📈 Crawling & Indexing
-
Ensure URL Is Indexed
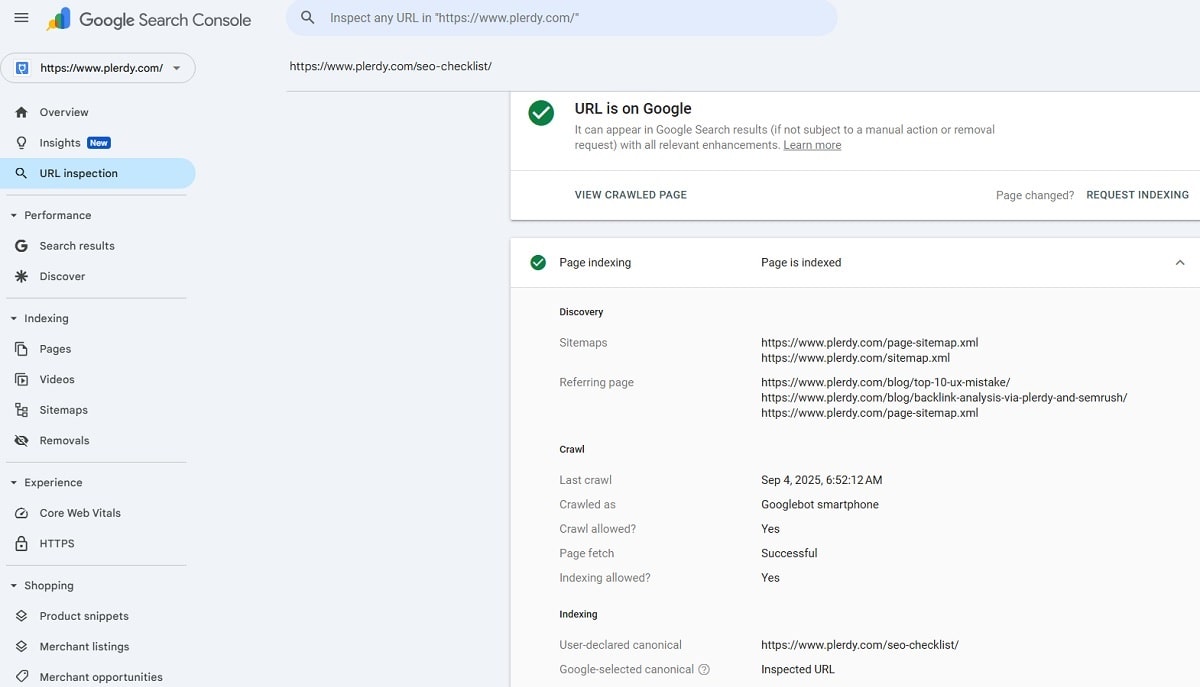
 Use Google Search Console → URL Inspection to confirm “Indexed?” status, Google-selected canonical, and last crawl. site: is only indicative—don’t rely on it alone. If not indexed: remove noindex, allow crawling in robots.txt, include in XML sitemap, add internal links, and click “Request indexing”. URL Inspection Tool
Use Google Search Console → URL Inspection to confirm “Indexed?” status, Google-selected canonical, and last crawl. site: is only indicative—don’t rely on it alone. If not indexed: remove noindex, allow crawling in robots.txt, include in XML sitemap, add internal links, and click “Request indexing”. URL Inspection Tool
-
Ensure Important Content Is Indexed
 Only index valuable templates/pages (categories, PDPs, articles). Check GSC Page indexing report, noindex, canonical, robots.txt, and sitemap status. Important pages need internal links, successful render, and 200 OK. MozBar
Only index valuable templates/pages (categories, PDPs, articles). Check GSC Page indexing report, noindex, canonical, robots.txt, and sitemap status. Important pages need internal links, successful render, and 200 OK. MozBar
-
Page Returns 200 (OK) Status Code
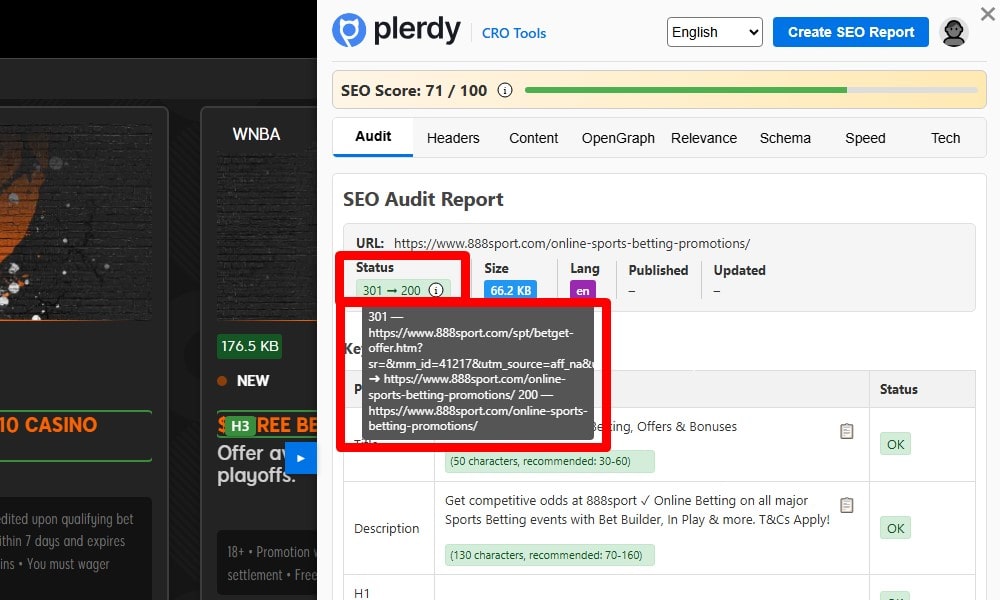 Verify 200 OK for the canonical URL and variants (http/https, www/non-www, trailing slash). Use a crawler (Screaming Frog/Ahrefs) and curl -I. Avoid JS redirects and any 4xx/5xx. Plerdy SEO Analyzer
Verify 200 OK for the canonical URL and variants (http/https, www/non-www, trailing slash). Use a crawler (Screaming Frog/Ahrefs) and curl -I. Avoid JS redirects and any 4xx/5xx. Plerdy SEO Analyzer
-
Allow Indexing via Meta Robots / X-Robots-Tag
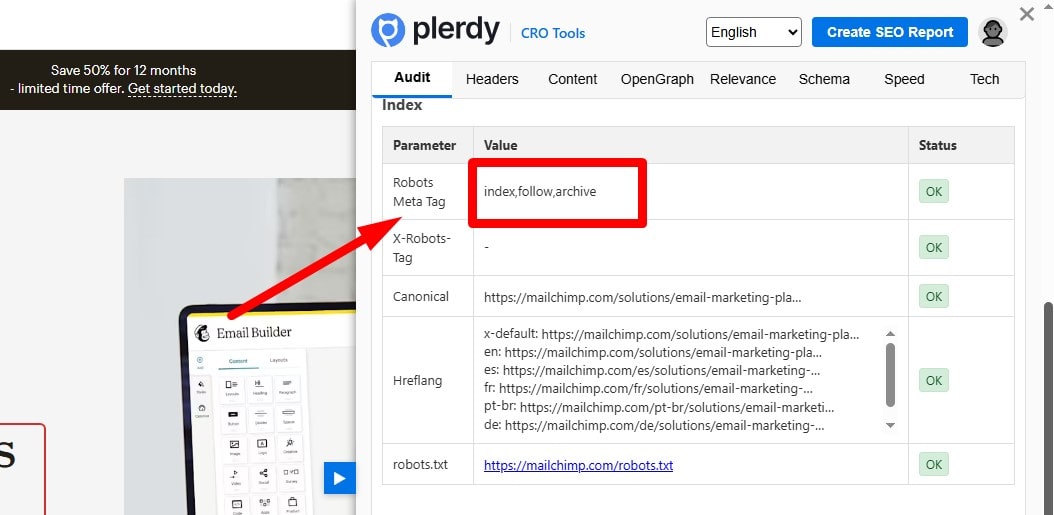 Indexable pages should be set to index, follow (default; explicit tag optional). For PDFs/images, use X-Robots-Tag in response headers. Don’t mix noindex with canonical to another URL. Plerdy SEO Analyzer
Indexable pages should be set to index, follow (default; explicit tag optional). For PDFs/images, use X-Robots-Tag in response headers. Don’t mix noindex with canonical to another URL. Plerdy SEO Analyzer
-
Do Not Block the URL in robots.txt
 Check robots.txt and the robots.txt report in Google Search Console. Remember: a Disallow stops crawling but doesn’t guarantee deindexing, and it prevents Google from seeing page-level meta tags. Don’t block templates intended to be indexed. Use Page indexing / URL Inspection to confirm whether a URL is blocked, and, if needed, test with a crawler (e.g., Screaming Frog) or an online validator.
Check robots.txt and the robots.txt report in Google Search Console. Remember: a Disallow stops crawling but doesn’t guarantee deindexing, and it prevents Google from seeing page-level meta tags. Don’t block templates intended to be indexed. Use Page indexing / URL Inspection to confirm whether a URL is blocked, and, if needed, test with a crawler (e.g., Screaming Frog) or an online validator.
-
Declare Sitemap Location in robots.txt
 Add Sitemap: https://example.com/sitemap.xml (multiple allowed). Ensure the sitemap returns 200 and lists only canonical, indexable URLs. Include
Add Sitemap: https://example.com/sitemap.xml (multiple allowed). Ensure the sitemap returns 200 and lists only canonical, indexable URLs. Include only if it reliably reflects the last significant update; otherwise, omit it to avoid misleading signals. -
Submit Sitemap to Search Engines
 Submit sitemap in Google Search Console and Bing Webmaster Tools. Respect limits (≤50k URLs or ≤50MB per file); use an index sitemap if needed. Monitor coverage/errors and keep lastmod current.
Submit sitemap in Google Search Console and Bing Webmaster Tools. Respect limits (≤50k URLs or ≤50MB per file); use an index sitemap if needed. Monitor coverage/errors and keep lastmod current.
-
Make the URL Discoverable via Internal Links/Navigation
 Avoid orphan pages: add 1–2 contextual internal links with descriptive anchors; keep click depth ≤3. Links must be crawlable (no nofollow, not JS-only). Add to nav/breadcrumbs where relevant.
Avoid orphan pages: add 1–2 contextual internal links with descriptive anchors; keep click depth ≤3. Links must be crawlable (no nofollow, not JS-only). Add to nav/breadcrumbs where relevant.
-
Serve Content at a Single Canonical URL
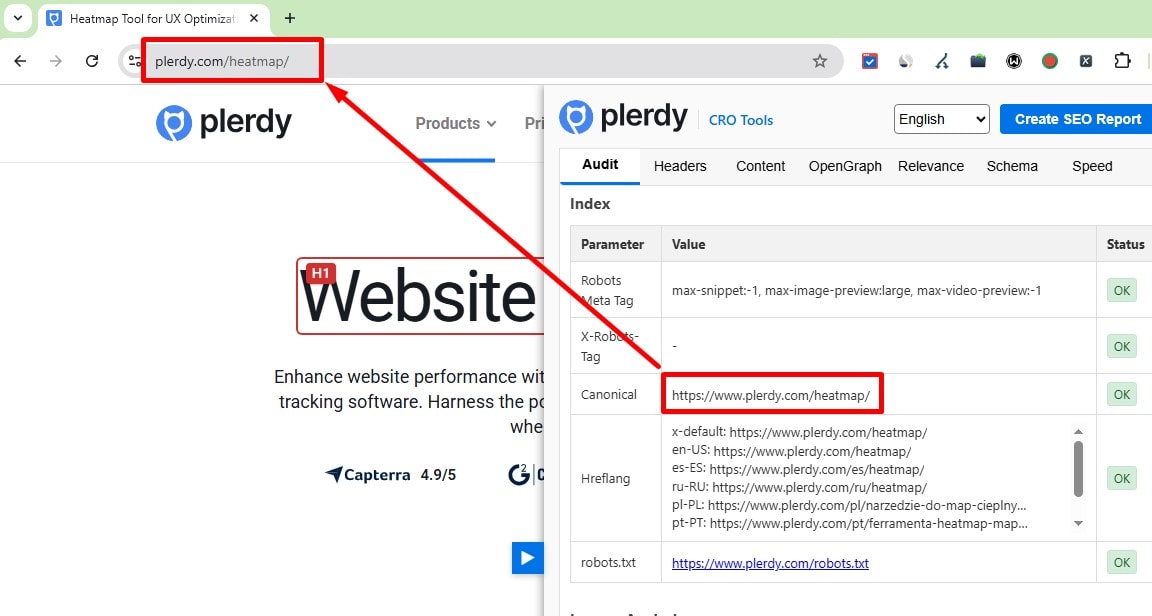 Use self-canonical on the primary version and 301 from duplicates (params/UTMs, http↔https, www↔non-www, slash variants). Don’t canonicalize pagination to page 1. Keep hreflang and canonicals consistent.
Use self-canonical on the primary version and 301 from duplicates (params/UTMs, http↔https, www↔non-www, slash variants). Don’t canonicalize pagination to page 1. Keep hreflang and canonicals consistent.
-
Align Google-Selected and Declared Canonical
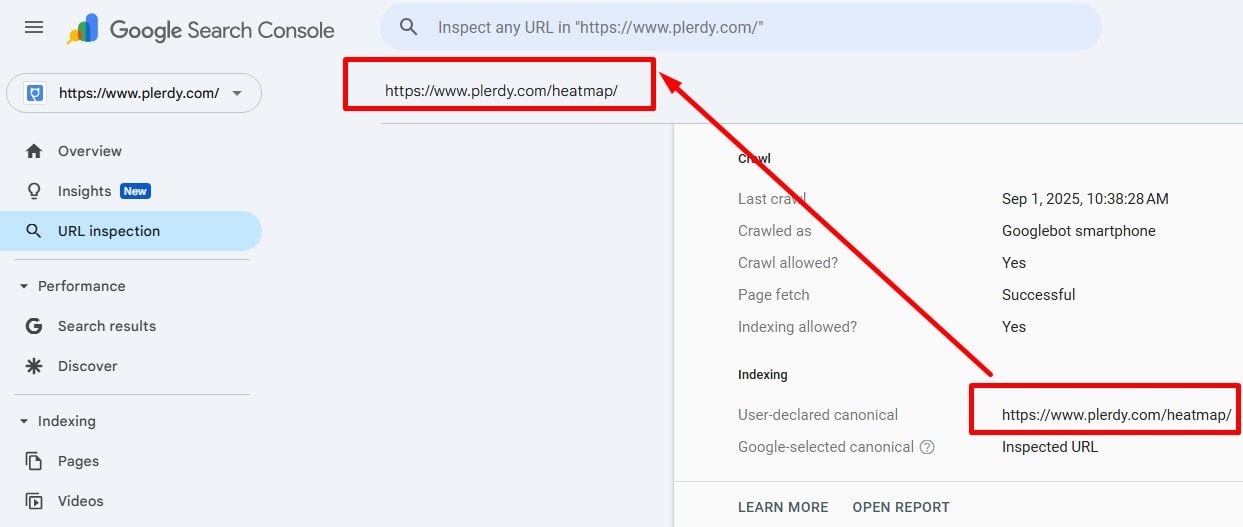 In GSC URL Inspection, compare “Google-selected canonical” to your rel=canonical. If different, strengthen signals: 301 from duplicates, internal links to canonical, canonical URLs in sitemap, remove noindex/blocks on the canonical page.
In GSC URL Inspection, compare “Google-selected canonical” to your rel=canonical. If different, strengthen signals: 301 from duplicates, internal links to canonical, canonical URLs in sitemap, remove noindex/blocks on the canonical page.
-
Avoid Canonical/Indexing Mixed Signals
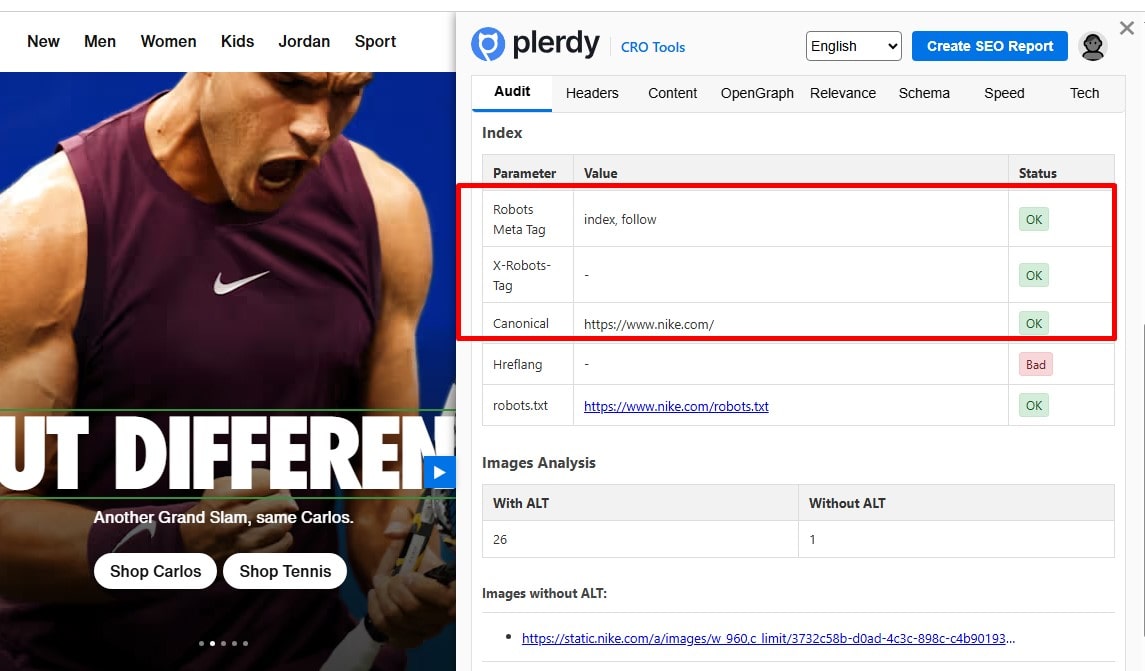 Don’t combine noindex with canonical to another URL; don’t canonicalize to blocked/4xx/noindex pages; avoid duplicate canonicals. Keep meta robots, X-Robots-Tag, robots.txt, and canonical aligned across mobile/desktop.
Don’t combine noindex with canonical to another URL; don’t canonicalize to blocked/4xx/noindex pages; avoid duplicate canonicals. Keep meta robots, X-Robots-Tag, robots.txt, and canonical aligned across mobile/desktop.
-
Use a Friendly URL Structure
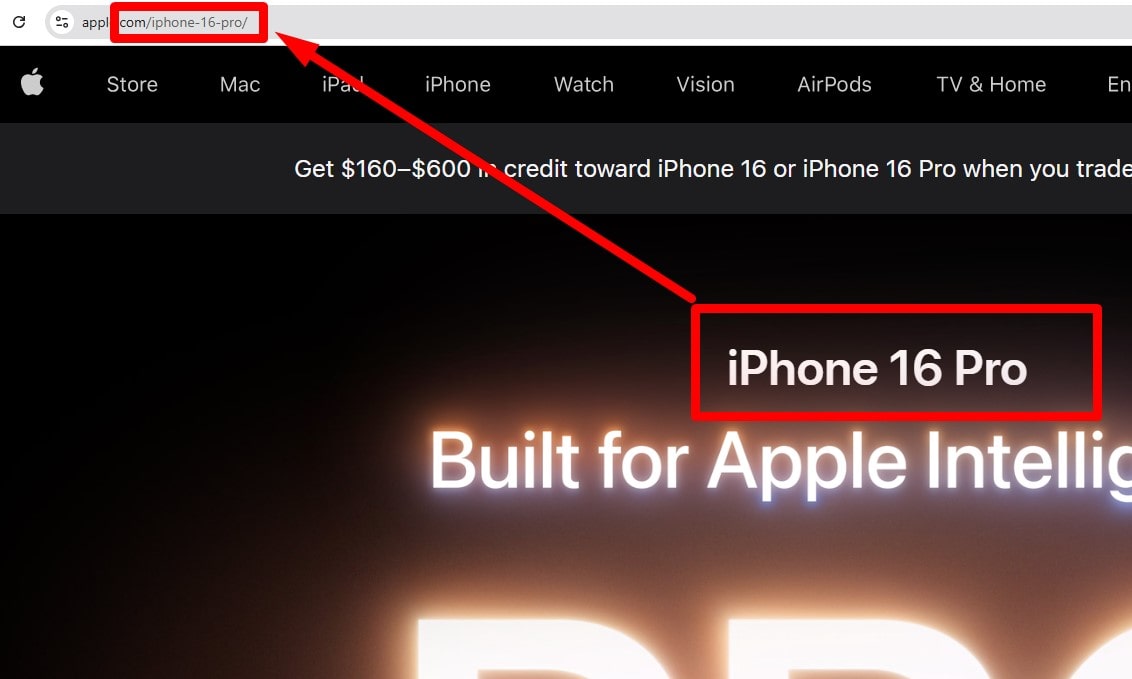 Keep URLs short, readable, lowercase, words separated by hyphens: bestsite.com/category/product-name. Enforce trailing-slash policy, avoid unnecessary params/IDs, and keep a stable hierarchy.
Keep URLs short, readable, lowercase, words separated by hyphens: bestsite.com/category/product-name. Enforce trailing-slash policy, avoid unnecessary params/IDs, and keep a stable hierarchy.
-
Do Not Block Critical CSS/JS/Images in robots.txt
 Ensure Google can render pages: don’t block /wp-includes/, /static/, or CDN assets. Check Rendered HTML in GSC and PageSpeed/Lighthouse. Remove patterns like Disallow: /*.css$.
Ensure Google can render pages: don’t block /wp-includes/, /static/, or CDN assets. Check Rendered HTML in GSC and PageSpeed/Lighthouse. Remove patterns like Disallow: /*.css$.
-
Use Correct Redirect Codes (No Chains/Loops)
 Use 301/308 for permanent, 302/307 for temporary. Eliminate chains/loops; update internal links to the final URL. Verify with Screaming Frog/redirect checkers.
Use 301/308 for permanent, 302/307 for temporary. Eliminate chains/loops; update internal links to the final URL. Verify with Screaming Frog/redirect checkers.
-
Eliminate 5xx Server Errors
 Set up uptime/log alerts (e.g., UptimeRobot). In GSC, check Page indexing → Server errors (5xx). Fix timeouts, resource limits, app exceptions. Add health checks and rollback plans for deployments.
Set up uptime/log alerts (e.g., UptimeRobot). In GSC, check Page indexing → Server errors (5xx). Fix timeouts, resource limits, app exceptions. Add health checks and rollback plans for deployments.
-
Provide Meaningful Image Alt Text
 Add descriptive alt to informative images; use empty alt="" for decorative ones. Avoid keyword stuffing. Audit via Screaming Frog/Lighthouse and by exporting IMG without alt from your crawler.
Add descriptive alt to informative images; use empty alt="" for decorative ones. Avoid keyword stuffing. Audit via Screaming Frog/Lighthouse and by exporting IMG without alt from your crawler.
-
Validate HTML (W3C)
 Valid, semantic HTML improves rendering, accessibility, and parser reliability (e.g., structured data). Use validators to catch broken markup. It’s not a direct ranking factor—focus on speed, content quality, and UX.
Valid, semantic HTML improves rendering, accessibility, and parser reliability (e.g., structured data). Use validators to catch broken markup. It’s not a direct ranking factor—focus on speed, content quality, and UX.
-
Analyze Logs & Manage Crawl Budget
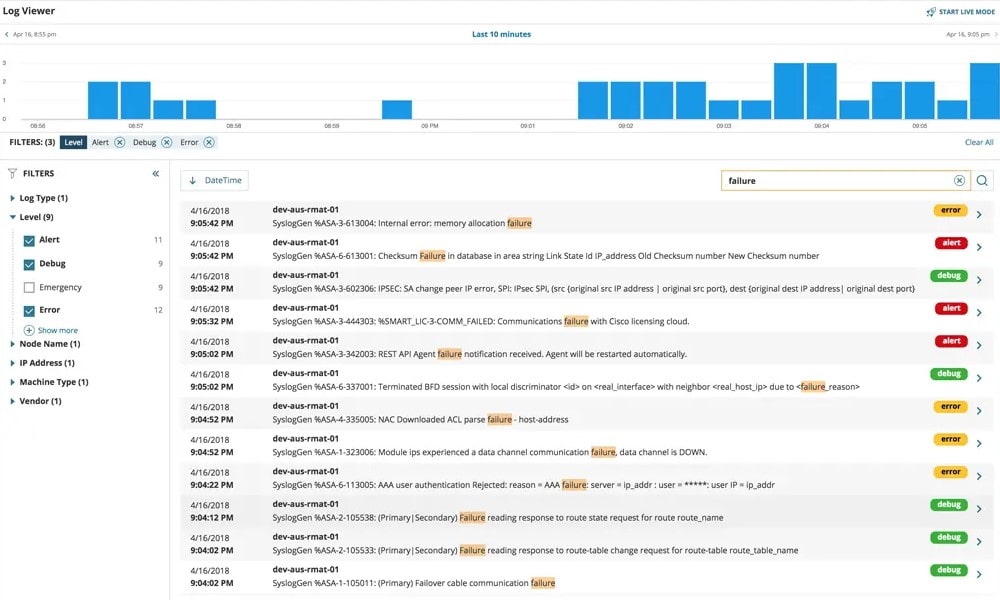 Analyze server logs (Googlebot UA): frequency, 404/soft-404s, parameterized URLs, infinite spaces. Prioritize key sections via internal links/sitemaps, curb noisy parameters, and streamline navigation. Crawl budget matters on large sites.
Analyze server logs (Googlebot UA): frequency, 404/soft-404s, parameterized URLs, infinite spaces. Prioritize key sections via internal links/sitemaps, curb noisy parameters, and streamline navigation. Crawl budget matters on large sites.
