most useful when only one element differs in each version. In this study, the researchers compare the two tests to see which version is more effective.
The average testing time is 6–7 days, and the number of participants is not limited. iIt can be anywhere from 50 to 500 users. Mind that it is better to equally divide the audience of users from the same traffic channel.
5-second Test
It evaluates whether a website can convey the desired message to the target audience in 5 seconds. We talked about the importance of the test in more detail in this video. The main point is that participants have 5 seconds for the answer. You can run Ssuch testing using focus groups or video-based sessions. If the user quickly leaves the site or does not notice the target element, you can form a hypothesis:
- The first screen of the site page does not convey the necessary information. The h1 heading may be wrong, or the user does not see some important elements.
- The advertising campaign was launched incorrectly. If it’s Google Ads, check your keywords and other settings.
The 5-second test is a classic user research method in which users initially view a website, an advertising medium, or other designs for only 5 seconds and then answer questions about it. 5-second tests are very convenient to use for:
- First impression: does the first impression of the testers matches your brand values? Following this 5-second test, a detailed usability test of the entire user journey is recommended.
- Relevance: is your offer (for example, on a landing page or an advertisement) relevant to your target group? Does it meet your needs?
- Design/Branding: does your design look appealing to users? What emotions does it arouse?
- Understanding: do people understand the contents of your design at first glance? Sometimes, it may also be a good idea to give a very short task that can be completed in 5 seconds.
The company determines the type of questions to ask. The method includes a survey of 20–50 respondents.
Phone Interview

In this subtype of moderated usability testing, a moderator provides instructions to users. A user behavior report is collected automatically as they answer questions.
A phone interview is one of the most helpful remote usability testing methods. In a telephone usability test, the moderator verbally instructs the participants while they complete tasks on the computer. This person collects feedback from them while recording everything on the respondent’s screen remotely. Phone interviews save money on testing users from different geographic areas. Since they are less expensive than in-person interviews, you can get more useful information in the same amount of time.
This method is best to get answers from respondents from different places – for example, different states or countries.
The survey requires 10–15 respondents and one trained moderator.
Eye Tracking

Eye tracking helps determine how people interact with the web design of a site and which part of it gets the most attention. In this usability testing method, users are tested with an eye tracker app.
You also need to collect the information on click frequency and cursor movements.
The average time is 20–30 minutes, and the test includes testing at least 40 participants.
List of Usability Experts
Usability testing is a crucial component of website design and user experience. It helps determe websiteperformance and how visitors utilize the site. In this post, we examine some of the most well-known usability specialists who have significantly impacted the industry.
- Nielsen Norman Group’s Jakob Nielsen is renowned as the “Pope of Usability” for his contributions to the field. He is the author of multiple books, including “Designing Web Usability: The Practice of Simplicity,” and has provided consulting services to some of the world’s largest corporations.
- Advanced Common Sense, LLC, founded by Steve Krug, author of the classic usability book “Don’t Make Me Think.” He is a sought-after consultant and lecturer on usability.
- Nielsen Norman Group’s Don Norman invented the phrase “user-centered design” and is a pioneer in usability and user experience. Among his influential works is “The Design of Everyday Things.”
- Jared Spool is the creator of User Interface Engineering, a major digital design, usability research and consultancy organization. In addition, he is a well-known public speaker and author of numerous articles and papers on usability.
- Luke Wroblewski, Google, is widely regarded as a pioneer in mobile and web design, with experience at Yahoo!, eBay, and Twitter. His works include “Mobile First” and “Web Form Design.”
- Aarron Walter is the author of “Designing for Emotion” and the former user experience director of MailChimp. He is a sought-after lecturer on UX design with recognizedcontributions to the subject.
- Carolyn Chandler is the creator of the user experience design consultancy Fresh Tilled Soil. She is famous for making difficult technologies accessible and useable as a lecturer and author.
- Bob Bailey is a usability specialist at BAINTERACTIVE with over 30 years of expertise. His contributions to the field of usability and UX have earned him recognition for his work on various high-profile projects.
- Whitney Hess is user experience consultant, coach, and writer at Whitney Hess Consulting. She is popular as a speaker on UX and design empathy.
- Laura Klein, a consultant on user experience and author of “Build Better Products,” has worked with startups and Fortune 500 firms. She is recognized for her product design, usability, and conversion optimization competence.
As the backbone of the sector, these usability professionals offer invaluable skills, knowledge, and insights to the design community. Their efforts aided in the development of the field and served as a guide for others. They continue to motivate and challenge web designers to produce user-friendly, open, and aesthetically pleasing websites.
Summary
Remember that usability testing should always be run in a real environment with real users. This approach allows the testing team to observe how users interact with the product in a natural setting, providing valuable insights into any issues or challenges they may face. When deciding on the right method, you must the difference between qualitative and quantitative metrics and the balance between free-form exploration and structured testing with heuristic guides. Knowing each method’s key features and special considerations will help you make informed decisions and start your testing on the right foot. An excellent way to gain a fresh perspective on your product is to bring in a team of experts or conduct user testing with various users who can provide new ideas and invaluable feedback.