-
Noindex System & Search Pages (/search, /cart, /checkout, /login)
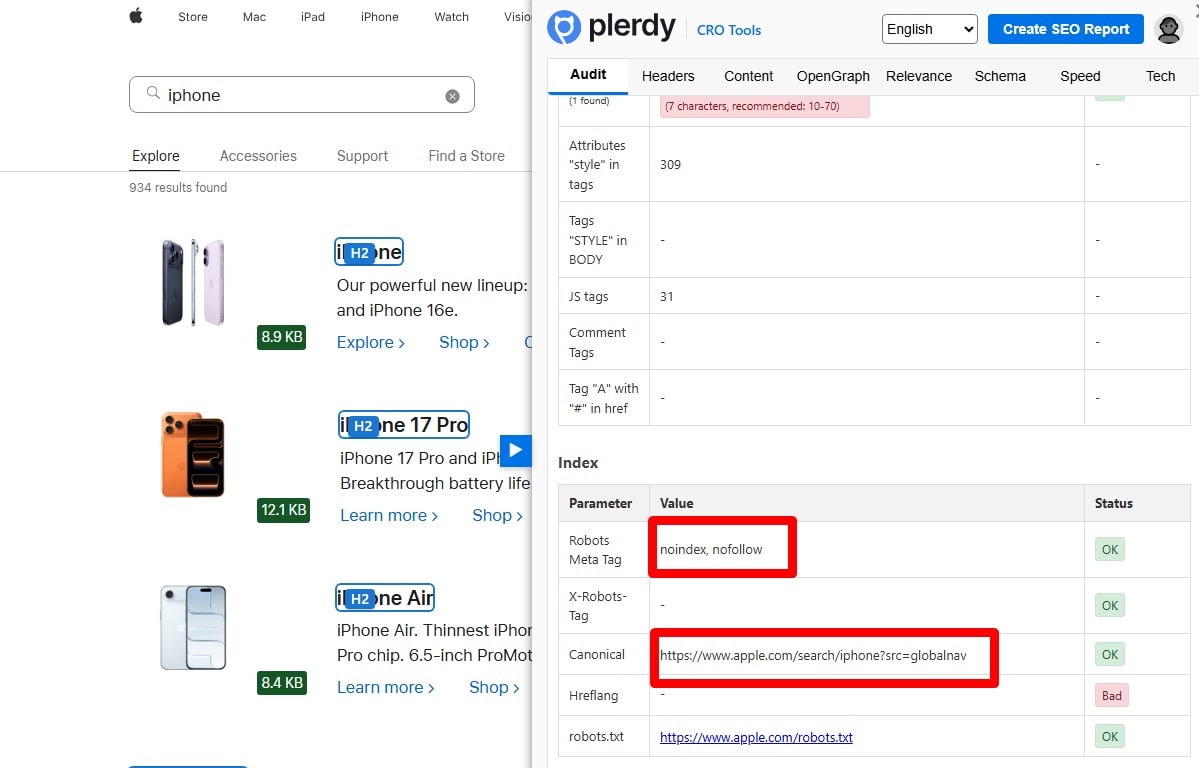 Add meta robots noindex,follow on internal search and system pages; exclude them from sitemaps. Prefer auth on sensitive areas. Check via GSC URL Inspection, Page Indexing report, and a crawler’s Indexability report.
Add meta robots noindex,follow on internal search and system pages; exclude them from sitemaps. Prefer auth on sensitive areas. Check via GSC URL Inspection, Page Indexing report, and a crawler’s Indexability report.
💡 Meta & Structured Data, Page-level & elements analysis
-
Keep Page Titles Concise (Avoid SERP Truncation)
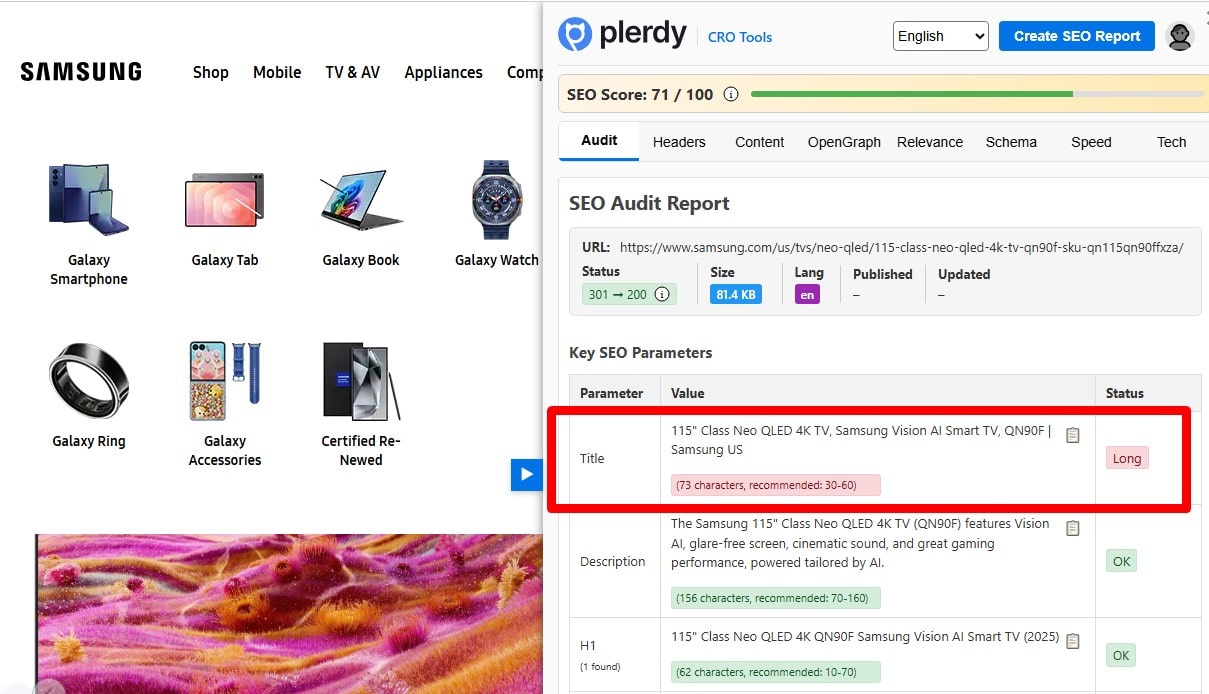 Aim for concise titles that won’t truncate in SERPs (≈600px on desktop, ~50–60 chars is a good proxy). Put the primary topic up front, brand at the end. Audit with a crawler (Plerdy, Screaming Frog, Ahrefs) and a SERP-width preview. Fix overlong titles and remove fluff.
Aim for concise titles that won’t truncate in SERPs (≈600px on desktop, ~50–60 chars is a good proxy). Put the primary topic up front, brand at the end. Audit with a crawler (Plerdy, Screaming Frog, Ahrefs) and a SERP-width preview. Fix overlong titles and remove fluff.
-
Avoid Overly Short Titles (<30 Characters)
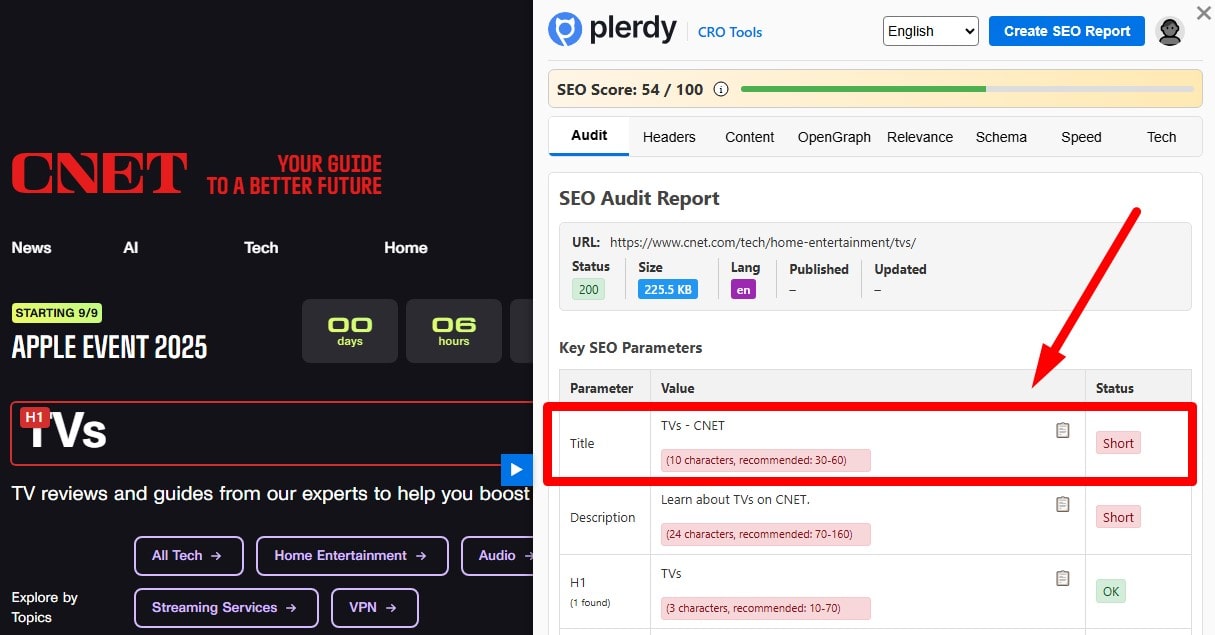 Flag titles under ~30 chars—they’re often too vague to match intent. Enrich with the primary keyword + qualifier (model, use case, region). Report short titles via crawler (Plerdy/Screaming Frog) and expand them to improve clarity and CTR.
Flag titles under ~30 chars—they’re often too vague to match intent. Enrich with the primary keyword + qualifier (model, use case, region). Report short titles via crawler (Plerdy/Screaming Frog) and expand them to improve clarity and CTR.
-
Remove Duplicate Page Titles (Handle Canonical/Pagination Correctly)
 Crawl for duplicate titles and map each URL to a unique intent. For true duplicates, de-duplicate content, consolidate with 301s, or set a clear canonical. For pagination, keep distinct titles (e.g., “Category — Page 2”) and don’t canonicalize page 2+ to page 1.
Crawl for duplicate titles and map each URL to a unique intent. For true duplicates, de-duplicate content, consolidate with 301s, or set a clear canonical. For pagination, keep distinct titles (e.g., “Category — Page 2”) and don’t canonicalize page 2+ to page 1.
-
Detect & Resolve Keyword Cannibalization
 Use GSC to find queries where multiple URLs compete. Decide the “owner” page, consolidate overlapping content, adjust internal links/anchors to favor it, and de-optimize or retarget the others. If needed, merge and 301 to the strongest URL.
Use GSC to find queries where multiple URLs compete. Decide the “owner” page, consolidate overlapping content, adjust internal links/anchors to favor it, and de-optimize or retarget the others. If needed, merge and 301 to the strongest URL.
-
Place Primary Keyword Early in the Title
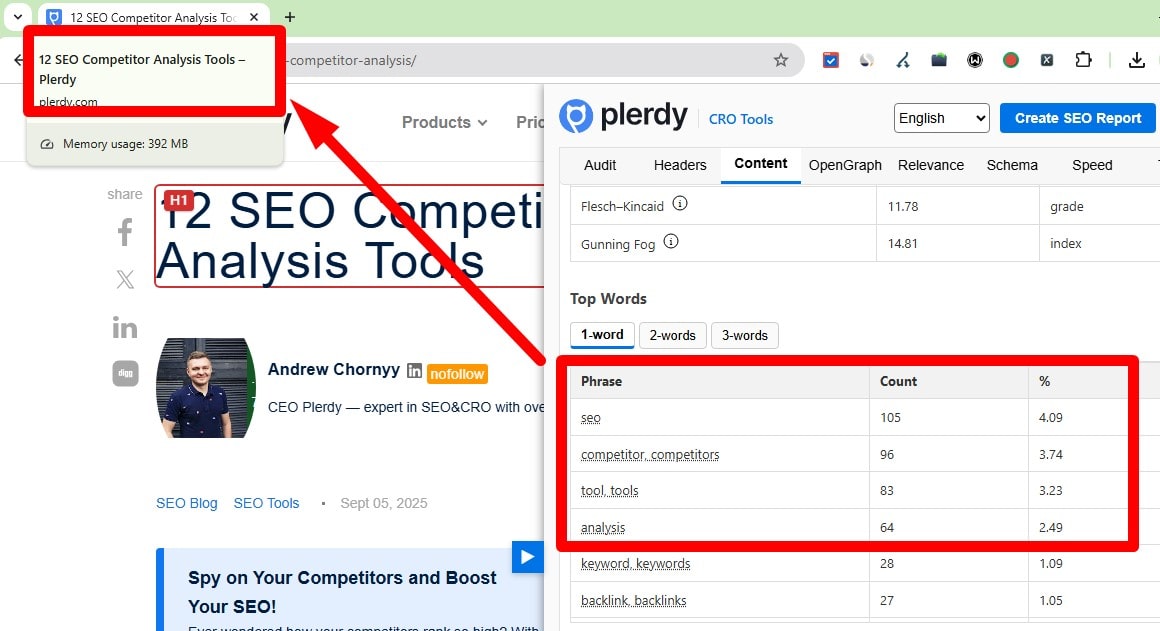 Lead with the main topic for relevance and scanning. Keep it readable; avoid stuffing. Brand at the end is fine. Verify positions via crawler exports (Plerdy/Screaming Frog) and spot titles where the focus term is buried.
Lead with the main topic for relevance and scanning. Keep it readable; avoid stuffing. Brand at the end is fine. Verify positions via crawler exports (Plerdy/Screaming Frog) and spot titles where the focus term is buried.
-
Make Titles Accurately Describe the Content
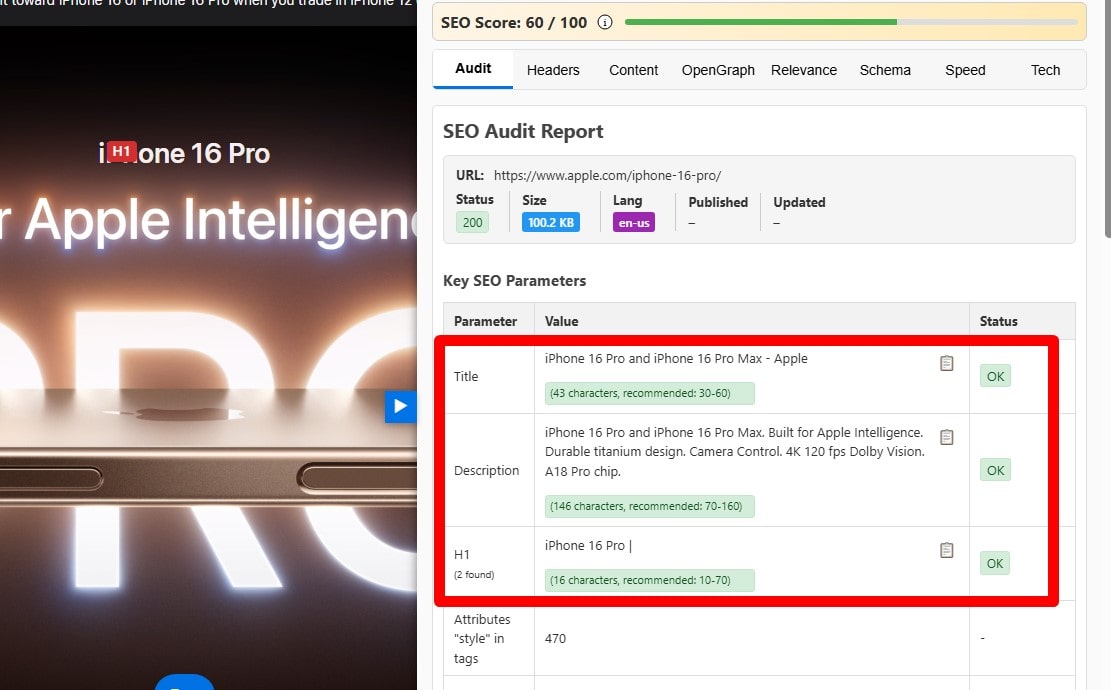 Ensure each title reflects on-page content and search intent. Avoid clickbait or generic labels (“Home,” “Products”). Crawl for mismatches and rewrite to set correct expectations; align H1, intro, and primary query.
Ensure each title reflects on-page content and search intent. Avoid clickbait or generic labels (“Home,” “Products”). Crawl for mismatches and rewrite to set correct expectations; align H1, intro, and primary query.
-
Ensure Every Page Has a Title
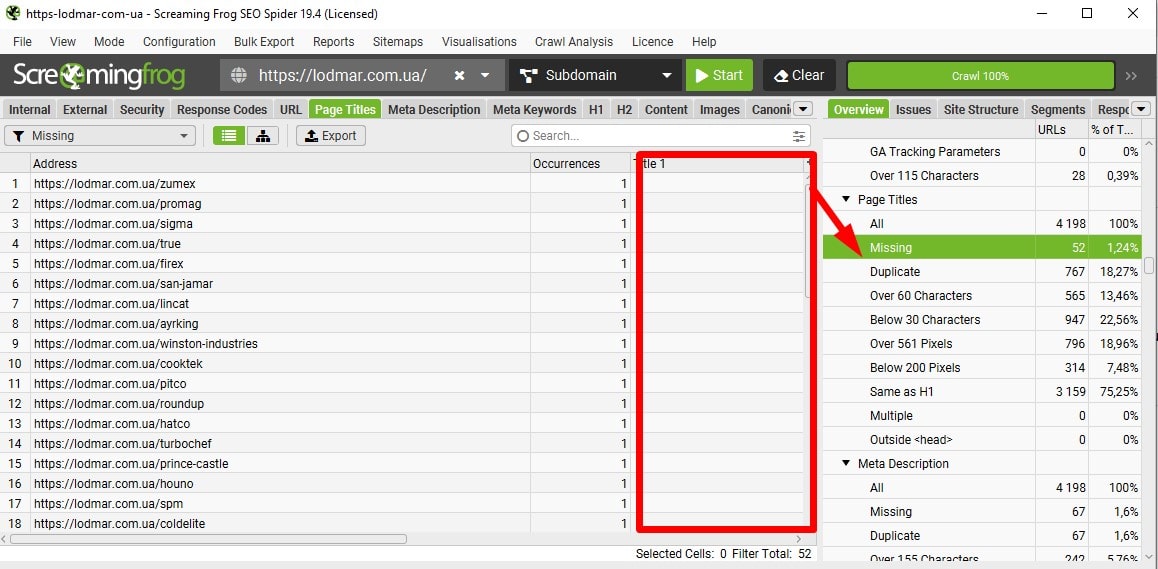 Export pages with missing/empty <title> and fix them first (templates, 404s, filters). Add safeguards in CMS to prevent publishing without titles. Watch for auto-generated duplicates from faceted navigation.
Export pages with missing/empty <title> and fix them first (templates, 404s, filters). Add safeguards in CMS to prevent publishing without titles. Watch for auto-generated duplicates from faceted navigation.
-
Write Unique, Compelling Meta Descriptions
 Meta descriptions aren’t a ranking factor, and Google may rewrite them, but good ones improve CTR. Write a clear, truthful summary that matches intent and includes a soft CTA. Keep them unique per URL and aligned with on-page copy.
Meta descriptions aren’t a ranking factor, and Google may rewrite them, but good ones improve CTR. Write a clear, truthful summary that matches intent and includes a soft CTA. Keep them unique per URL and aligned with on-page copy.
-
Fill Missing Meta Descriptions (High-Value Pages First)
 Prioritize meta descriptions for key pages (money pages, top articles). Where omitted, Google will pull a snippet—often fine for long-tail pages. Use crawler reports to find missing ones and add concise, relevant summaries.
Prioritize meta descriptions for key pages (money pages, top articles). Where omitted, Google will pull a snippet—often fine for long-tail pages. Use crawler reports to find missing ones and add concise, relevant summaries.
-
Eliminate Duplicate Meta Descriptions
 Duplicate descriptions hurt clarity and CTR (not a “duplicate content” penalty, but poor UX). Give each page a distinct summary that reflects its unique value. For pagination/variants, include differentiators (page number, filter).
Duplicate descriptions hurt clarity and CTR (not a “duplicate content” penalty, but poor UX). Give each page a distinct summary that reflects its unique value. For pagination/variants, include differentiators (page number, filter).
-
Keep Meta Descriptions ~150–160 Characters (Clear & Relevant)
 Very short snippets under-inform users. Target ~150–160 chars so the idea fits without truncation; focus on usefulness over exact length. Match search intent and on-page content; avoid keyword stuffing.
Very short snippets under-inform users. Target ~150–160 chars so the idea fits without truncation; focus on usefulness over exact length. Match search intent and on-page content; avoid keyword stuffing.
-
Do Not Use Meta Keywords
 Meta keywords are not considered important for SEO because search engines, such as Google, no longer use them as a ranking factor in their algorithms. Instead, search engines use the content of a page to determine its relevance to a user's query.
Meta keywords are not considered important for SEO because search engines, such as Google, no longer use them as a ranking factor in their algorithms. Instead, search engines use the content of a page to determine its relevance to a user's query.
-
Implement & Validate Structured Data (Where Relevant)
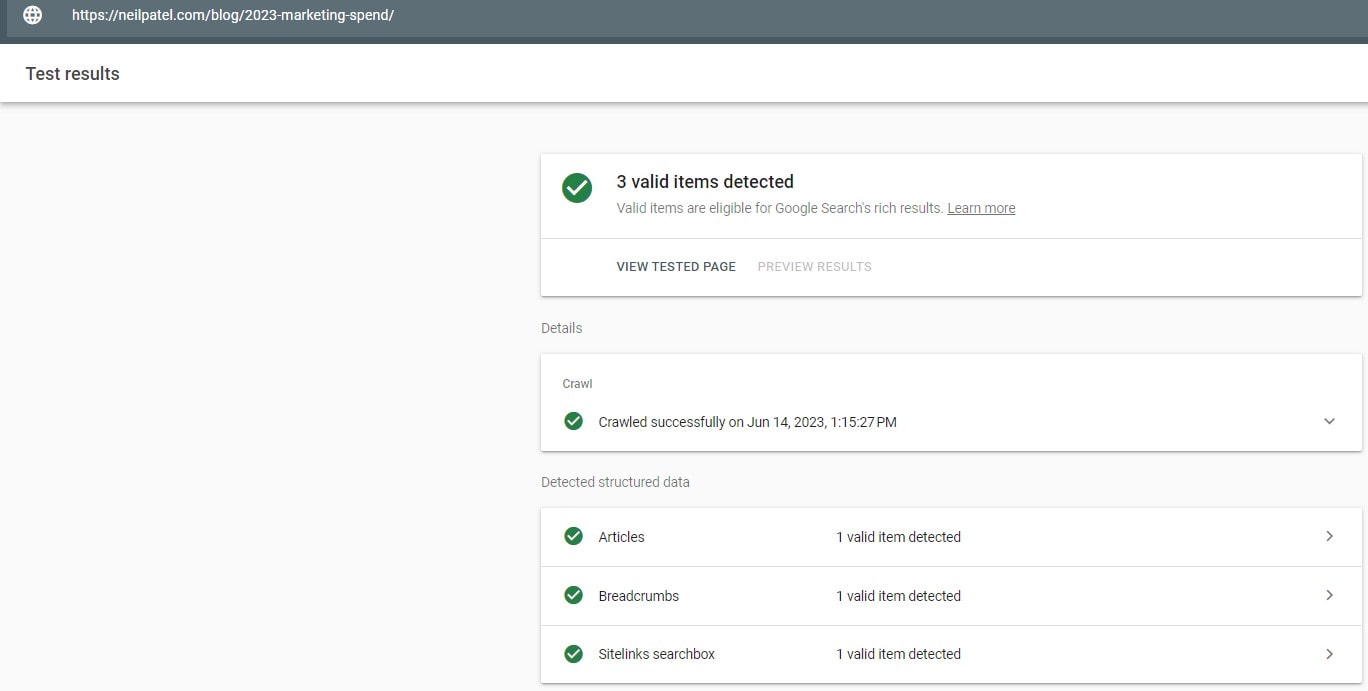 Implement and validate Organization/Person, Breadcrumb, Article, Product/Offer/Review, FAQ, and Sitelinks Search Box where relevant. Keep markup consistent with visible content and fix errors/warnings.
Implement and validate Organization/Person, Breadcrumb, Article, Product/Offer/Review, FAQ, and Sitelinks Search Box where relevant. Keep markup consistent with visible content and fix errors/warnings.
-
Add Social Preview Tags (Open Graph & Twitter Cards)
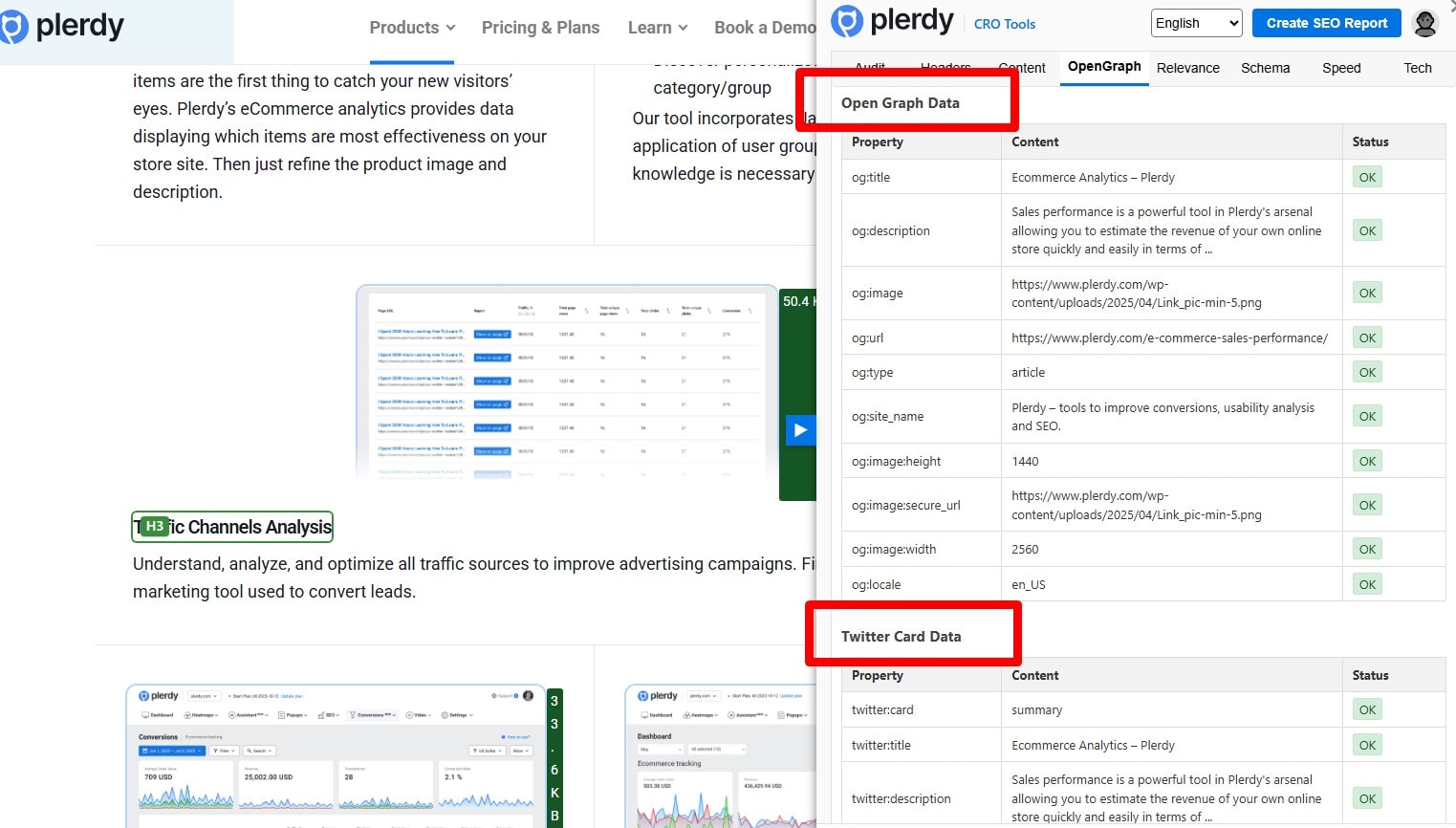 Add og:title, og:description, og:image (~1200×630), and twitter:card=summary_large_image for every indexable page; localize where you use hreflang. Validate with Facebook Sharing Debugger, Twitter Card Validator, and by checking HTML source.
Add og:title, og:description, og:image (~1200×630), and twitter:card=summary_large_image for every indexable page; localize where you use hreflang. Validate with Facebook Sharing Debugger, Twitter Card Validator, and by checking HTML source.
✍ Content
-
Ensure Readable Font Sizes
 Use a base font size of ≥16px with line-height ~1.4–1.7. Check legibility across devices and languages. Test real pages (not just components) and verify Core Web Vitals aren’t hurt by custom fonts (preload critical, use font-display: swap). Good readability reduces pogo-sticking and improves engagement.
Use a base font size of ≥16px with line-height ~1.4–1.7. Check legibility across devices and languages. Test real pages (not just components) and verify Core Web Vitals aren’t hurt by custom fonts (preload critical, use font-display: swap). Good readability reduces pogo-sticking and improves engagement.
-
Make Hyperlinks Clear and Distinct
 Links should be visually distinct (underline by default or a clearly different color) with sufficient contrast and a visible focus state. Use descriptive anchor text (not “click here”), avoid nofollow internally, and provide a visited state. Clear links help users navigate and concentrate link equity.
Links should be visually distinct (underline by default or a clearly different color) with sufficient contrast and a visible focus state. Use descriptive anchor text (not “click here”), avoid nofollow internally, and provide a visited state. Clear links help users navigate and concentrate link equity.
-
Ensure Sufficient Text Contrast
 Meet at least WCAG AA contrast (normal text 4.5:1, large text 3:1). Test dark mode and overlays on images/video. Insufficient contrast tanks readability and can increase bounces. Fix with palette tweaks, backgrounds, or text-shadow only if necessary.
Meet at least WCAG AA contrast (normal text 4.5:1, large text 3:1). Test dark mode and overlays on images/video. Insufficient contrast tanks readability and can increase bounces. Fix with palette tweaks, backgrounds, or text-shadow only if necessary.
-
Differentiate Primary vs. Supplementary Content
 Make main content obvious; separate supplementary elements (nav, sidebars, related items, ads). Label ads/sponsored blocks and avoid blending them with main content. Clear hierarchy improves comprehension and aligns with quality rater guidelines.
Make main content obvious; separate supplementary elements (nav, sidebars, related items, ads). Label ads/sponsored blocks and avoid blending them with main content. Clear hierarchy improves comprehension and aligns with quality rater guidelines.
-
Balance Evergreen and Fresh Content
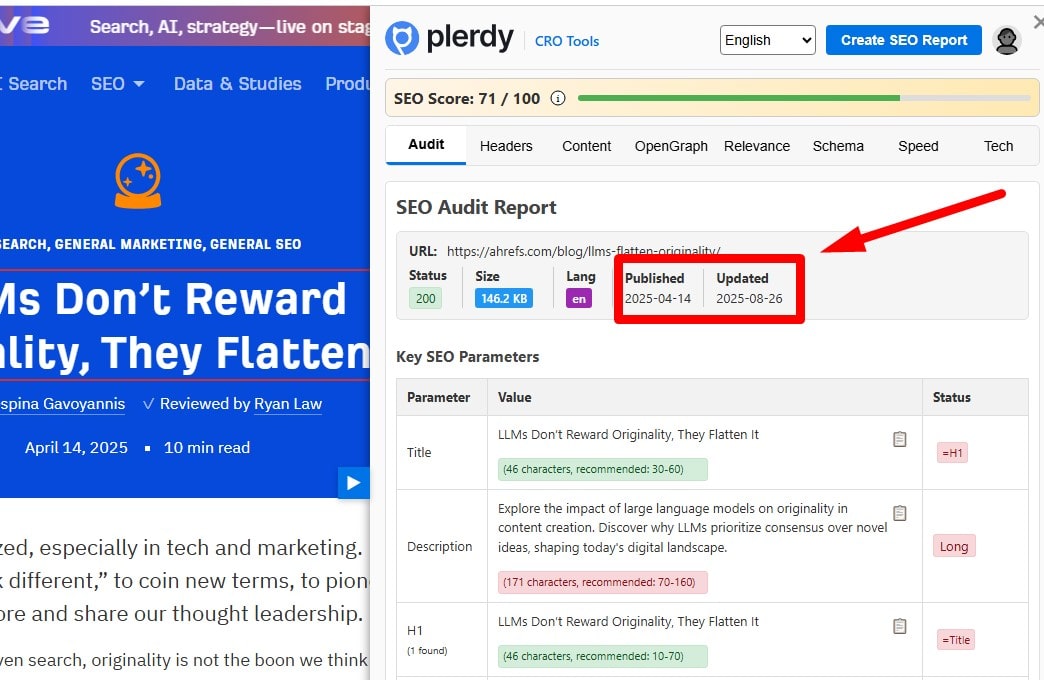 Maintain evergreen hubs that earn links over time, then layer timely updates (new data, screenshots, features). Show datePublished/dateModified where relevant and update titles/intros when the year changes. Don’t “fake-refresh” with trivial edits.
Maintain evergreen hubs that earn links over time, then layer timely updates (new data, screenshots, features). Show datePublished/dateModified where relevant and update titles/intros when the year changes. Don’t “fake-refresh” with trivial edits.
-
Eliminate Low-Value/Thin Pages
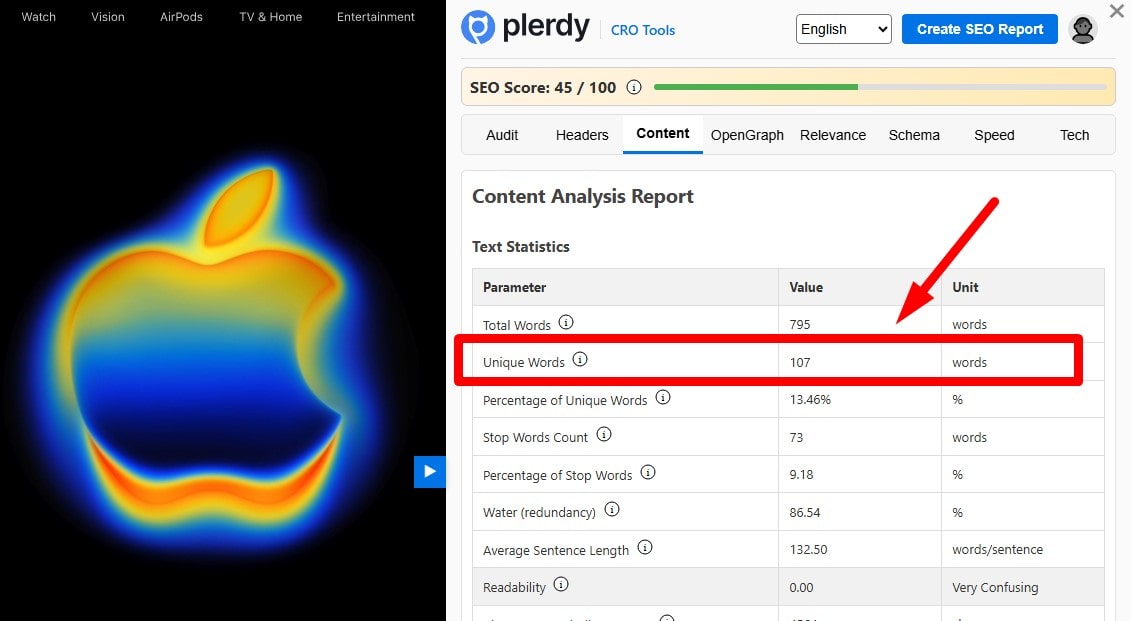 Word count isn’t a ranking factor—value is. Identify pages with little unique main content, near-duplicates, empty category/tag pages, or boilerplate. Consolidate, improve, or noindex them; add internal links and unique purpose before reindexing.
Word count isn’t a ranking factor—value is. Identify pages with little unique main content, near-duplicates, empty category/tag pages, or boilerplate. Consolidate, improve, or noindex them; add internal links and unique purpose before reindexing.
-
Publish an Up-to-Date Privacy Policy
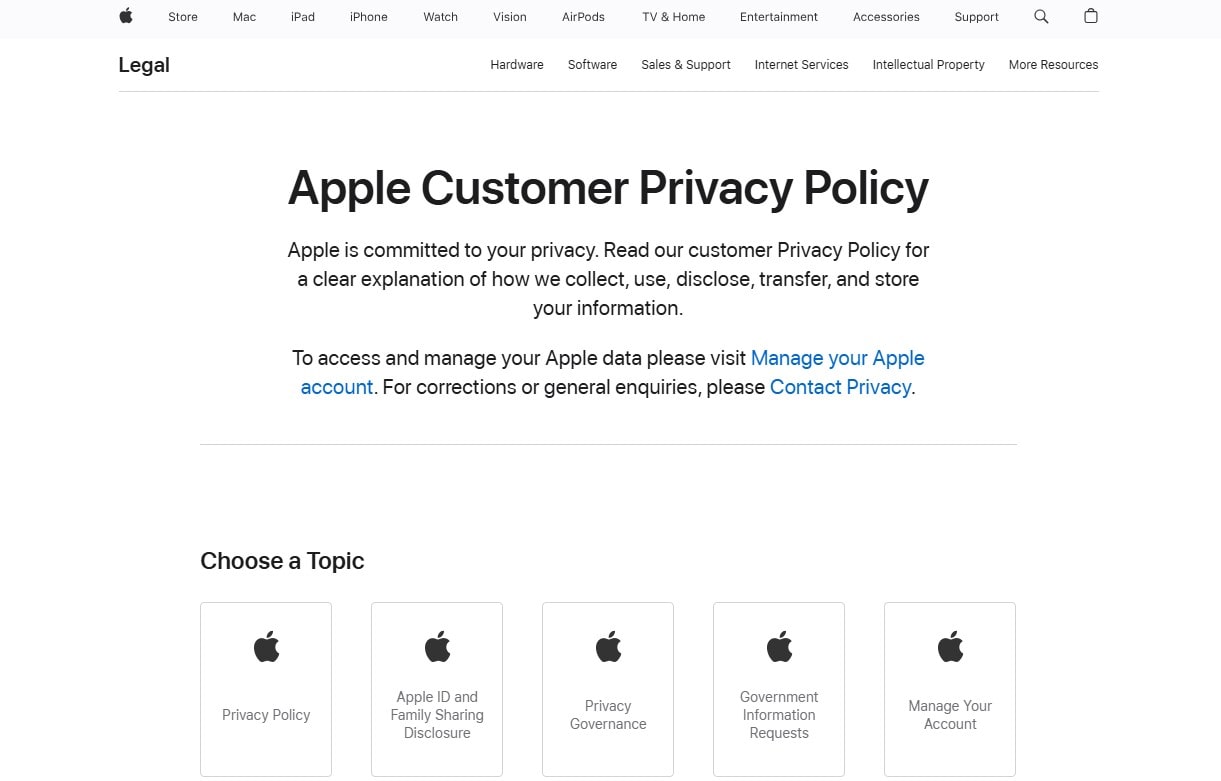 Link Privacy (and Terms) in the footer; keep it current with data practices (GDPR/CCPA, cookies, opt-outs). It’s a trust signal for users and reviewers; pair with a contact route and brand info (address, company, VAT where relevant).
Link Privacy (and Terms) in the footer; keep it current with data practices (GDPR/CCPA, cookies, opt-outs). It’s a trust signal for users and reviewers; pair with a contact route and brand info (address, company, VAT where relevant).
-
Eliminate Internal Duplicate Content
 Audit duplicates from parameters, faceted nav, print pages, HTTP/HTTPS, and www variants. Canonicalize to a single URL, block crawl of junk parameters, and 301 consolidate when appropriate. Keep only one indexable version per intent.
Audit duplicates from parameters, faceted nav, print pages, HTTP/HTTPS, and www variants. Canonicalize to a single URL, block crawl of junk parameters, and 301 consolidate when appropriate. Keep only one indexable version per intent.
-
Address External Duplicates/Syndication
 If you syndicate, use canonical back to the original (or noindex on partners). For scraped copies, strengthen internal linking, publish first, and request removal when needed. Focus on unique analysis, data, and visuals.
If you syndicate, use canonical back to the original (or noindex on partners). For scraped copies, strengthen internal linking, publish first, and request removal when needed. Focus on unique analysis, data, and visuals.
-
Avoid Scraped/Plagiarized Content
 Don’t republish others’ content verbatim. Quote briefly with attribution, then add unique commentary, data, or experiments. Use canonical when republishing your own work elsewhere.
Don’t republish others’ content verbatim. Quote briefly with attribution, then add unique commentary, data, or experiments. Use canonical when republishing your own work elsewhere.
-
Provide a Clear, Easy-to-Find Contact Page
 Link “Contact” in the header/footer; include email/phone, form, and business details (NAP). Add spam protection and expected response times. For local businesses, add map and opening hours; consider LocalBusiness schema.
Link “Contact” in the header/footer; include email/phone, form, and business details (NAP). Add spam protection and expected response times. For local businesses, add map and opening hours; consider LocalBusiness schema.
-
Run Content Gap Analysis
 Map target topics vs. competitors and SERP features. Fill gaps with pages that match intent (informational vs. commercial), then connect them via internal links to pillar pages. Use crawler/GSC exports to prioritize by opportunity and difficulty.
Map target topics vs. competitors and SERP features. Fill gaps with pages that match intent (informational vs. commercial), then connect them via internal links to pillar pages. Use crawler/GSC exports to prioritize by opportunity and difficulty.
-
Review Copy Quality and Content Classification
 Fix tone, clarity, and factual accuracy; avoid jargon bloat. Classify content consistently (categories, tags) and prevent low-value tag archives from indexing. Add summaries, intros, and clear subheads for scanning.
Fix tone, clarity, and factual accuracy; avoid jargon bloat. Classify content consistently (categories, tags) and prevent low-value tag archives from indexing. Add summaries, intros, and clear subheads for scanning.
-
Check Grammar and Spelling
 Proofread headlines, CTAs, tables, and image captions. Typos erode trust and can confuse searchers. Build editorial checks into your publishing workflow; run language-specific QA for localized pages.
Proofread headlines, CTAs, tables, and image captions. Typos erode trust and can confuse searchers. Build editorial checks into your publishing workflow; run language-specific QA for localized pages.
-
Use Hierarchical Headings and Semantic HTML
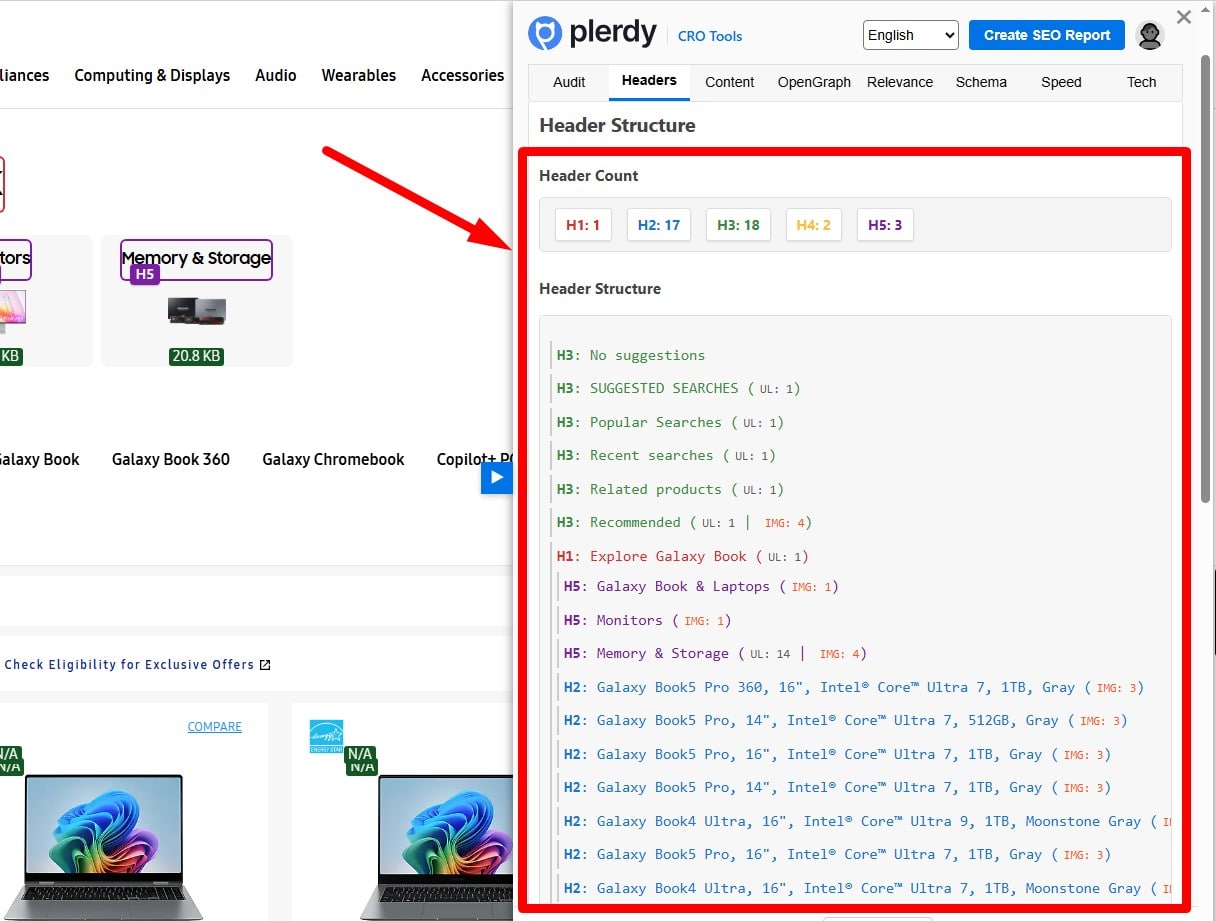 Use a clear heading outline (one primary H1, then H2/H3), lists for steps, tables for comparisons, and descriptive alt text. Add a table of contents for long guides. Semantic structure improves comprehension and machine parsing.
Use a clear heading outline (one primary H1, then H2/H3), lists for steps, tables for comparisons, and descriptive alt text. Add a table of contents for long guides. Semantic structure improves comprehension and machine parsing.
-
Target Topics and Queries (Not Just Keywords)
 Cover the user intent thoroughly: include entities, FAQs, and supporting subtopics. Place the main query in the title/H1/intro naturally. Avoid stuffing—opt for clarity, examples, and original assets (diagrams, screenshots, data).
Cover the user intent thoroughly: include entities, FAQs, and supporting subtopics. Place the main query in the title/H1/intro naturally. Avoid stuffing—opt for clarity, examples, and original assets (diagrams, screenshots, data).
-
Follow Google Search Essentials (Quality/Spam Policies)
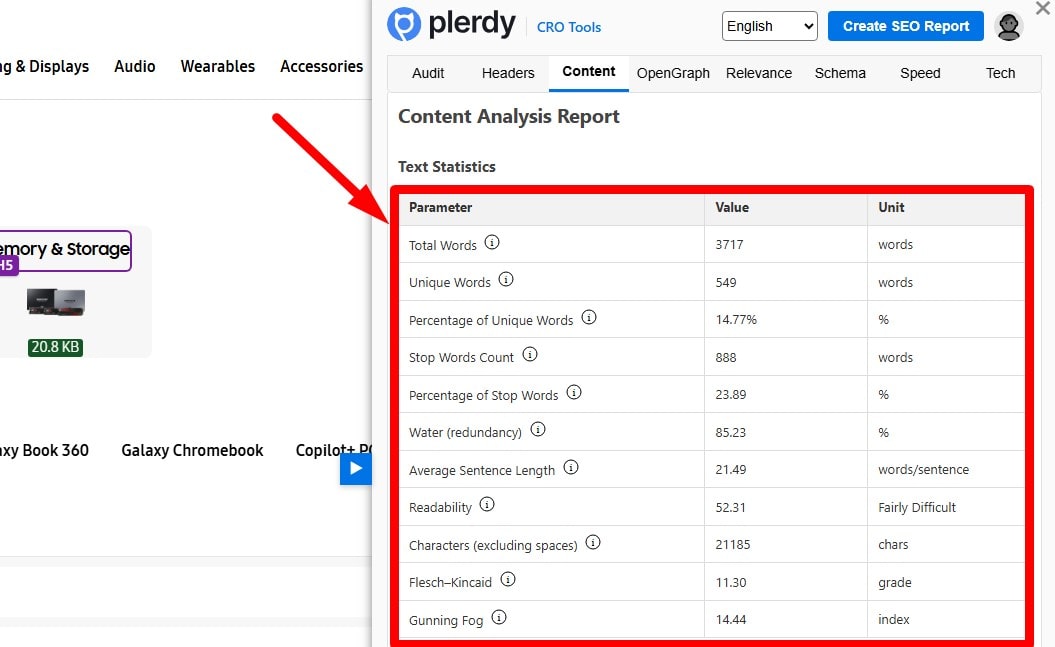 Avoid auto-generated fluff, doorway pages, hidden text, link schemes, and deceptive UX. Demonstrate expertise, cite sources, and provide helpful, original information aligned with Search Essentials.
Avoid auto-generated fluff, doorway pages, hidden text, link schemes, and deceptive UX. Demonstrate expertise, cite sources, and provide helpful, original information aligned with Search Essentials.
-
Avoid Intrusive Interstitials (Especially on Mobile)
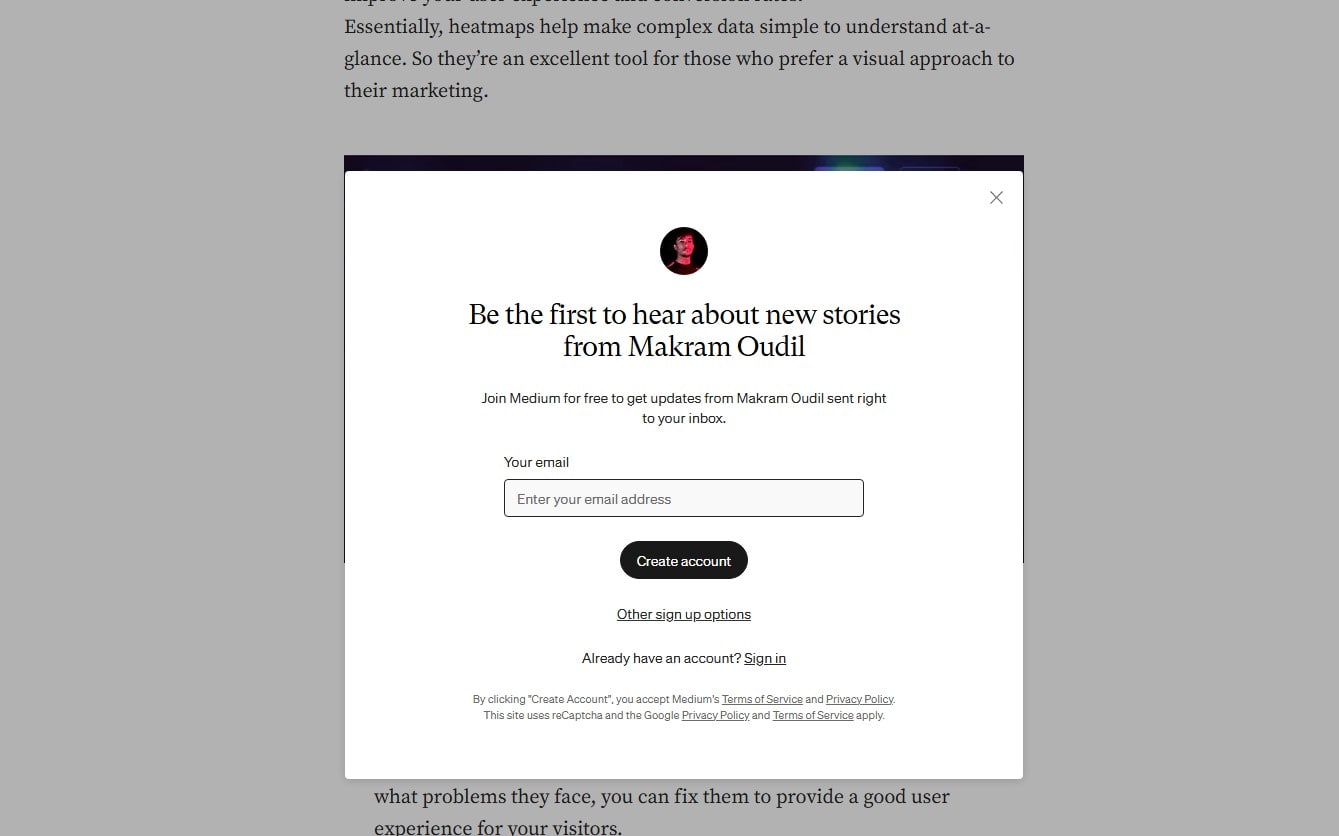 Legal notices (cookie consent, age gates) are fine when minimal. Avoid full-screen popups that block main content on landing. Delay promos until interaction or time-on-page; provide easy dismissal.
Legal notices (cookie consent, age gates) are fine when minimal. Avoid full-screen popups that block main content on landing. Delay promos until interaction or time-on-page; provide easy dismissal.
-
Limit Heavy Above-the-Fold Ads
 Keep primary content visible on load. Compress ad scripts, lazy-load below-the-fold, and cap ad density. Watch CLS/LCP in Core Web Vitals; reserve space to prevent layout shifts.
Keep primary content visible on load. Compress ad scripts, lazy-load below-the-fold, and cap ad density. Watch CLS/LCP in Core Web Vitals; reserve space to prevent layout shifts.
-
Avoid Critical Content in iFrames
 Google can index iframes, but content counts for the iframe source URL, not the parent. Don’t put essential copy/links only in an iframe. If embedding tools/video, allow bot access to the source and add contextual text on the page. Set width/height to prevent CLS; loading="lazy" is fine.
Google can index iframes, but content counts for the iframe source URL, not the parent. Don’t put essential copy/links only in an iframe. If embedding tools/video, allow bot access to the source and add contextual text on the page. Set width/height to prevent CLS; loading="lazy" is fine.
-
Ensure Lazy-Loaded Content Is Discoverable
 Use native lazy-loading for images/iframes; for content lists, load initial items server-side and expose links/JSON in HTML. Avoid requiring user interaction for critical content. Test rendering with a crawler and URL Inspection.
Use native lazy-loading for images/iframes; for content lists, load initial items server-side and expose links/JSON in HTML. Avoid requiring user interaction for critical content. Test rendering with a crawler and URL Inspection.
-
Make Infinite Scroll Crawlable (Paginated URLs)
 Provide unique, linked URLs for each page/state (e.g., ?page=2) using anchor links or “Load more” that updates the URL (pushState). Ensure each page is reachable without JS and is internally linked. Consider a “view all” option when feasible. (Don’t rely on deprecated rel="next/prev".)
Provide unique, linked URLs for each page/state (e.g., ?page=2) using anchor links or “Load more” that updates the URL (pushState). Ensure each page is reachable without JS and is internally linked. Consider a “view all” option when feasible. (Don’t rely on deprecated rel="next/prev".)
-
Show Publication and Updated Dates
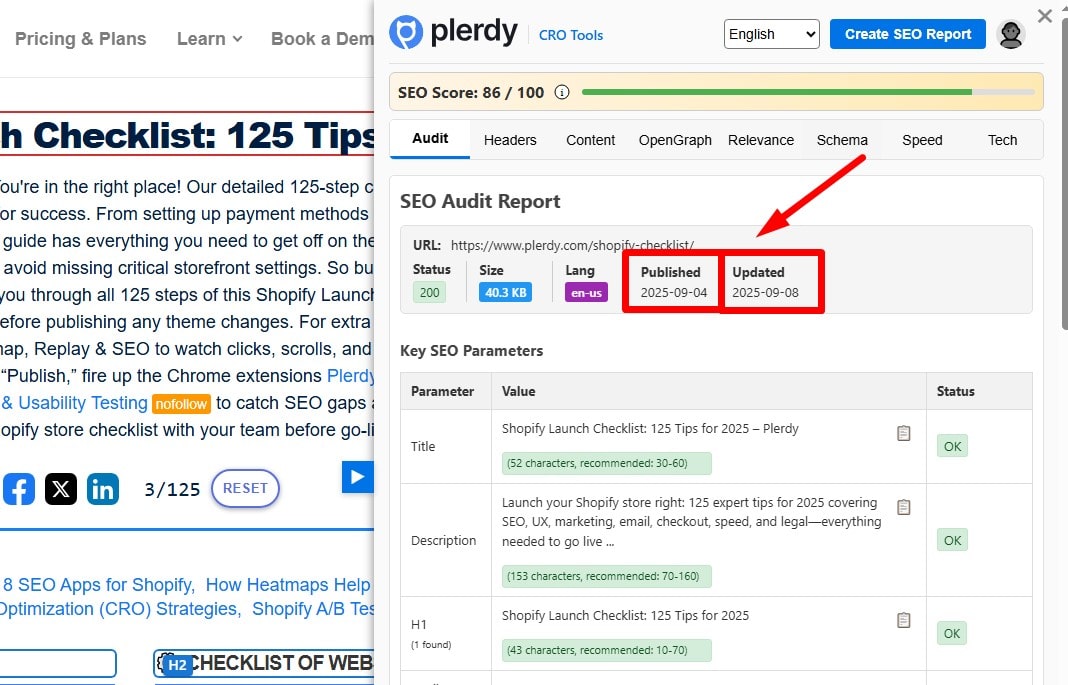 Display datePublished and meaningful dateModified when you actually update substance (not typos). Use structured data where relevant (Article/BlogPosting). Don’t spam “Updated” badges without changes.
Display datePublished and meaningful dateModified when you actually update substance (not typos). Use structured data where relevant (Article/BlogPosting). Don’t spam “Updated” badges without changes.
-
Show Author and Publisher Clearly
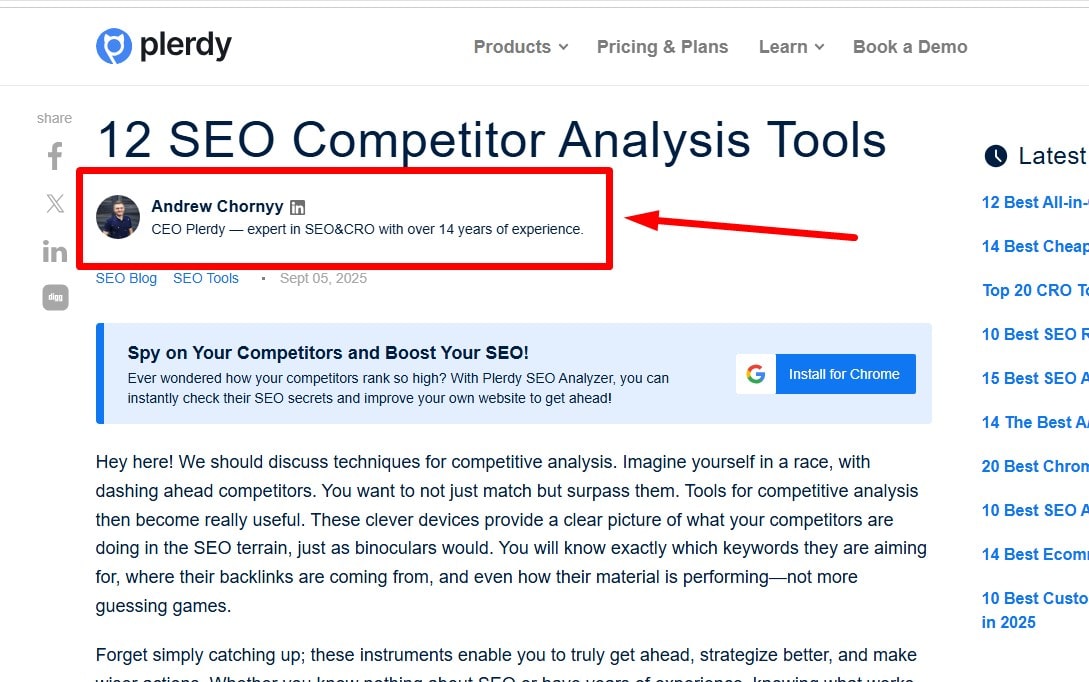 Add an author box with credentials, links to profiles, and editorial standards. Include an About page. Use sameAs and Organization markup where appropriate. Transparency supports trust and expertise.
Add an author box with credentials, links to profiles, and editorial standards. Include an About page. Use sameAs and Organization markup where appropriate. Transparency supports trust and expertise.
-
Avoid Content Flagged by SafeSearch
 If your audience is general, avoid explicit imagery/terms and ensure thumbnails/snippets are safe. Use proper tagging and context for sensitive topics. Remember SafeSearch can filter results for opted-in users.
If your audience is general, avoid explicit imagery/terms and ensure thumbnails/snippets are safe. Use proper tagging and context for sensitive topics. Remember SafeSearch can filter results for opted-in users.
-
Avoid Hidden Text Meant to Manipulate
 Do not hide keyword-stuffed text (e.g., same-color text, off-screen positioning). Hiding for legitimate UX (tabs/accordions) is fine if content is visible on interaction and not deceptive.
Do not hide keyword-stuffed text (e.g., same-color text, off-screen positioning). Hiding for legitimate UX (tabs/accordions) is fine if content is visible on interaction and not deceptive.
-
Do Not Cloak
 Serve the same primary content to users and crawlers. Personalization/A/B tests are OK when experiences are equivalent. Avoid UA/IP-based swaps meant to manipulate rankings.
Serve the same primary content to users and crawlers. Personalization/A/B tests are OK when experiences are equivalent. Avoid UA/IP-based swaps meant to manipulate rankings.
-
Avoid Doorway Pages
 Don’t create many near-duplicate pages targeting slight geo/keyword variations that funnel to the same destination. Build robust hub pages or localized pages with real unique value.
Don’t create many near-duplicate pages targeting slight geo/keyword variations that funnel to the same destination. Build robust hub pages or localized pages with real unique value.
-
Avoid Excessive Ad Density
 Keep ads reasonable, clearly labeled, and secondary to content. Measure scroll depth and time-to-content; reduce ad slots if they impede reading or tank Core Web Vitals.
Keep ads reasonable, clearly labeled, and secondary to content. Measure scroll depth and time-to-content; reduce ad slots if they impede reading or tank Core Web Vitals.
-
Do Not Overuse Pop-Ups
 Cap the frequency, delay initial promos, and never block main content on entry—especially on mobile. Provide clear close controls and avoid deceptive patterns.
Cap the frequency, delay initial promos, and never block main content on entry—especially on mobile. Provide clear close controls and avoid deceptive patterns.
-
Use Clear Calls to Action
 Each page should have a primary CTA (text + prominent button) and supporting CTAs where relevant. Make it specific (“Start free trial”), place it high and repeat at logical points. Test copy and placement.
Each page should have a primary CTA (text + prominent button) and supporting CTAs where relevant. Make it specific (“Start free trial”), place it high and repeat at logical points. Test copy and placement.
-
Use a Clear H1 Per Page
 Prefer one descriptive H1 that matches the page’s primary intent. HTML5 allows multiple H1s, but a single main H1 is simpler and less error-prone. Align H1 with title and intro; avoid empty/duplicate H1s across templates.
Prefer one descriptive H1 that matches the page’s primary intent. HTML5 allows multiple H1s, but a single main H1 is simpler and less error-prone. Align H1 with title and intro; avoid empty/duplicate H1s across templates.
-
Use H2 Subheadings for Structure
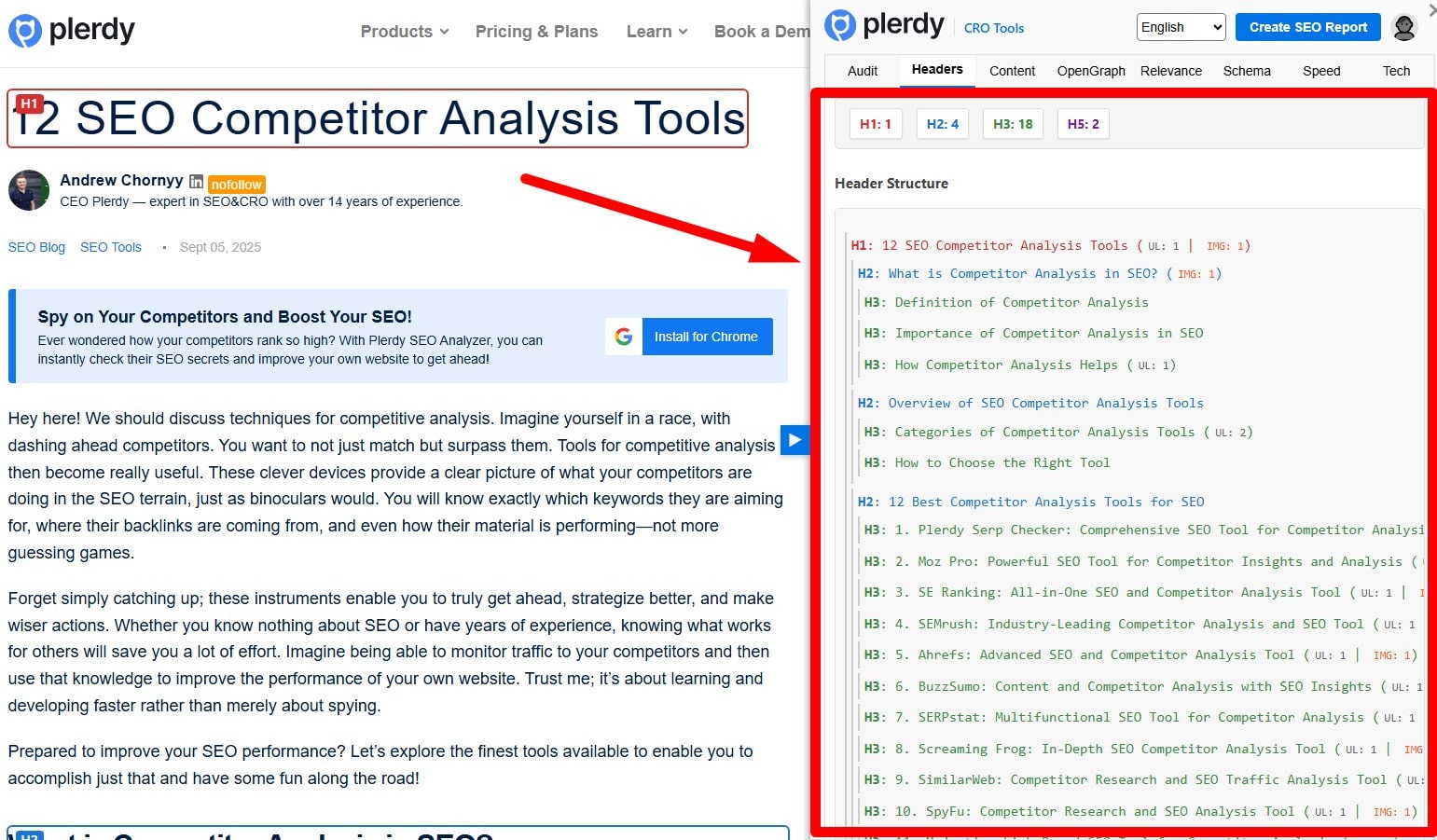 Break content into logical sections with H2/H3s for scannability. Keep headings descriptive and avoid stuffing keywords. Headings should reflect the outline users expect from the query.
Break content into logical sections with H2/H3s for scannability. Keep headings descriptive and avoid stuffing keywords. Headings should reflect the outline users expect from the query.
-
Publish People-First Content (AI-Assisted Is Fine)
 Search systems don’t reward or punish “AI-detected” content; they reward helpful, original work. If you use AI, edit for accuracy, add unique insights, examples, and first-hand experience. Cite sources, update regularly, and ensure factual correctness.
Search systems don’t reward or punish “AI-detected” content; they reward helpful, original work. If you use AI, edit for accuracy, add unique insights, examples, and first-hand experience. Cite sources, update regularly, and ensure factual correctness.
-
Strengthen Authorship & E-E-A-T Signals
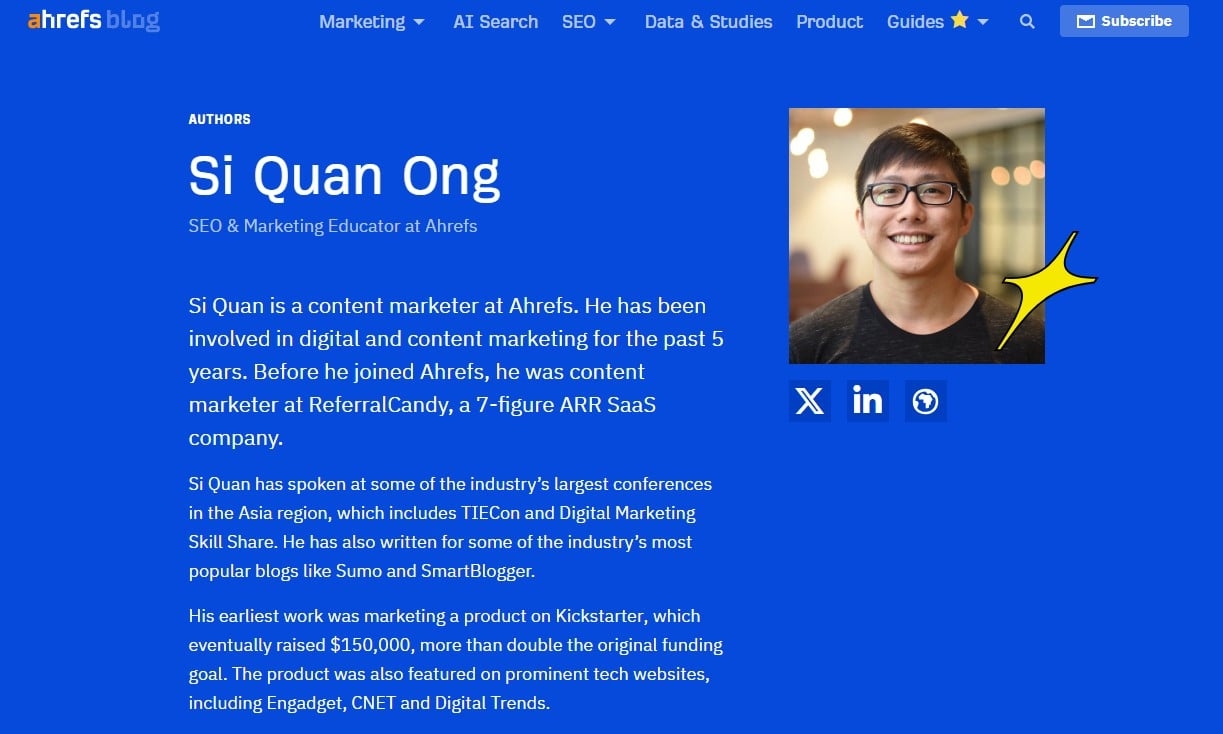 Add author bios/credentials, About/Editorial pages, and sameAs links to real profiles. Cite reliable sources, disclose monetization/ads, keep articles updated, and weave in hands-on expertise (screenshots, data, case studies).
Add author bios/credentials, About/Editorial pages, and sameAs links to real profiles. Cite reliable sources, disclose monetization/ads, keep articles updated, and weave in hands-on expertise (screenshots, data, case studies).
🗝 Keyword analysis
-
Do Keyword Research and Set Benchmarks
 Define topics and intent (informational, commercial, local). Build clusters with head terms + long-tails and map them to pages. Record baselines: GSC clicks/impressions/CTR/position, non-brand vs. brand, share of voice vs. key competitors, and SERP features present. Revisit quarterly; prioritize high-value, realistic wins.
Define topics and intent (informational, commercial, local). Build clusters with head terms + long-tails and map them to pages. Record baselines: GSC clicks/impressions/CTR/position, non-brand vs. brand, share of voice vs. key competitors, and SERP features present. Revisit quarterly; prioritize high-value, realistic wins.
-
Own Your Branded Query (Homepage Ranks #1)
 Search your exact brand name and variants. The homepage should rank #1 with sitelinks; knowledge panel and social profiles should be accurate. Fix issues by consolidating duplicates (301), using Organization schema, aligning brand name in titles/H1, consistent NAP, and linking to official profiles. Remove confusing “brand + login/help” pages from title dominance if needed.
Search your exact brand name and variants. The homepage should rank #1 with sitelinks; knowledge panel and social profiles should be accurate. Fix issues by consolidating duplicates (301), using Organization schema, aligning brand name in titles/H1, consistent NAP, and linking to official profiles. Remove confusing “brand + login/help” pages from title dominance if needed.
-
Is there evidence of keyword duplication or overuse?
 Scan titles/headings/body for repeated head terms that read unnaturally. Replace repetition with synonyms/entities, answer sub-questions, and tighten sentences. Keep anchors varied and human. If multiple pages chase the same query, retarget one to another topic and adjust internal links to reduce competition.
Scan titles/headings/body for repeated head terms that read unnaturally. Replace repetition with synonyms/entities, answer sub-questions, and tighten sentences. Keep anchors varied and human. If multiple pages chase the same query, retarget one to another topic and adjust internal links to reduce competition.
-
Use the Primary Topic in the Title
 Lead with the core topic; add a useful qualifier (model, use case, region). Keep concise to avoid truncation and avoid repeating the brand twice. Expect occasional Google rewrites—ensure H1/intro match the title so the chosen snippet stays relevant.
Lead with the core topic; add a useful qualifier (model, use case, region). Keep concise to avoid truncation and avoid repeating the brand twice. Expect occasional Google rewrites—ensure H1/intro match the title so the chosen snippet stays relevant.
-
Include the Primary Keyword in the H1
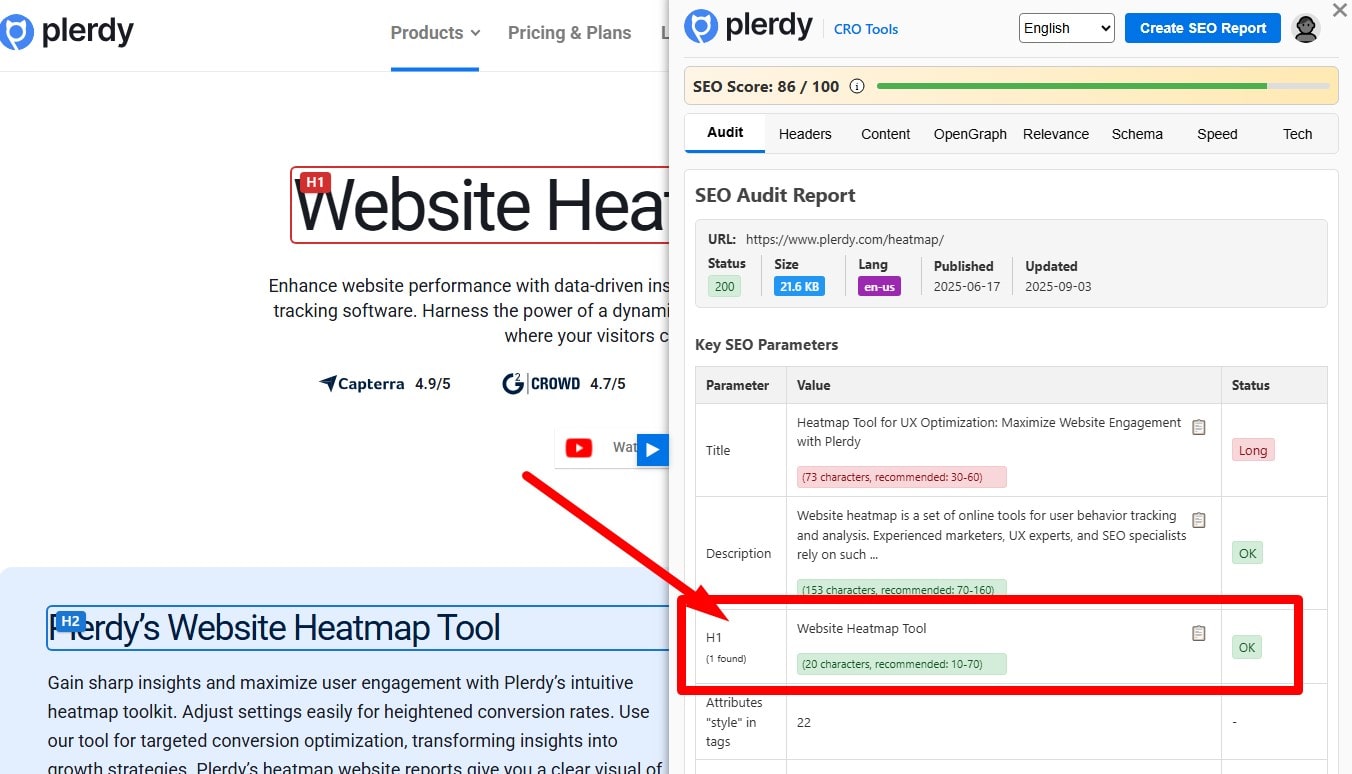 Use a single, clear H1 per page and include the primary keyword naturally—ideally near the start if it reads well. Align the H1 with the <title> and opening paragraph so they all reflect the same intent (they don’t have to be identical). Avoid stuffing; let H2/H3s cover related entities and subtopics. Audit by exporting H1s in a crawler (Plerdy/Screaming Frog) and fix empty, duplicate, or mismatched H1s across templates.
Use a single, clear H1 per page and include the primary keyword naturally—ideally near the start if it reads well. Align the H1 with the <title> and opening paragraph so they all reflect the same intent (they don’t have to be identical). Avoid stuffing; let H2/H3s cover related entities and subtopics. Audit by exporting H1s in a crawler (Plerdy/Screaming Frog) and fix empty, duplicate, or mismatched H1s across templates.
-
Include the Primary Keyword (or Close Variant) in an H2
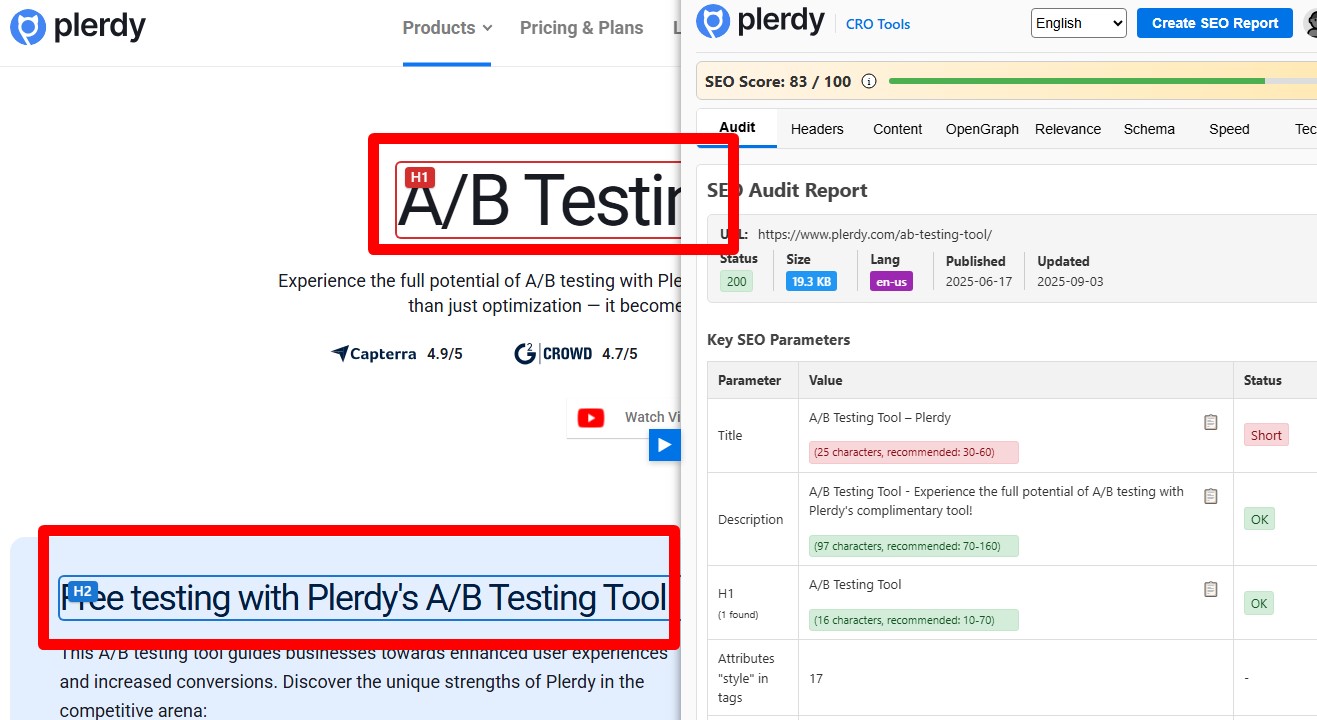 At least one H2 should naturally include the primary keyword or a close variant (e.g., singular/plural, stem, or a question form). Don’t stuff the same head term into every H2—use related entities for the rest. Keep headings readable and aligned with search intent. Audit by exporting H2s with a crawler (Plerdy/Screaming Frog) and fix pages where no H2 reflects the core topic.
At least one H2 should naturally include the primary keyword or a close variant (e.g., singular/plural, stem, or a question form). Don’t stuff the same head term into every H2—use related entities for the rest. Keep headings readable and aligned with search intent. Audit by exporting H2s with a crawler (Plerdy/Screaming Frog) and fix pages where no H2 reflects the core topic.
-
Include the Primary Keyword in the Meta Description (for CTR)
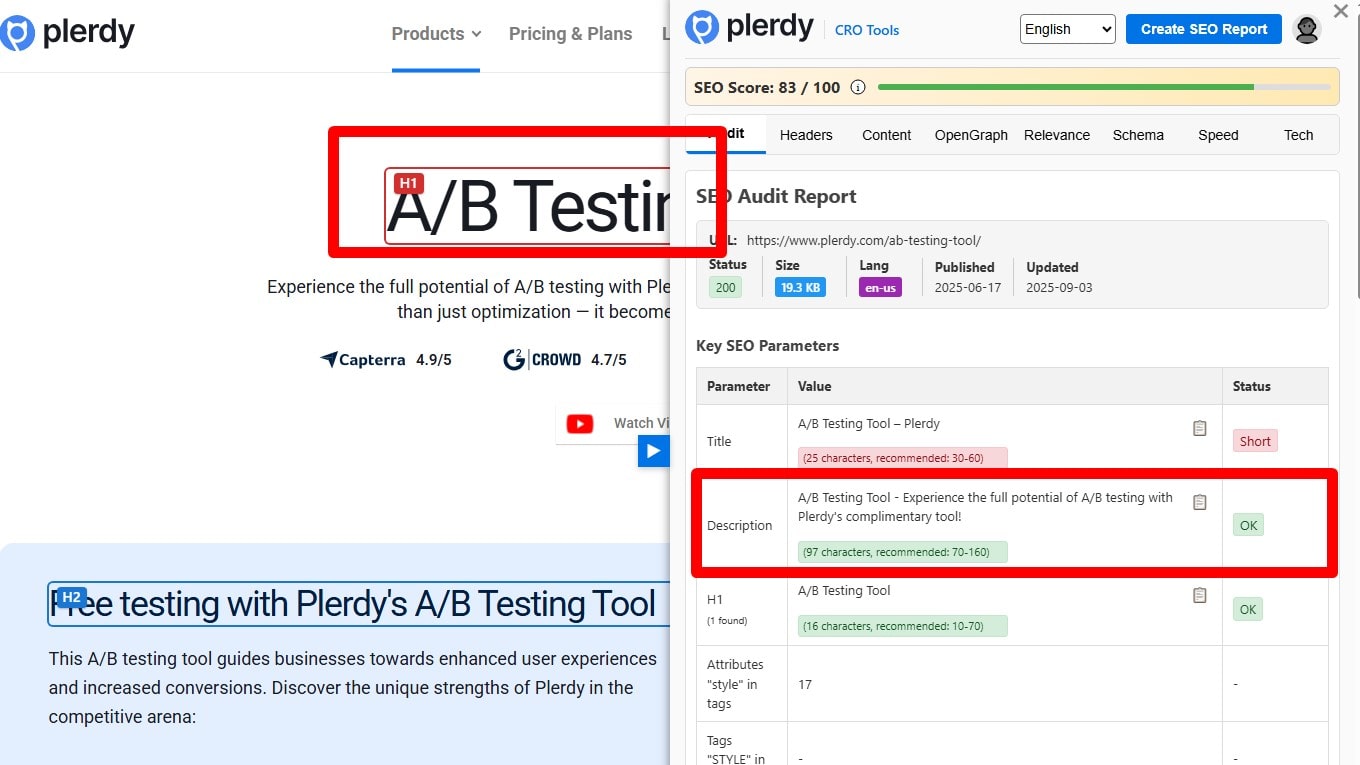 Meta descriptions aren’t a ranking factor, but including the primary keyword (or a close variant) once—ideally near the start—can bold in SERPs and lift CTR. Write a truthful ~150–160-character summary that matches on-page content and search intent; add 1–2 natural supporting terms, not stuffing. Keep each description unique per URL, use the page’s language, and include a clear value prop + soft CTA. For templates (e.g., product/category), dynamically pull specifics (price, stock, rating). If Google rewrites your snippet often, tighten the opening paragraph and headings so the auto-snippet still contains the keyword and value.
Meta descriptions aren’t a ranking factor, but including the primary keyword (or a close variant) once—ideally near the start—can bold in SERPs and lift CTR. Write a truthful ~150–160-character summary that matches on-page content and search intent; add 1–2 natural supporting terms, not stuffing. Keep each description unique per URL, use the page’s language, and include a clear value prop + soft CTA. For templates (e.g., product/category), dynamically pull specifics (price, stock, rating). If Google rewrites your snippet often, tighten the opening paragraph and headings so the auto-snippet still contains the keyword and value.
-
Include the Primary Keyword in Body Copy
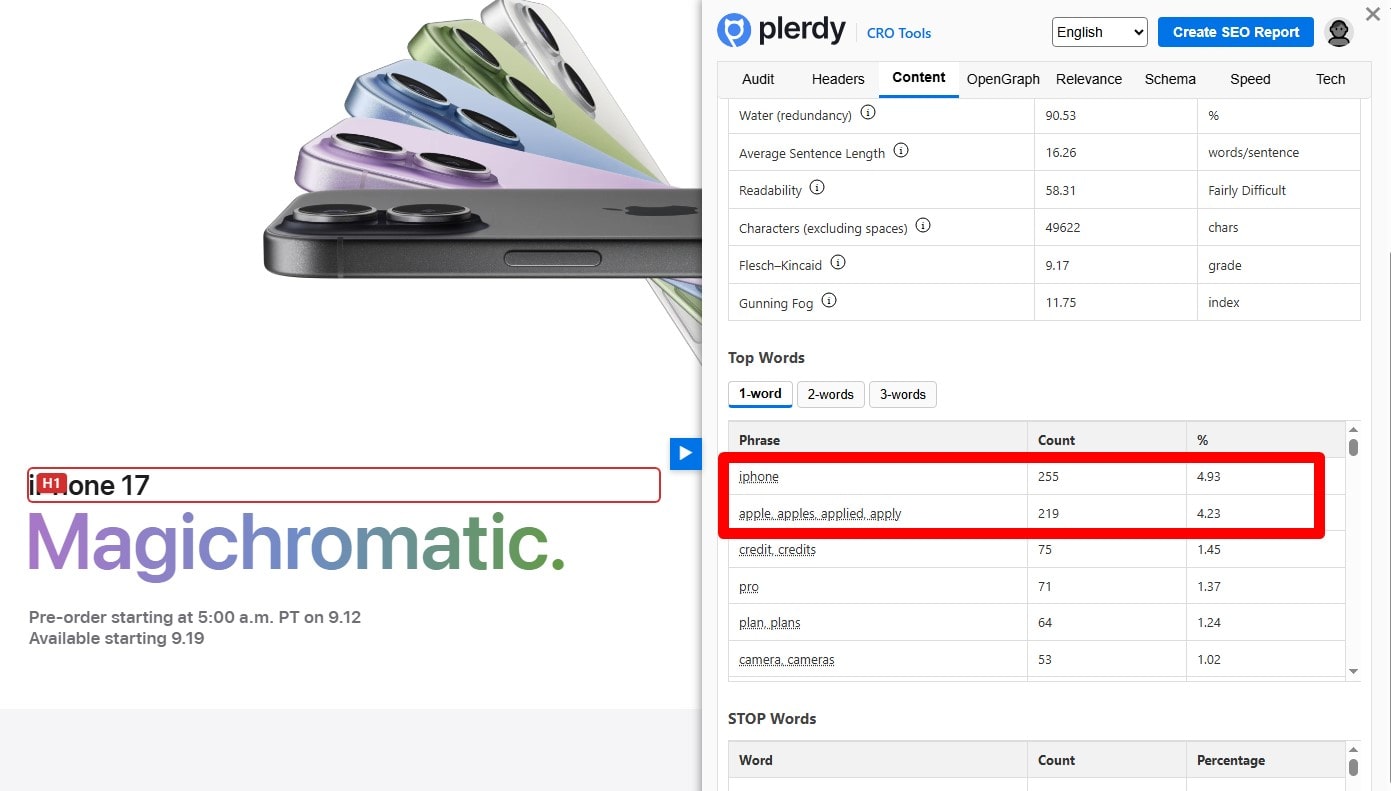 Use the primary keyword naturally throughout the body—not just headings. Mention it early, then support with related entities, synonyms, examples, and FAQs. Avoid density targets; write for clarity and intent satisfaction. Link to relevant internal pages and ensure the visible copy (not only images/widgets) contains the term.
Use the primary keyword naturally throughout the body—not just headings. Mention it early, then support with related entities, synonyms, examples, and FAQs. Avoid density targets; write for clarity and intent satisfaction. Link to relevant internal pages and ensure the visible copy (not only images/widgets) contains the term.
-
Include the Primary Keyword in the Opening Paragraph
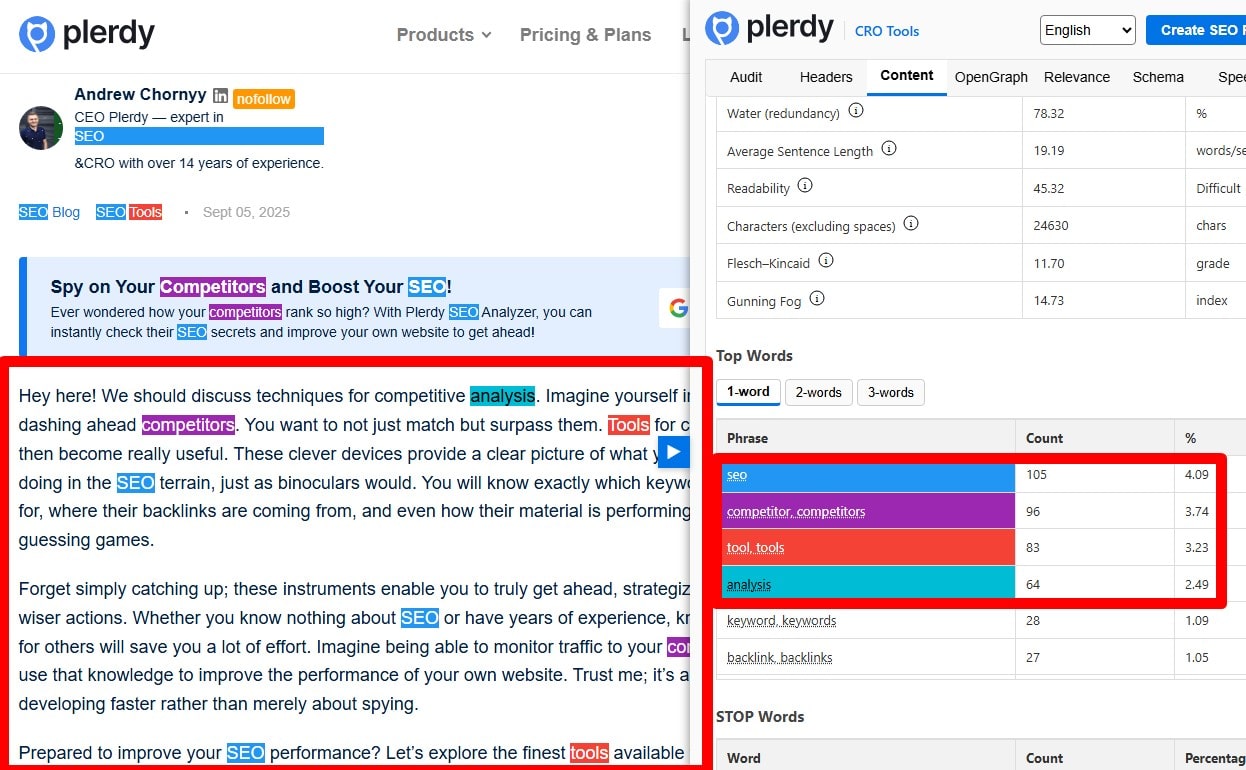 State the page’s topic in the first 1–2 sentences and include the primary keyword (or close variant) once near the start if it reads naturally. Align with the <title> and H1; don’t force awkward phrasing. For templates (product/category), surface concrete detail (model, brand, use case) alongside the keyword.
State the page’s topic in the first 1–2 sentences and include the primary keyword (or close variant) once near the start if it reads naturally. Align with the <title> and H1; don’t force awkward phrasing. For templates (product/category), surface concrete detail (model, brand, use case) alongside the keyword.
🖇 Backlinks
-
Assess Backlink Health & Authority
 Evaluate quality over “scores.” Benchmark referring domains growth, topical relevance, link types (editorial vs. UGC/sponsored), dofollow/nofollow mix, language/geo, and spam percentage vs. competitors. Prioritize earned, contextually relevant links on authoritative pages; don’t chase vanity metrics.
Evaluate quality over “scores.” Benchmark referring domains growth, topical relevance, link types (editorial vs. UGC/sponsored), dofollow/nofollow mix, language/geo, and spam percentage vs. competitors. Prioritize earned, contextually relevant links on authoritative pages; don’t chase vanity metrics.
-
Identify Spammy Referring Domains
 Flag obvious spam (hacked sites, link farms/PBNs, casino/adult/pharma, gibberish anchors, auto-generated pages). Try removal or let Google ignore them; use disavow only for clearly manipulative links you can’t remove or if you have a manual action risk.
Flag obvious spam (hacked sites, link farms/PBNs, casino/adult/pharma, gibberish anchors, auto-generated pages). Try removal or let Google ignore them; use disavow only for clearly manipulative links you can’t remove or if you have a manual action risk.
-
Use a Disavow File Only When Necessary
 Disavow is a last resort—not routine hygiene. Use it for unremovable, unnatural links pointing at you (paid, manipulative, or part of link schemes). Prefer domain-wide entries, keep evidence of outreach, review quarterly, and avoid over-disavowing legitimate sites.
Disavow is a last resort—not routine hygiene. Use it for unremovable, unnatural links pointing at you (paid, manipulative, or part of link schemes). Prefer domain-wide entries, keep evidence of outreach, review quarterly, and avoid over-disavowing legitimate sites.
-
Keep Anchor Text Natural and Varied
 Healthy profiles mix branded, URL, generic (“learn more”), and partial-match anchors; exact-match should be rare and editorial. Watch for sitewide exact-match, foreign-language spam, or identical anchors across many domains. Internally, use descriptive anchors that match the target page’s intent.
Healthy profiles mix branded, URL, generic (“learn more”), and partial-match anchors; exact-match should be rare and editorial. Watch for sitewide exact-match, foreign-language spam, or identical anchors across many domains. Internally, use descriptive anchors that match the target page’s intent.
-
Monitor and Reclaim Lost Backlinks
 Track “lost” links (page removed/noindexed, link removed, redirect changed). Reclaim by restoring/redirecting the target URL, updating the linker to the new URL, or recreating a relevant resource. Prioritize high-authority referrers and 404s with link equity.
Track “lost” links (page removed/noindexed, link removed, redirect changed). Reclaim by restoring/redirecting the target URL, updating the linker to the new URL, or recreating a relevant resource. Prioritize high-authority referrers and 404s with link equity.
-
Fix Broken Backlinks (Redirect or Update Link)
 Broken backlinks, or dead links, can also negatively impact
user experience and potentially harm your search engine
rankings.
Broken backlinks, or dead links, can also negatively impact
user experience and potentially harm your search engine
rankings.
-
Check for Unnatural Link Concentration from Single Domains
 Many links from one domain can be normal (navigation/sitewide citations) but have diminishing returns. Investigate paid/footer/widget links and repetitive exact-match anchors. If necessary, remove or add rel="nofollow sponsored" and work on diversifying referring domains.
Many links from one domain can be normal (navigation/sitewide citations) but have diminishing returns. Investigate paid/footer/widget links and repetitive exact-match anchors. If necessary, remove or add rel="nofollow sponsored" and work on diversifying referring domains.
-
Do Not Optimize for Domain Age
 Domain age itself isn’t a ranking factor. Older domains often rank due to accumulated quality content and links—not age. Don’t buy “aged” domains for ranking alone; invest in content, UX, and authoritative links.
Domain age itself isn’t a ranking factor. Older domains often rank due to accumulated quality content and links—not age. Don’t buy “aged” domains for ranking alone; invest in content, UX, and authoritative links.
-
Track Total Backlinks (Quality Over Quantity)
 Ahrefs is an all-in-one SEO tool that makes exploring a website's backlink profile quick and easy. Monitor new vs. lost links and link velocity, but judge by source quality and context. Filter out junk (spam, scraped, sitewide noise). A few strong editorial links beat thousands of weak ones.
Ahrefs is an all-in-one SEO tool that makes exploring a website's backlink profile quick and easy. Monitor new vs. lost links and link velocity, but judge by source quality and context. Filter out junk (spam, scraped, sitewide noise). A few strong editorial links beat thousands of weak ones.
-
Track Total Linking Root Domains
 Referring domains correlate better with authority than raw link counts. Aim to grow unique, relevant domains across diverse sites/pages. Avoid inflating totals with sitewide links from the same domain.
Referring domains correlate better with authority than raw link counts. Aim to grow unique, relevant domains across diverse sites/pages. Avoid inflating totals with sitewide links from the same domain.
-
Earn Topically Relevant Backlinks to the URL
 Pursue links from pages about your topic (industry publications, resource pages, data/research, case studies). Provide link-worthy assets (original data, tools, visuals). Ensure the surrounding context and anchor naturally fit the target page.
Pursue links from pages about your topic (industry publications, resource pages, data/research, case studies). Provide link-worthy assets (original data, tools, visuals). Ensure the surrounding context and anchor naturally fit the target page.
-
Ensure the Disavow File Doesn’t Include Valuable Links
 Audit the disavow list for mistakes. Never disavow high-quality or relevant referrers; remove erroneous entries and resubmit. Keep a change log and revisit after major link audits or migrations.
Audit the disavow list for mistakes. Never disavow high-quality or relevant referrers; remove erroneous entries and resubmit. Keep a change log and revisit after major link audits or migrations.
-
Create and Optimize Social Profiles Where Your Audience Is
 Claim consistent handles; complete bios with value prop and site link (UTMs ok). Most social links are nofollow, but profiles can improve brand SERPs, knowledge panels, and referral traffic. Keep branding, NAP, and imagery consistent; post regularly.
Claim consistent handles; complete bios with value prop and site link (UTMs ok). Most social links are nofollow, but profiles can improve brand SERPs, knowledge panels, and referral traffic. Keep branding, NAP, and imagery consistent; post regularly.
-
Publish on LinkedIn Articles (and Company Page)
 Repurpose articles as LinkedIn posts/articles/newsletters to reach your audience. Link back to the full guide on your site (expect nofollow). Include a byline, resources, and a clear CTA; don’t duplicate entire long-form verbatim if cannibalizing your own page.
Repurpose articles as LinkedIn posts/articles/newsletters to reach your audience. Link back to the full guide on your site (expect nofollow). Include a byline, resources, and a clear CTA; don’t duplicate entire long-form verbatim if cannibalizing your own page.
-
Pitch and Appear on Relevant Podcasts
 Target shows your buyers follow, pitch a specific, unique angle, and prep assets. Request a show-notes link to a helpful resource page (with UTM). Add the episode to your media page and repurpose quotes/clips for further reach.
Target shows your buyers follow, pitch a specific, unique angle, and prep assets. Request a show-notes link to a helpful resource page (with UTM). Add the episode to your media page and repurpose quotes/clips for further reach.
📱 Mobile
-
Ensure Responsive Layout (Mobile-First)
 Use fluid grids, flexible media, and CSS breakpoints starting from small screens. Test key templates on common devices. Avoid desktop-only hover states; ensure touch-friendly controls and readable type (base ≥16px, line-height ~1.5). Verify no horizontal scroll and content fits the viewport.
Use fluid grids, flexible media, and CSS breakpoints starting from small screens. Test key templates on common devices. Avoid desktop-only hover states; ensure touch-friendly controls and readable type (base ≥16px, line-height ~1.5). Verify no horizontal scroll and content fits the viewport.
-
Avoid Intrusive Interstitials on Mobile
 Do not block main content on entry. Keep consent/age gates minimal and dismissible. Delay promos until interaction or time-on-page; cap frequency; provide a clear close target. Ensure overlays don’t trap focus and don’t tank Core Web Vitals.
Do not block main content on entry. Keep consent/age gates minimal and dismissible. Delay promos until interaction or time-on-page; cap frequency; provide a clear close target. Ensure overlays don’t trap focus and don’t tank Core Web Vitals.
-
Keep Mobile Page Weight Light
 Minimize JS/CSS, defer non-critical scripts, and compress assets. Serve only what’s needed above the fold; code-split routes; inline critical CSS. Aim for fast LCP and low JavaScript execution time. Remove unused libraries, trackers, and heavy widgets.
Minimize JS/CSS, defer non-critical scripts, and compress assets. Serve only what’s needed above the fold; code-split routes; inline critical CSS. Aim for fast LCP and low JavaScript execution time. Remove unused libraries, trackers, and heavy widgets.
-
Use Responsive Images
 Serve the right image per viewport with srcset/sizes. Provide width/height (or aspect-ratio) to prevent CLS, and lazy-load below-the-fold images. Prefer loading="lazy" and decode off the main thread (decoding="async").
Serve the right image per viewport with srcset/sizes. Provide width/height (or aspect-ratio) to prevent CLS, and lazy-load below-the-fold images. Prefer loading="lazy" and decode off the main thread (decoding="async").
-
Optimize Image Formats & Compression
 Use modern formats (WebP/AVIF) with fallbacks, compress aggressively (visually lossless), and strip metadata. Deliver via CDN with caching and HTTP/2/3. Alt text is for accessibility/SEO context; the title attribute is optional and not required for optimization.
Use modern formats (WebP/AVIF) with fallbacks, compress aggressively (visually lossless), and strip metadata. Deliver via CDN with caching and HTTP/2/3. Alt text is for accessibility/SEO context; the title attribute is optional and not required for optimization.
-
Serve Properly Sized Images
 Avoid upscaling or sending desktop-size images to mobile. Generate responsive variants from your media pipeline/CMS. Cap hero images; compress thumbnails; avoid oversized background images. Audit with a crawler/Lighthouse for “properly sized images” issues.
Avoid upscaling or sending desktop-size images to mobile. Generate responsive variants from your media pipeline/CMS. Cap hero images; compress thumbnails; avoid oversized background images. Audit with a crawler/Lighthouse for “properly sized images” issues.
-
Check Google Search Console (Mobile Signals)
 Review Core Web Vitals (mobile) and Page indexing. Use URL Inspection (smartphone crawler) to see rendered HTML/screenshots, blocked resources, and mobile parity issues. Fix discovered problems and request re-crawl where needed.
Review Core Web Vitals (mobile) and Page indexing. Use URL Inspection (smartphone crawler) to see rendered HTML/screenshots, blocked resources, and mobile parity issues. Fix discovered problems and request re-crawl where needed.
-
Fix Mobile UX Issues (see UX)
 Address slow loads, confusing nav, poor readability/contrast, and obstructive UI. Test forms, filters, and checkout on real devices. Ensure accessible focus order, visible states, and keyboard/touch operability.
Address slow loads, confusing nav, poor readability/contrast, and obstructive UI. Test forms, filters, and checkout on real devices. Ensure accessible focus order, visible states, and keyboard/touch operability.
-
Make Mobile Navigation Thumb-Friendly
 Use clear labels, a predictable menu (hamburger or visible tabs), and persistent search. Keep depth shallow; add breadcrumbs. Ensure focus styles and adequate spacing; test one-handed reach for primary actions.
Use clear labels, a predictable menu (hamburger or visible tabs), and persistent search. Keep depth shallow; add breadcrumbs. Ensure focus styles and adequate spacing; test one-handed reach for primary actions.
-
Optimize Video for Mobile
 Use adaptive streaming (HLS/DASH), provide a poster image, captions/subtitles, and playsinline on iOS. Avoid autoplay with sound; defer loading until interaction; host via a performant CDN. Ensure transcripts for accessibility and indexability.
Use adaptive streaming (HLS/DASH), provide a poster image, captions/subtitles, and playsinline on iOS. Avoid autoplay with sound; defer loading until interaction; host via a performant CDN. Ensure transcripts for accessibility and indexability.
-
Make Tap Targets Easy to Click
 Minimum target size ~44×44 CSS px with adequate spacing. Avoid tiny text links; prefer buttons for primary actions. Provide visible focus/active states and prevent overlapping elements that steal taps.
Minimum target size ~44×44 CSS px with adequate spacing. Avoid tiny text links; prefer buttons for primary actions. Provide visible focus/active states and prevent overlapping elements that steal taps.
-
Ensure Favicon Displays in Mobile SERPs
 Provide a square favicon (multiple sizes, at least 48×48) via . Use a high-contrast design; host on the same domain and keep it crawlable. Verify in live results and update caches when rebranding.
Provide a square favicon (multiple sizes, at least 48×48) via . Use a high-contrast design; host on the same domain and keep it crawlable. Verify in live results and update caches when rebranding.
-
Ensure Parity: Content, Meta & Directives Match Desktop
 Mobile-first indexing uses your mobile version. Keep the same primary content, internal links, structured data, meta robots, canonical/hreflang, and robots.txt access on mobile and desktop. Avoid hiding critical copy or links on mobile.
Mobile-first indexing uses your mobile version. Keep the same primary content, internal links, structured data, meta robots, canonical/hreflang, and robots.txt access on mobile and desktop. Avoid hiding critical copy or links on mobile.
-
Test on Real Devices (Pre-/Post-Release)
 Run Lighthouse (mobile), field data checks, and device labs. Validate templates after releases, especially nav, forms, and media. Track mobile Core Web Vitals, crash/JS error logs, and regressions; ship fixes behind flags and re-test before full rollout.
Run Lighthouse (mobile), field data checks, and device labs. Validate templates after releases, especially nav, forms, and media. Track mobile Core Web Vitals, crash/JS error logs, and regressions; ship fixes behind flags and re-test before full rollout.
💨 Speed
-
Load Content Fast (Prioritize Above-the-Fold)
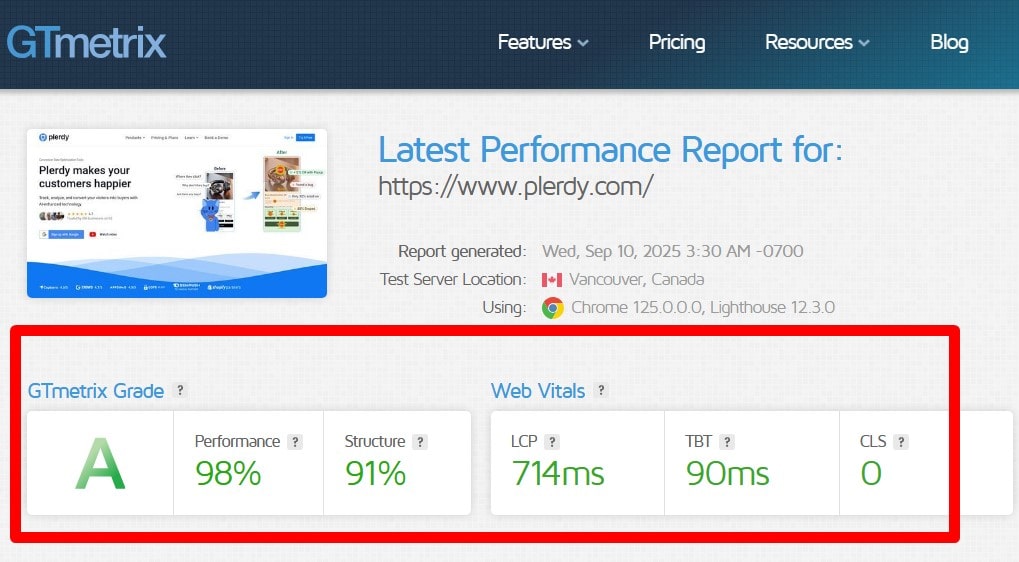 Aim for fast first view: ship only critical HTML/CSS/JS for above-the-fold, defer the rest. Preload the hero image/font, minimize render-blocking CSS/JS, code-split, and cache via CDN/HTTP/2/3. Reduce server TTFB with caching and efficient queries. Track LCP element, total JS execution time, and image weights per template.
Aim for fast first view: ship only critical HTML/CSS/JS for above-the-fold, defer the rest. Preload the hero image/font, minimize render-blocking CSS/JS, code-split, and cache via CDN/HTTP/2/3. Reduce server TTFB with caching and efficient queries. Track LCP element, total JS execution time, and image weights per template.
-
Pass Core Web Vitals (Field Data)
 A URL (or origin) passes when the 75th percentile (mobile, then desktop) of all three metrics is “Good”: LCP ≤ 2.5s, CLS ≤ 0.1, INP ≤ 200 ms. Check in Search Console → Core Web Vitals and PageSpeed Insights (Field Data). Fix the bottleneck metric first (e.g., LCP image size/priority, layout shifts, input delay from heavy JS).
A URL (or origin) passes when the 75th percentile (mobile, then desktop) of all three metrics is “Good”: LCP ≤ 2.5s, CLS ≤ 0.1, INP ≤ 200 ms. Check in Search Console → Core Web Vitals and PageSpeed Insights (Field Data). Fix the bottleneck metric first (e.g., LCP image size/priority, layout shifts, input delay from heavy JS).
-
Fix Common Speed Traps
 Eliminate: oversized images/video, render-blocking CSS/JS, unused JS/CSS, excessive third-party tags, large DOM trees, webfont FOIT/FOUT, chat widgets loading on every page, client-side rendering without streaming/SSR, missing caching/compression, and unoptimized hero images. Lazy-load below-the-fold media; preconnect/preload critical origins/resources.
Eliminate: oversized images/video, render-blocking CSS/JS, unused JS/CSS, excessive third-party tags, large DOM trees, webfont FOIT/FOUT, chat widgets loading on every page, client-side rendering without streaming/SSR, missing caching/compression, and unoptimized hero images. Lazy-load below-the-fold media; preconnect/preload critical origins/resources.
-
Run a Comprehensive Speed Audit
 Test templates on throttled mobile. Use PageSpeed Insights (field + lab), Lighthouse, and WebPageTest (filmstrip/CPU). Compare field vs. lab gaps, group issues by template, and create an optimization backlog. Add performance budgets to CI, monitor regressions, and re-test after releases.
Test templates on throttled mobile. Use PageSpeed Insights (field + lab), Lighthouse, and WebPageTest (filmstrip/CPU). Compare field vs. lab gaps, group issues by template, and create an optimization backlog. Add performance budgets to CI, monitor regressions, and re-test after releases.
-
Check Core Web Vitals (Desktop) in Search Console
 In Search Console → Core Web Vitals (Desktop), review failing URL groups and the example URLs. Follow the “Learn more” diagnostics to PageSpeed Insights, fix by template (e.g., LCP images, CLS from ads/carousels), deploy, and Validate Fix to reprocess groups.
In Search Console → Core Web Vitals (Desktop), review failing URL groups and the example URLs. Follow the “Learn more” diagnostics to PageSpeed Insights, fix by template (e.g., LCP images, CLS from ads/carousels), deploy, and Validate Fix to reprocess groups.
-
Check Core Web Vitals (Mobile) in Search Console
 Mobile data is the priority for ranking. Inspect Core Web Vitals (Mobile) groups, open examples in PSI, and focus on mobile LCP (image priority/size), CLS (reserve space; avoid late-loading banners), and INP (trim JS, split bundles, defer non-critical listeners). Validate fixes after rollout.
Mobile data is the priority for ranking. Inspect Core Web Vitals (Mobile) groups, open examples in PSI, and focus on mobile LCP (image priority/size), CLS (reserve space; avoid late-loading banners), and INP (trim JS, split bundles, defer non-critical listeners). Validate fixes after rollout.
-
Meet Core Web Vitals Thresholds
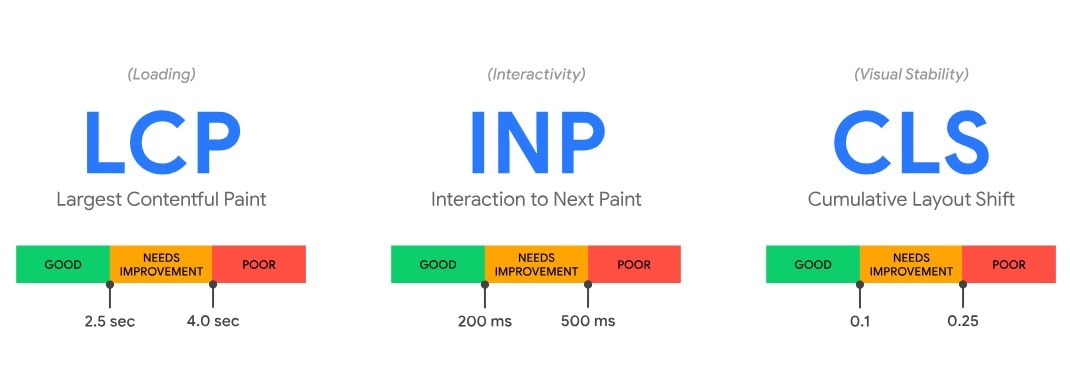 Target LCP ≤ 2.5s, CLS ≤ 0.1, INP ≤ 200 ms at the 75th percentile (mobile-first). Use CrUX/GA4 for field data where available. Improve LCP by optimizing the hero image, server TTFB, and resource priority; prevent CLS with fixed dimensions/placeholders; reduce INP by cutting long tasks, scheduling work off the main thread, and deferring non-essential JS.
Target LCP ≤ 2.5s, CLS ≤ 0.1, INP ≤ 200 ms at the 75th percentile (mobile-first). Use CrUX/GA4 for field data where available. Improve LCP by optimizing the hero image, server TTFB, and resource priority; prevent CLS with fixed dimensions/placeholders; reduce INP by cutting long tasks, scheduling work off the main thread, and deferring non-essential JS.
🔒 Security
-
Run Malware & Security Checks
 Scan regularly for hacked content and malware (GSC Security issues, Safe Browsing, server/WAF scans). Patch CMS, plugins, themes; enforce 2FA for admins; use least-privilege access; keep daily offsite backups. Monitor file integrity and server logs; set alerts for unusual spikes, new admin users, or outbound spam.
Scan regularly for hacked content and malware (GSC Security issues, Safe Browsing, server/WAF scans). Patch CMS, plugins, themes; enforce 2FA for admins; use least-privilege access; keep daily offsite backups. Monitor file integrity and server logs; set alerts for unusual spikes, new admin users, or outbound spam.
-
Enable HSTS (HTTP Strict Transport Security)
 Force browsers to use HTTPS with the header:
Strict-Transport-Security: max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload
Only enable after all traffic works on HTTPS and HTTP→HTTPS 301s are in place (including subdomains). Consider HSTS preload once confident; don’t set on staging. HSTS helps prevent protocol downgrade and cookie hijacking.
Force browsers to use HTTPS with the header:
Strict-Transport-Security: max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload
Only enable after all traffic works on HTTPS and HTTP→HTTPS 301s are in place (including subdomains). Consider HSTS preload once confident; don’t set on staging. HSTS helps prevent protocol downgrade and cookie hijacking.
-
Ensure No Hacked Content or Malware
 Check GSC Security issues, server AV/WAF reports, and error logs. Remove injected code/links, update credentials, and patch the entry point (plugin/theme/core). Request Review in GSC after cleanup. Add a WAF/CDN, rate limiting, and bot rules to reduce future risk.
Check GSC Security issues, server AV/WAF reports, and error logs. Remove injected code/links, update credentials, and patch the entry point (plugin/theme/core). Request Review in GSC after cleanup. Add a WAF/CDN, rate limiting, and bot rules to reduce future risk.
-
Force HTTPS Across the Site (Single Canonical Protocol)
 Serve one protocol: 301 all http:// to https:// (and enforce one host, e.g., www or root). Fix mixed content (upgrade assets to HTTPS), update canonicals, hreflang, sitemaps, and internal links to HTTPS. Pair with HSTS and secure cookies (Secure, HttpOnly, SameSite).
Serve one protocol: 301 all http:// to https:// (and enforce one host, e.g., www or root). Fix mixed content (upgrade assets to HTTPS), update canonicals, hreflang, sitemaps, and internal links to HTTPS. Pair with HSTS and secure cookies (Secure, HttpOnly, SameSite).
-
Maintain a Valid TLS Certificate (HTTPS)
 Use a trusted CA (e.g., Let’s Encrypt) with auto-renewal and the correct chain. Enable modern TLS versions, OCSP stapling, and strong ciphers. Verify the certificate matches all hostnames (SANs) and that renewal doesn’t break redirects. Test with an SSL/TLS checker; fix warnings promptly.
Use a trusted CA (e.g., Let’s Encrypt) with auto-renewal and the correct chain. Enable modern TLS versions, OCSP stapling, and strong ciphers. Verify the certificate matches all hostnames (SANs) and that renewal doesn’t break redirects. Test with an SSL/TLS checker; fix warnings promptly.
-
Make Cookie Banners Lightweight (No CLS)
 Keep consent banners small, accessible, and non-blocking. Reserve space to avoid CLS, provide clear choices (accept/reject/customize), and trap focus correctly for keyboard users. Delay non-essential scripts until consent; store preferences and avoid re-prompt spam.
Keep consent banners small, accessible, and non-blocking. Reserve space to avoid CLS, provide clear choices (accept/reject/customize), and trap focus correctly for keyboard users. Delay non-essential scripts until consent; store preferences and avoid re-prompt spam.
-
Harden Security Headers (CSP, Permissions-Policy, Referrer-Policy)
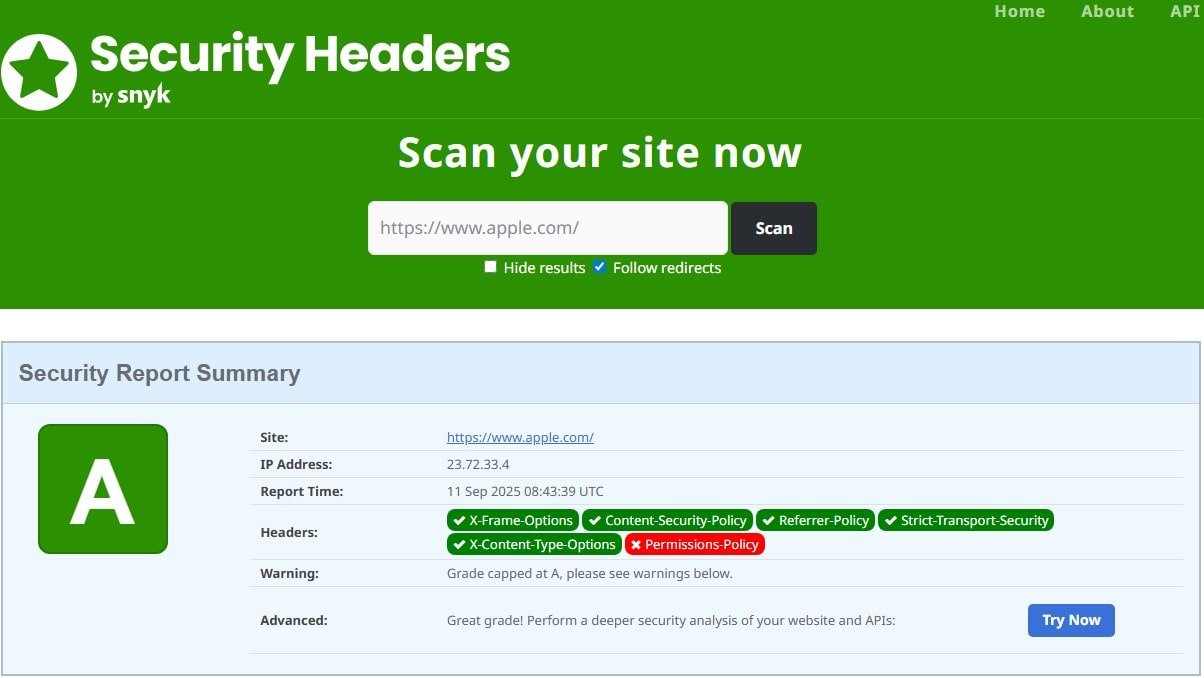 Ship X-Content-Type-Options: nosniff, Referrer-Policy: strict-origin-when-cross-origin, Permissions-Policy to limit sensors (camera/mic/geo), and a CSP with allowlists (and/or frame-ancestors for embedding control). Verify on securityheaders.com, Mozilla Observatory, and Chrome DevTools → Network/Headers.
Ship X-Content-Type-Options: nosniff, Referrer-Policy: strict-origin-when-cross-origin, Permissions-Policy to limit sensors (camera/mic/geo), and a CSP with allowlists (and/or frame-ancestors for embedding control). Verify on securityheaders.com, Mozilla Observatory, and Chrome DevTools → Network/Headers.
🌍 International & Multilingual Sites
-
Configure Geo-Targeting Signals
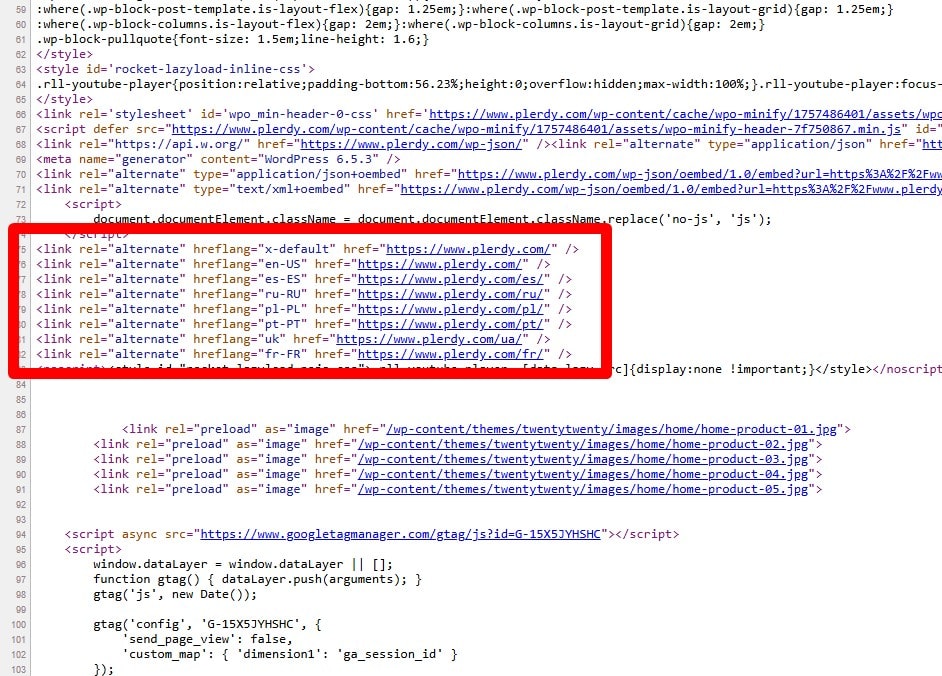 Use clear geo signals: ccTLDs (e.g., .de) or locale subfolders (/de/, /fr-fr/), consistent local currency/phone/address, local contact pages, and language selectors. Pair with correct hreflang and avoid relying on server location. Keep one canonical per locale and link between alternates.
Use clear geo signals: ccTLDs (e.g., .de) or locale subfolders (/de/, /fr-fr/), consistent local currency/phone/address, local contact pages, and language selectors. Pair with correct hreflang and avoid relying on server location. Keep one canonical per locale and link between alternates.
-
Implement Valid hreflang (With Return Tags)
 Add reciprocal hreflang for each language/region pair using ISO codes (e.g., en-gb, fr-fr) plus a self-referencing tag. Use x-default for the global/selector page. Place tags in HTML <head> or XML sitemaps—be consistent with canonicals (only indexable canonicals should be referenced). Fix common errors: wrong codes, missing returns, mixing HTTP/HTTPS, pointing to non-200 pages.
Add reciprocal hreflang for each language/region pair using ISO codes (e.g., en-gb, fr-fr) plus a self-referencing tag. Use x-default for the global/selector page. Place tags in HTML <head> or XML sitemaps—be consistent with canonicals (only indexable canonicals should be referenced). Fix common errors: wrong codes, missing returns, mixing HTTP/HTTPS, pointing to non-200 pages.
-
Make Page Language Obvious
 Set the HTML lang attribute (e.g., <html lang="uk">), keep copy in a single language per URL, and match UI elements (navigation, forms). Use localized dates, units, and currency. Avoid auto-translating on the fly without giving users a stable, linkable localized URL.
Set the HTML lang attribute (e.g., <html lang="uk">), keep copy in a single language per URL, and match UI elements (navigation, forms). Use localized dates, units, and currency. Avoid auto-translating on the fly without giving users a stable, linkable localized URL.
-
Avoid Forced Geo/Language Redirects
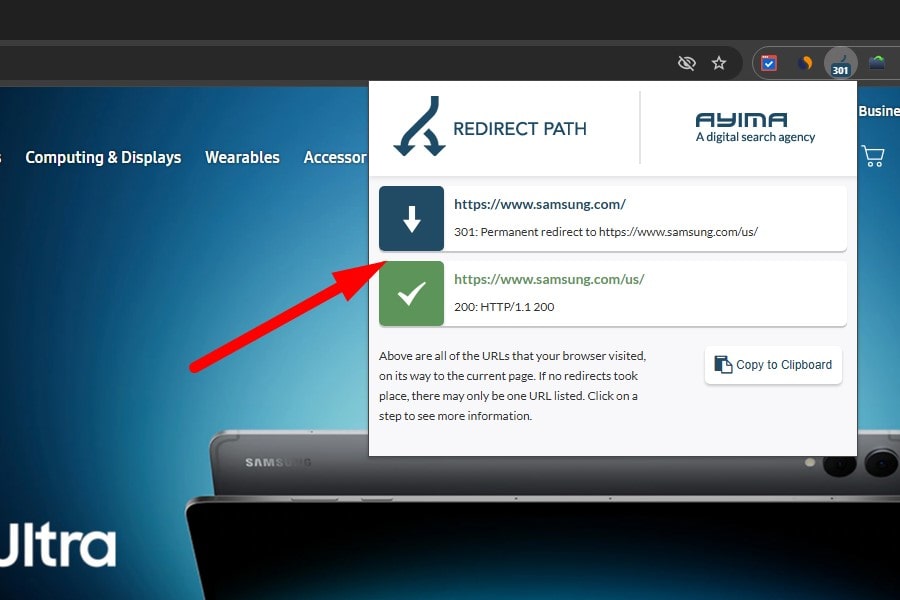 Don’t auto-redirect users (or crawlers) based on IP/Accept-Language to another locale; it breaks discovery and annoys travelers/expats. Instead, show a non-blocking locale banner and remember user choice. If redirects are absolutely required, never redirect Googlebot, keep alternate links, and allow manual switching.
Don’t auto-redirect users (or crawlers) based on IP/Accept-Language to another locale; it breaks discovery and annoys travelers/expats. Instead, show a non-blocking locale banner and remember user choice. If redirects are absolutely required, never redirect Googlebot, keep alternate links, and allow manual switching.
-
Define International Audiences and Markets
 List target countries/languages, search behavior, and SERP competitors. Prioritize markets by demand and resources, then map pages/sections to each locale. Align keywords, pricing, shipping, and support to each market before rolling out URLs and hreflang.
List target countries/languages, search behavior, and SERP competitors. Prioritize markets by demand and resources, then map pages/sections to each locale. Align keywords, pricing, shipping, and support to each market before rolling out URLs and hreflang.
-
Provide High-Quality, Human-Reviewed Translations
 Use professional translation or expert review—don’t ship raw machine output. Localize terminology, CTAs, legal text, images/screenshots, and schema (e.g., inLanguage). Check slugs, alt text, and metadata. QA for placeholders, broken characters, and layout overflow in long languages.
Use professional translation or expert review—don’t ship raw machine output. Localize terminology, CTAs, legal text, images/screenshots, and schema (e.g., inLanguage). Check slugs, alt text, and metadata. QA for placeholders, broken characters, and layout overflow in long languages.
-
Use a Clear International URL Structure
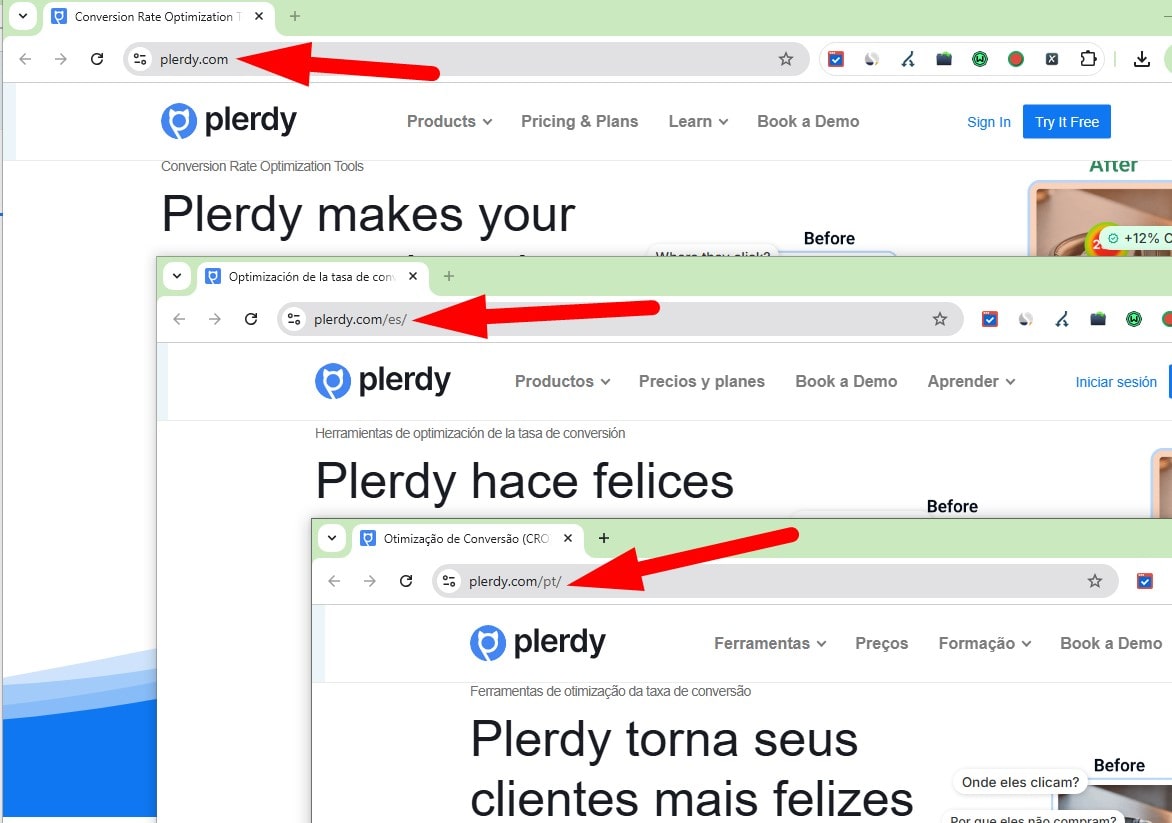 Choose one model per market: ccTLD (example.de), subdomain (de.example.com), or subfolder (example.com/de/). Prefer subfolders for easier consolidation unless strong geo signals (ccTLD) are required. Keep structure mirrored across locales and avoid mixing patterns.
Choose one model per market: ccTLD (example.de), subdomain (de.example.com), or subfolder (example.com/de/). Prefer subfolders for easier consolidation unless strong geo signals (ccTLD) are required. Keep structure mirrored across locales and avoid mixing patterns.
-
Serve the Correct Localized Page
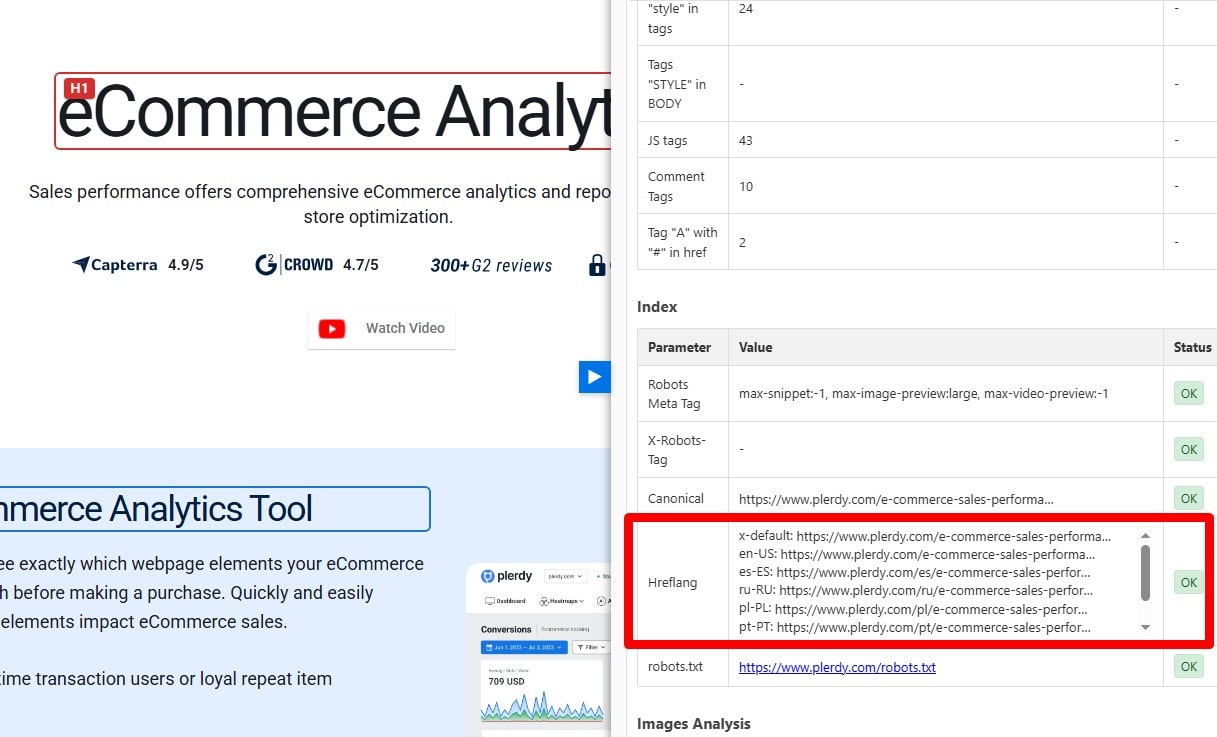 Ensure each locale page links to its alternates via hreflang and that internal links stay within the locale (e.g., /fr/ → /fr/). Preserve user-chosen locale across sessions. Use x-default for the selector and provide visible language/country switchers.
Ensure each locale page links to its alternates via hreflang and that internal links stay within the locale (e.g., /fr/ → /fr/). Preserve user-chosen locale across sessions. Use x-default for the selector and provide visible language/country switchers.
-
Earn Local Backlinks in Target Markets
 Pursue links from relevant sites in each country/language (local media, associations, universities, partners). Local TLDs and same-language context strengthen geo relevance. Create locale-specific assets (data, guides, events) that deserve local coverage.
Pursue links from relevant sites in each country/language (local media, associations, universities, partners). Local TLDs and same-language context strengthen geo relevance. Create locale-specific assets (data, guides, events) that deserve local coverage.
-
Clarify Site Type: Multilingual, Multiregional, or Both
 Multilingual targets multiple languages; multiregional targets different countries/regions. Many sites are both (e.g., en-us, en-gb, fr-fr). Reflect this in URL structure, hreflang, content, pricing, and legal info. Document rules for when to split by language vs. by region and keep them consistent across templates.
Multilingual targets multiple languages; multiregional targets different countries/regions. Many sites are both (e.g., en-us, en-gb, fr-fr). Reflect this in URL structure, hreflang, content, pricing, and legal info. Document rules for when to split by language vs. by region and keep them consistent across templates.
-
Install & Configure Google Analytics 4
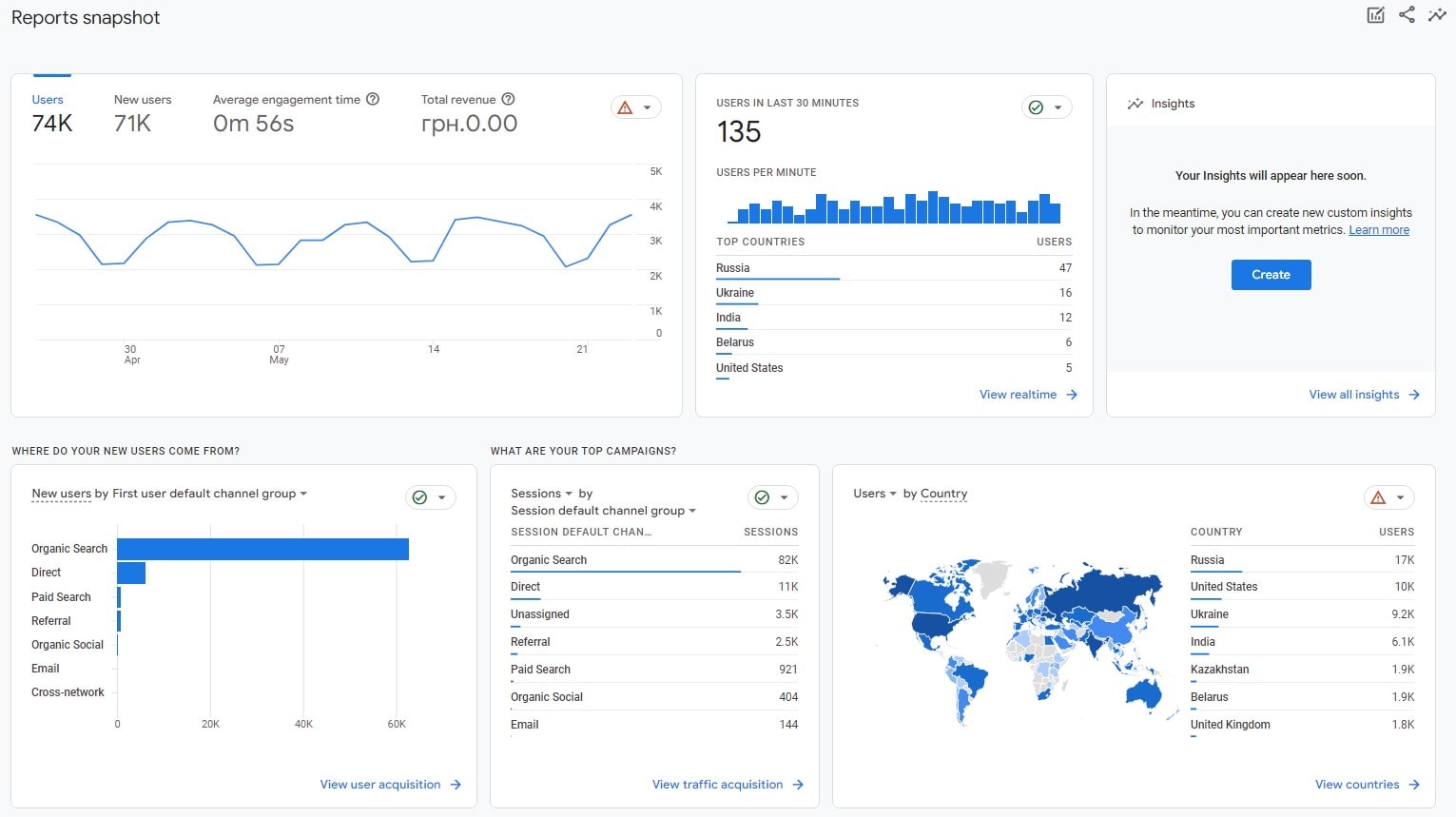 Create a GA4 property and web data stream, enable Enhanced Measurement, define key conversions (signup, lead, purchase), and standardize event names. Set cross-domain where needed, filter internal traffic/bots, implement Consent Mode v2, and link BigQuery. Validate in DebugView; avoid firing duplicate page_view/events.
Create a GA4 property and web data stream, enable Enhanced Measurement, define key conversions (signup, lead, purchase), and standardize event names. Set cross-domain where needed, filter internal traffic/bots, implement Consent Mode v2, and link BigQuery. Validate in DebugView; avoid firing duplicate page_view/events.
-
Prevent GA4 Tag Duplication
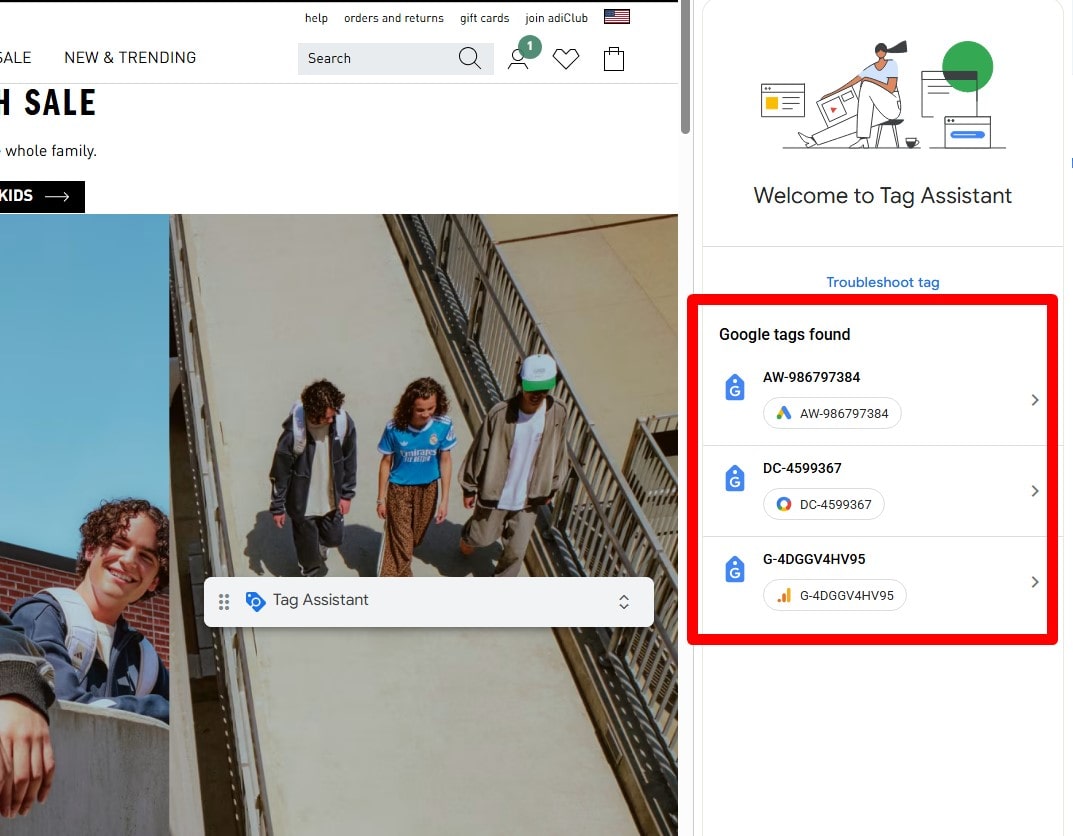 Ensure a single measurement ID fires once per page. Audit with Tag Assistant and GA4 DebugView. Avoid mixing hard-coded gtag.js with GTM duplicates; dedupe ecommerce events; gate tags behind consent to prevent double fires on reloads.
Ensure a single measurement ID fires once per page. Audit with Tag Assistant and GA4 DebugView. Avoid mixing hard-coded gtag.js with GTM duplicates; dedupe ecommerce events; gate tags behind consent to prevent double fires on reloads.
-
Set Up Google Search Console (Domain Property)
 Verify a Domain property via DNS, add users/permissions, submit XML sitemaps, and monitor Page Indexing, Core Web Vitals, Manual actions, and Security issues. Use URL Inspection for indexability, canonicals, and live tests.
Verify a Domain property via DNS, add users/permissions, submit XML sitemaps, and monitor Page Indexing, Core Web Vitals, Manual actions, and Security issues. Use URL Inspection for indexability, canonicals, and live tests.
-
Resolve Search Console Issues
 Triage by report: Page Indexing (excluded types), Core Web Vitals (mobile first), Sitemaps, Manual actions/Security. Fix by template, deploy, then Validate Fix. Track regressions after releases.
Triage by report: Page Indexing (excluded types), Core Web Vitals (mobile first), Sitemaps, Manual actions/Security. Fix by template, deploy, then Validate Fix. Track regressions after releases.
-
Use URL Inspection & Rendered HTML
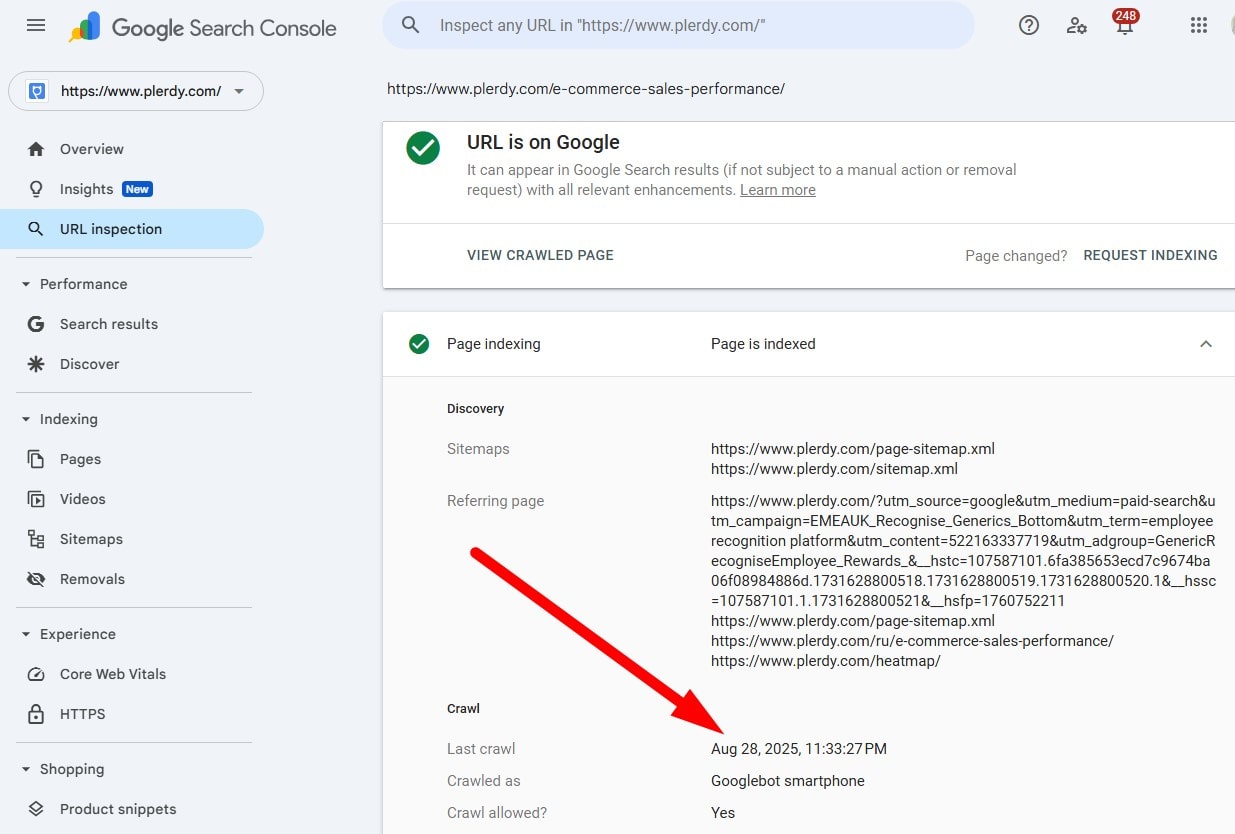 Cache views are unreliable. Use URL Inspection to see last crawl, selected canonical, robots, and rendered HTML/screenshot. Test live URL after fixes and request re-crawl.
Cache views are unreliable. Use URL Inspection to see last crawl, selected canonical, robots, and rendered HTML/screenshot. Test live URL after fixes and request re-crawl.
-
Provide Clean XML Sitemaps
 Include only 200/Indexable/Canonical URLs (HTTPS). Keep files <50k URLs/<50MB, split by type (pages, posts, products), include <lastmod>, submit in GSC, and reference in robots.txt. Update quickly on adds/removes.
Include only 200/Indexable/Canonical URLs (HTTPS). Keep files <50k URLs/<50MB, split by type (pages, posts, products), include <lastmod>, submit in GSC, and reference in robots.txt. Update quickly on adds/removes.
-
Reconcile Indexed Pages vs. Sitemaps
 Compare GSC → Page Indexing with Sitemaps. Investigate common excludes: Duplicate, not selected as canonical; Crawled—currently not indexed; Discovered—currently not indexed; Soft 404; Alternate with proper canonical. Remove non-indexables from sitemaps and fix root causes.
Compare GSC → Page Indexing with Sitemaps. Investigate common excludes: Duplicate, not selected as canonical; Crawled—currently not indexed; Discovered—currently not indexed; Soft 404; Alternate with proper canonical. Remove non-indexables from sitemaps and fix root causes.
-
Remove Invalid URLs from Sitemaps
 Purge 3xx/4xx/5xx, noindex, blocked, parameter/tracking, and cross-canonical URLs. List the HTTPS final URL only. Re-submit sitemaps and verify zero errors/warnings.
Purge 3xx/4xx/5xx, noindex, blocked, parameter/tracking, and cross-canonical URLs. List the HTTPS final URL only. Re-submit sitemaps and verify zero errors/warnings.
-
Monitor & Improve Brand SERPs
 Track branded queries, autosuggests, and first page results. Strengthen entity home (About/Contact), Organization schema, consistent NAP, and verified social profiles. Publish authoritative content and PR to earn positive coverage; address reviews/FAQs transparently.
Track branded queries, autosuggests, and first page results. Strengthen entity home (About/Contact), Organization schema, consistent NAP, and verified social profiles. Publish authoritative content and PR to earn positive coverage; address reviews/FAQs transparently.
-
Provide a Google News Sitemap (If Eligible)
 For news publishers, supply a separate News sitemap listing the latest articles (last ~48h, up to 1,000 URLs) with proper <news:> tags. Keep parity with canonical pages and follow News policies. Otherwise, skip this item.
For news publishers, supply a separate News sitemap listing the latest articles (last ~48h, up to 1,000 URLs) with proper <news:> tags. Keep parity with canonical pages and follow News policies. Otherwise, skip this item.
-
Check for Manual Actions
 Open GSC → Manual actions. If any exist, fix the precise issues (unnatural links, spam, misleading structured data, thin/AI-spam), document remediation, and submit a reconsideration request.
Open GSC → Manual actions. If any exist, fix the precise issues (unnatural links, spam, misleading structured data, thin/AI-spam), document remediation, and submit a reconsideration request.
-
Fix Crawl & Indexing Issues
 Use Page Indexing and URL Inspection plus server logs to find 404/soft 404, 5xx, rate limiting, blocked resources, and robots/X-Robots-Tag problems. Repair internal links, add redirects, stabilize servers, and unblock essential assets.
Use Page Indexing and URL Inspection plus server logs to find 404/soft 404, 5xx, rate limiting, blocked resources, and robots/X-Robots-Tag problems. Repair internal links, add redirects, stabilize servers, and unblock essential assets.
-
Optimize for Sitelinks & Sitelinks Search Box
 Sitelinks are algorithmic. Clarify IA and navigation, use concise/unique titles, and consistent anchor text. Add Breadcrumbs (HTML + schema) and implement Sitelinks Search Box structured data for internal search. Reduce duplication and orphaned pages.
Sitelinks are algorithmic. Clarify IA and navigation, use concise/unique titles, and consistent anchor text. Add Breadcrumbs (HTML + schema) and implement Sitelinks Search Box structured data for internal search. Reduce duplication and orphaned pages.
-
Optimize for Featured Snippets
 Target queries that show snippets. Provide an answer-first 40–60-word paragraph, or a clean list/table matching the query. Use question-style H2s, define terms, and add concise how-to steps. Support with FAQ/HowTo schema and keep content updated.
Target queries that show snippets. Provide an answer-first 40–60-word paragraph, or a clean list/table matching the query. Use question-style H2s, define terms, and add concise how-to steps. Support with FAQ/HowTo schema and keep content updated.
-
Optimize for AI Overviews & Zero-Click SERPs
 Supply concise answer blocks, FAQs, and clear tables; demonstrate E-E-A-T (author bios, citations, about/editorial pages). Use schema (FAQ/HowTo/Product/Article), strong internal links, and fresh sources. You can’t force inclusion—design pages so the summary conveys brand value even when clicks drop.
Supply concise answer blocks, FAQs, and clear tables; demonstrate E-E-A-T (author bios, citations, about/editorial pages). Use schema (FAQ/HowTo/Product/Article), strong internal links, and fresh sources. You can’t force inclusion—design pages so the summary conveys brand value even when clicks drop.
🧱 Website Architecture
-
Check Pagination
 Google doesn’t use rel="next/prev" anymore. Keep page 1 and page 2+ as separate, indexable URLs with self-canonical (don’t canonical all to page 1). Use HTML links (Prev/Next and numbered lists), unique titles (e.g., “Page 2”), and expose URL pages for infinite scroll via href/History API (e.g., ?page=2). Avoid noindex on deeper pages if they carry unique items.
Google doesn’t use rel="next/prev" anymore. Keep page 1 and page 2+ as separate, indexable URLs with self-canonical (don’t canonical all to page 1). Use HTML links (Prev/Next and numbered lists), unique titles (e.g., “Page 2”), and expose URL pages for infinite scroll via href/History API (e.g., ?page=2). Avoid noindex on deeper pages if they carry unique items.
-
Use Short, Descriptive URLs
 Keep slugs short, lowercase, hyphen-separated, and meaningful. Avoid IDs, dates, stop-word clutter, file extensions, and tracking params. Be consistent with trailing slash and prefer a single, stable path per page.
Keep slugs short, lowercase, hyphen-separated, and meaningful. Avoid IDs, dates, stop-word clutter, file extensions, and tracking params. Be consistent with trailing slash and prefer a single, stable path per page.
-
Visualize Site Architecture
 Crawl and graph the internal link structure to check click depth (keep priority pages ≤3 clicks), find orphan/near-orphan URLs, identify hubs, and expose thin clusters. Fix dead ends and ensure nav/hubs link to key revenue pages.
Crawl and graph the internal link structure to check click depth (keep priority pages ≤3 clicks), find orphan/near-orphan URLs, identify hubs, and expose thin clusters. Fix dead ends and ensure nav/hubs link to key revenue pages.
-
Eliminate Internal Redirects
 Update all internal links to the final URL (no 301/302 hops). Use 301/308 for permanent moves, 302/307 for temporary. After changes, recrawl to confirm no remaining redirect hops and refresh sitemaps/canonicals.
Update all internal links to the final URL (no 301/302 hops). Use 301/308 for permanent moves, 302/307 for temporary. After changes, recrawl to confirm no remaining redirect hops and refresh sitemaps/canonicals.
-
Remove Redirect Chains and Loops
 Map legacy → current URLs and enforce one-hop redirects. Kill loops and long chains, fix internal links at source, and monitor 3xx in logs. Update canonicals, hreflang, and sitemaps to the live destination.
Map legacy → current URLs and enforce one-hop redirects. Kill loops and long chains, fix internal links at source, and monitor 3xx in logs. Update canonicals, hreflang, and sitemaps to the live destination.
-
Provide a Correct robots.txt
 Use robots.txt to manage crawl, not indexing or security. Disallowed URLs can still be indexed if linked. To exclude pages, use noindex (meta/X-Robots-Tag) or auth. Include Sitemap: lines and don’t block essential CSS/JS.
Use robots.txt to manage crawl, not indexing or security. Disallowed URLs can still be indexed if linked. To exclude pages, use noindex (meta/X-Robots-Tag) or auth. Include Sitemap: lines and don’t block essential CSS/JS.
-
Block Crawl Strategically with robots.txt
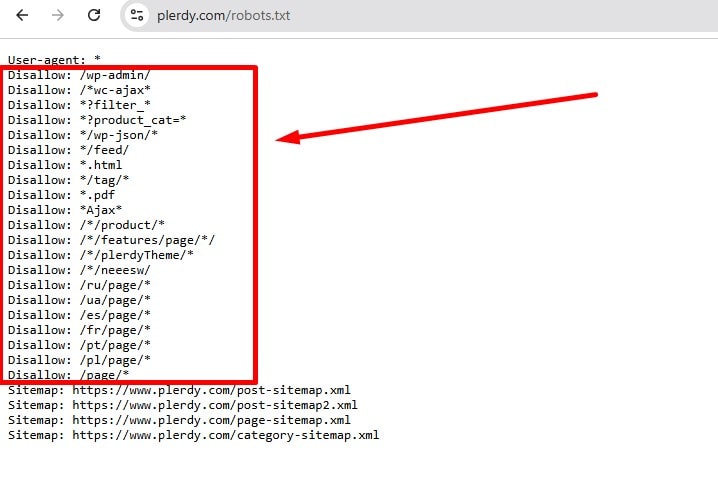 Block low-value crawl paths (e.g., infinite filters, session/search pages), but don’t rely on robots.txt to hide content—it doesn’t prevent indexing. For sensitive/private pages, require auth or apply noindex and remove from sitemaps.
Block low-value crawl paths (e.g., infinite filters, session/search pages), but don’t rely on robots.txt to hide content—it doesn’t prevent indexing. For sensitive/private pages, require auth or apply noindex and remove from sitemaps.
-
Design Clear Topic Hubs (Silos)
 Group content into topic hubs with hub → subpage linking, breadcrumbs, and related links. Keep paths shallow, avoid duplicate paths to the same content, and ensure each hub targets a distinct intent/keyword set.
Group content into topic hubs with hub → subpage linking, breadcrumbs, and related links. Keep paths shallow, avoid duplicate paths to the same content, and ensure each hub targets a distinct intent/keyword set.
-
Optimize E-commerce Category Pages
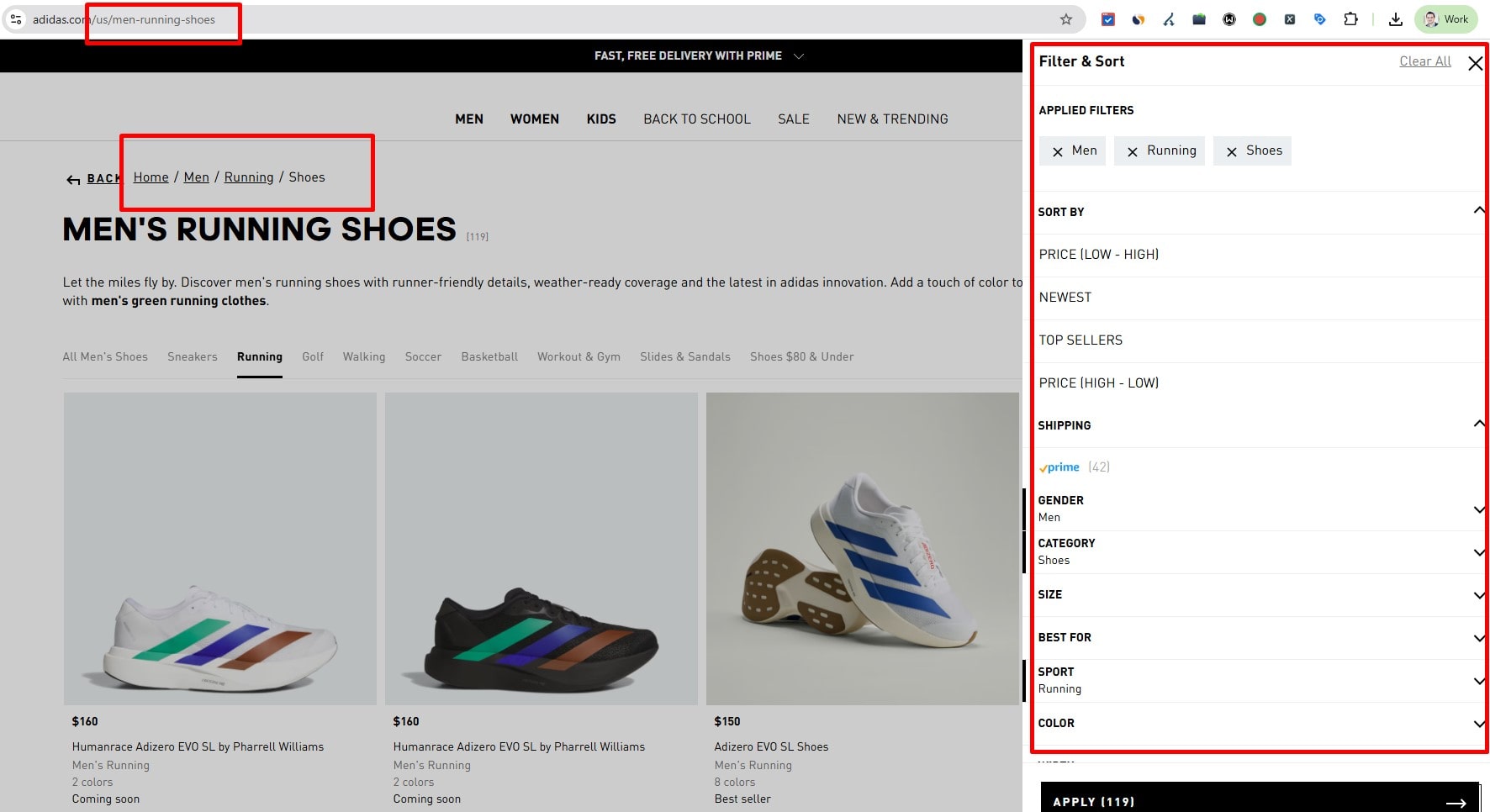 Use clear category hierarchies, unique intro copy above the grid, indexable category URLs with self-canonicals, and clean pagination. Manage filters/facets to avoid index bloat (see “Faceted navigation”). Add BreadcrumbList schema.
Use clear category hierarchies, unique intro copy above the grid, indexable category URLs with self-canonicals, and clean pagination. Manage filters/facets to avoid index bloat (see “Faceted navigation”). Add BreadcrumbList schema.
-
Use Consistent, Descriptive URL Slugs
 Standardize slugs: lowercase, hyphens, concise keywords, no tracking params. Keep one canonical path, be consistent with trailing slash, and avoid changing slugs unless necessary (redirect old → new if you must).
Standardize slugs: lowercase, hyphens, concise keywords, no tracking params. Keep one canonical path, be consistent with trailing slash, and avoid changing slugs unless necessary (redirect old → new if you must).
-
Provide Helpful 404 Pages
 Serve a custom 404 with search, popular links, and paths back to hubs. Fix internal links causing 404s; use 410 for permanently removed content; redirect only when a clear equivalent exists. Exclude 404s from sitemaps.
Serve a custom 404 with search, popular links, and paths back to hubs. Fix internal links causing 404s; use 410 for permanently removed content; redirect only when a clear equivalent exists. Exclude 404s from sitemaps.
-
Use Tag Pages Strategically
 Avoid thin, duplicate tag archives. Default to noindex unless a tag page is curated with unique copy and strong internal demand. Prevent tag/category duplication and keep pagination clean with self-canonicals.
Avoid thin, duplicate tag archives. Default to noindex unless a tag page is curated with unique copy and strong internal demand. Prevent tag/category duplication and keep pagination clean with self-canonicals.
-
Implement Breadcrumbs (UI + Schema)
 Add breadcrumbs in templates and mark up with BreadcrumbList schema. Keep anchors descriptive and ensure trails reflect the real hierarchy (don’t invent paths). Link breadcrumbs sitewide to improve crawl and context.
Add breadcrumbs in templates and mark up with BreadcrumbList schema. Keep anchors descriptive and ensure trails reflect the real hierarchy (don’t invent paths). Link breadcrumbs sitewide to improve crawl and context.
-
Simplify Primary Navigation
 Limit top-level items, prioritize key hubs, and use crawlable HTML links (not JS-only). Make it keyboard-accessible, consistent across desktop/mobile, and avoid mega-menus that dump hundreds of links on every page.
Limit top-level items, prioritize key hubs, and use crawlable HTML links (not JS-only). Make it keyboard-accessible, consistent across desktop/mobile, and avoid mega-menus that dump hundreds of links on every page.
-
Optimize Footer Navigation
 Use the footer for utility and trust (About, Contact, Policies, Key categories). Avoid link farms or keyword-stuffed lists. Keep anchors consistent and ensure links point to canonical URLs.
Use the footer for utility and trust (About, Contact, Policies, Key categories). Avoid link farms or keyword-stuffed lists. Keep anchors consistent and ensure links point to canonical URLs.
-
Design Clear Menus (Header & Mobile)
 Keep header/mobile menus aligned, expose essential links without deep nesting, and maintain a persistent mobile menu. Ensure LCP elements aren’t blocked by heavy menu JS and that menu links are indexable anchors.
Keep header/mobile menus aligned, expose essential links without deep nesting, and maintain a persistent mobile menu. Ensure LCP elements aren’t blocked by heavy menu JS and that menu links are indexable anchors.
-
Strengthen Internal Links and Remove Orphans
 Identify and fix orphan pages (add links from hubs, nav, or relevant articles). Use descriptive anchor text, surface money pages from category hubs, and keep priority pages within ≤3 clicks. Keep sitemaps in sync with canonical URLs.
Identify and fix orphan pages (add links from hubs, nav, or relevant articles). Use descriptive anchor text, surface money pages from category hubs, and keep priority pages within ≤3 clicks. Keep sitemaps in sync with canonical URLs.
-
Control Faceted Navigation (E-commerce)
Pick one clean indexable path (category) and prevent combinatorial crawl.
- Index only valuable facets (e.g.,
/shoes/black/), each with self-canonical and unique content. - Disallow infinite combos via robots patterns and nofollow UI where needed; avoid blocking essential CSS/JS.
- Provide static links to top facets; keep sort/order params non-indexable.
- Index only valuable facets (e.g.,
-
Handle Out-of-Stock/Discontinued Products (301/410 + UX)
 Temporarily OOS: keep indexable, show alternatives, set Product schema availability=OutOfStock. Permanently discontinued: 301 to the closest relevant product/category; if none, 410 and remove from sitemaps. Preserve reviews/specs on successor SKUs. Check GSC Page Indexing, Rich Results Test, and crawler for soft-404s.
Temporarily OOS: keep indexable, show alternatives, set Product schema availability=OutOfStock. Permanently discontinued: 301 to the closest relevant product/category; if none, 410 and remove from sitemaps. Preserve reviews/specs on successor SKUs. Check GSC Page Indexing, Rich Results Test, and crawler for soft-404s.
⚙️ Technical SEO Checks
-
Choose Subdomains or Subdirectories
 Choose based on architecture/ownership, not “SEO hacks.” If you use subdomains, interlink them prominently, verify each in Search Console, include them in sitemaps/hreflang, align schema/branding, and keep signals consistent.
Choose based on architecture/ownership, not “SEO hacks.” If you use subdomains, interlink them prominently, verify each in Search Console, include them in sitemaps/hreflang, align schema/branding, and keep signals consistent.
-
Add a Favicon
 Provide a valid <link rel="icon"> (SVG or 32×32 PNG) and Apple touch icon. Avoid 404s/mismatched MIME types. Test on dark/light backgrounds and confirm it renders in mobile SERPs and browser tabs.
Provide a valid <link rel="icon"> (SVG or 32×32 PNG) and Apple touch icon. Avoid 404s/mismatched MIME types. Test on dark/light backgrounds and confirm it renders in mobile SERPs and browser tabs.
-
Monitor Site Uptime
 Set up 24/7 monitoring and alerts with a public status page. Target ≥99.9% uptime. Track issues by layer (DNS, TLS/CDN, origin). Add health checks and auto-rollback for deployments.
Set up 24/7 monitoring and alerts with a public status page. Target ≥99.9% uptime. Track issues by layer (DNS, TLS/CDN, origin). Add health checks and auto-rollback for deployments.
-
Fix Broken & Redirected Links
 Crawl regularly. Resolve 4xx, remove soft-404s, and replace chains with direct 200s. Update internal links to the final URL and audit outbound links for quality/availability.
Crawl regularly. Resolve 4xx, remove soft-404s, and replace chains with direct 200s. Update internal links to the final URL and audit outbound links for quality/availability.
-
Optimize JavaScript Rendering & Crawlability
 Allow bots to fetch JS/CSS. Prefer SSR/SSG or reliable hydration for primary content. Avoid render-blocking for critical content and JS-only routes for core navigation/content.
Allow bots to fetch JS/CSS. Prefer SSR/SSG or reliable hydration for primary content. Avoid render-blocking for critical content and JS-only routes for core navigation/content.
-
Configure Server Rewrites & Headers
 Centralize canonical host/protocol redirects, HSTS, compression (Brotli/Gzip), caching, and security headers. Use proper equivalents on Nginx/others. Version-control and test all changes.
Centralize canonical host/protocol redirects, HSTS, compression (Brotli/Gzip), caching, and security headers. Use proper equivalents on Nginx/others. Version-control and test all changes.
-
Run Blocklist & Safe-Browsing Checks
 Check Google Safe Browsing, Bing, major malware/phishing lists, and spam DNSBLs. If listed, clean the issue, harden the site, and request review. Re-scan periodically.
Check Google Safe Browsing, Bing, major malware/phishing lists, and spam DNSBLs. If listed, clean the issue, harden the site, and request review. Re-scan periodically.
-
Implement Structured Data Correctly
 Mark up only visible/relevant content (Organization, Breadcrumb, Article/Product/FAQ/HowTo). Validate with Rich Results Test, fix warnings, avoid spam/duplication, and keep markup in sync with the page.
Mark up only visible/relevant content (Organization, Breadcrumb, Article/Product/FAQ/HowTo). Validate with Rich Results Test, fix warnings, avoid spam/duplication, and keep markup in sync with the page.
-
Fix Console Errors
 Audit for JS exceptions, failed asset requests, mixed content/CORS/CSP issues. Fix anything that blocks render or interactivity. Defer non-critical third-party scripts.
Audit for JS exceptions, failed asset requests, mixed content/CORS/CSP issues. Fix anything that blocks render or interactivity. Defer non-critical third-party scripts.
-
Minify & Optimize CSS
 Minify and combine where sensible, extract critical CSS, preload key styles, and purge unused rules. Ensure CSS files return 200, are cacheable, and aren’t blocked in robots.txt.
Minify and combine where sensible, extract critical CSS, preload key styles, and purge unused rules. Ensure CSS files return 200, are cacheable, and aren’t blocked in robots.txt.
-
Secure Pages & Eliminate Errors
 Enforce HTTPS with valid TLS and HSTS. Remove mixed content and fix 4xx/5xx. Run security scans and patch platform/plugins promptly.
Enforce HTTPS with valid TLS and HSTS. Remove mixed content and fix 4xx/5xx. Run security scans and patch platform/plugins promptly.
-
Fix Canonicalization Issues
 Use self-canonicals on indexable pages. Don’t canonicalize to blocked/4xx/noindex URLs or mix noindex with canonical to another page. Keep canonicals consistent across desktop/mobile and in sitemaps.
Use self-canonicals on indexable pages. Don’t canonicalize to blocked/4xx/noindex URLs or mix noindex with canonical to another page. Keep canonicals consistent across desktop/mobile and in sitemaps.
-
Ensure No-JS Access & Crawlability
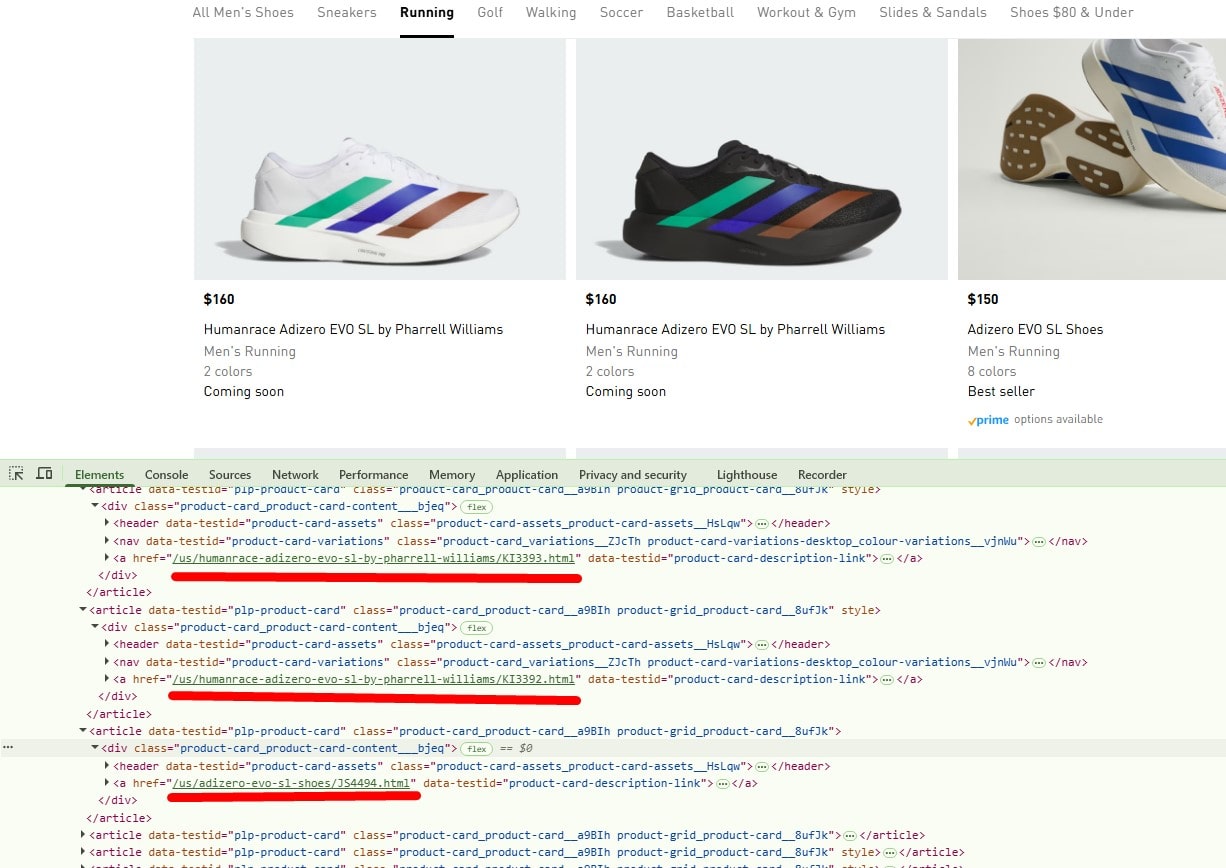 Expose key content/links in HTML. Provide URL-based navigation (not JS-only). Pre-render/SSR heavy JS pages and support paginated URLs for infinite scroll.
Expose key content/links in HTML. Provide URL-based navigation (not JS-only). Pre-render/SSR heavy JS pages and support paginated URLs for infinite scroll.
-
Audit Neighboring Sites on the Server
 Review other vhosts on the same server/IP for spam/malware that could harm reputation. Isolate risky apps, patch software, and ensure proper TLS/SNI and robots/security headers per host.
Review other vhosts on the same server/IP for spam/malware that could harm reputation. Isolate risky apps, patch software, and ensure proper TLS/SNI and robots/security headers per host.
-
Review Domain History & Reputation
 Check the Wayback Machine, previous owners/uses, past redirects, and penalties. Clean up legacy issues (remove bad pages, keep/update disavow) before migrations or relaunches.
Check the Wayback Machine, previous owners/uses, past redirects, and penalties. Clean up legacy issues (remove bad pages, keep/update disavow) before migrations or relaunches.
-
Meet Accessibility (WCAG) Basics
 Deliver core WCAG: color contrast, keyboard navigation, focus states, semantic landmarks, labels/alt text, and minimal/accurate ARIA. Audit with Lighthouse/axe and fix blockers.
Deliver core WCAG: color contrast, keyboard navigation, focus states, semantic landmarks, labels/alt text, and minimal/accurate ARIA. Audit with Lighthouse/axe and fix blockers.
-
Validate HTML (W3C)
 Validate templates and fix broken markup that affects rendering, DOM parsing, or structured data. Use semantic elements. Prioritize issues impacting UX, indexing, or schema.
Validate templates and fix broken markup that affects rendering, DOM parsing, or structured data. Use semantic elements. Prioritize issues impacting UX, indexing, or schema.
-
Show a Compliant Cookie Banner
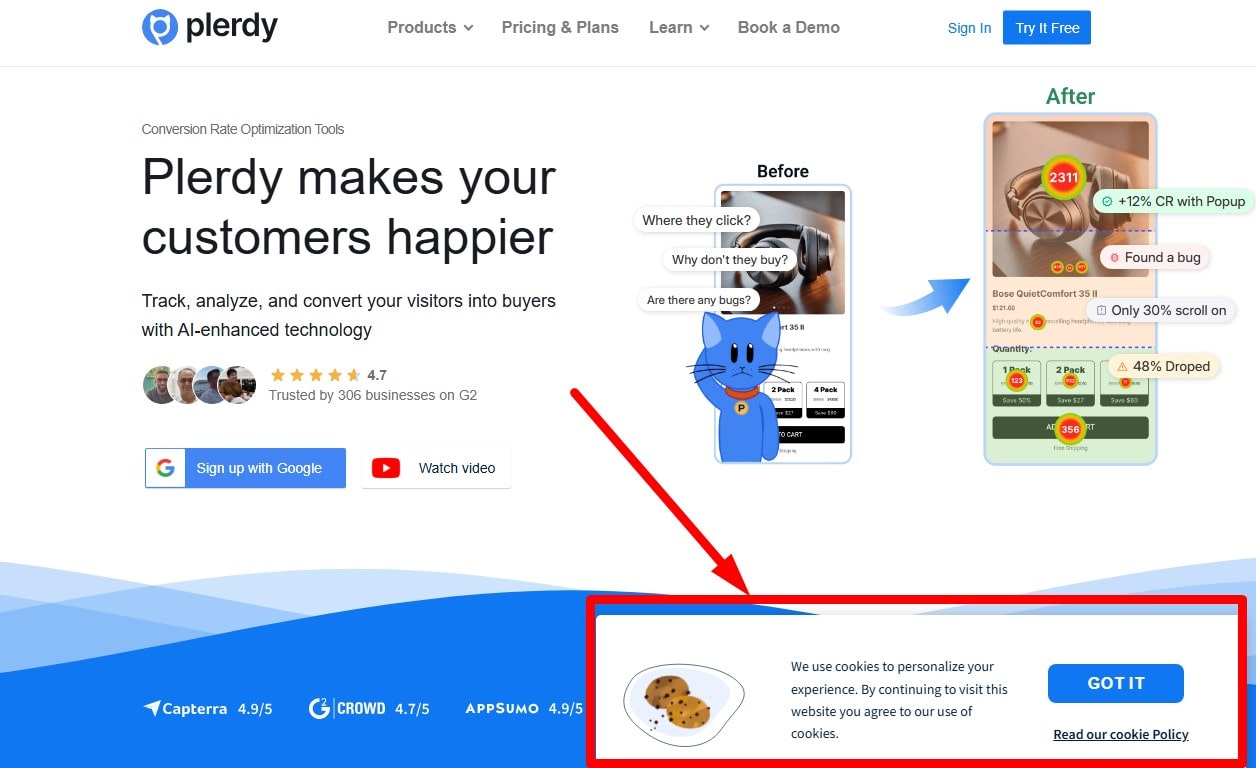 Display a lightweight, accessible banner that doesn’t block content or cause CLS. Honor regional consent rules; don’t load non-essential trackers before consent. Store/renew consent and provide easy preferences.
Display a lightweight, accessible banner that doesn’t block content or cause CLS. Honor regional consent rules; don’t load non-essential trackers before consent. Store/renew consent and provide easy preferences.
-
Handle Migrations, Parameters & Status Codes
 Plan migrations carefully. Use 301/308 for permanent moves, avoid chains/loops, and update internal links. Canonicalize or noindex tracking params (UTM, etc.). Use 410 for removed content and 304 for unchanged resources.
Plan migrations carefully. Use 301/308 for permanent moves, avoid chains/loops, and update internal links. Canonicalize or noindex tracking params (UTM, etc.). Use 410 for removed content and 304 for unchanged resources.
📷 Images/Video
-
Audit Sitewide Image Usage
 Too many images can slow down the page, leading to poor user experience and lower ranking. Measure image count and total bytes by template (home, PLP, PDP, blog). Remove decorative bloat, compress aggressively, and avoid image-heavy carousels. Prioritize content images that support the task and LCP. Track image bytes and LCP in field data; cut or replace non-essential assets.
Too many images can slow down the page, leading to poor user experience and lower ranking. Measure image count and total bytes by template (home, PLP, PDP, blog). Remove decorative bloat, compress aggressively, and avoid image-heavy carousels. Prioritize content images that support the task and LCP. Track image bytes and LCP in field data; cut or replace non-essential assets.
-
Optimize Images
 Serve modern formats (AVIF/WebP with fallbacks), compress to perceptual quality, and export at the exact display dimensions. Add width/height (or intrinsic size) to prevent CLS, lazy-load below-the-fold, and use fetchpriority="high"/preload for the hero image. Verify with Lighthouse/PageSpeed and CrUX.
Serve modern formats (AVIF/WebP with fallbacks), compress to perceptual quality, and export at the exact display dimensions. Add width/height (or intrinsic size) to prevent CLS, lazy-load below-the-fold, and use fetchpriority="high"/preload for the hero image. Verify with Lighthouse/PageSpeed and CrUX.
-
Provide Meaningful Alt Text
 Write concise, contextual alt text for informative images; use empty alt="" for purely decorative ones. Don’t stuff keywords. Ensure icons/SVGs conveying meaning have labels. Audit with axe/Lighthouse and your crawler’s “images without alt” report.
Write concise, contextual alt text for informative images; use empty alt="" for purely decorative ones. Don’t stuff keywords. Ensure icons/SVGs conveying meaning have labels. Audit with axe/Lighthouse and your crawler’s “images without alt” report.
-
Fix Broken Images
 Crawl for 404/410 image requests and broken src/CDN links. Replace or remove dead assets, update internal references, and add resilient fallbacks (e.g., placeholder). Monitor image errors in logs/console and validate that critical images return 200 and cache correctly.
Crawl for 404/410 image requests and broken src/CDN links. Replace or remove dead assets, update internal references, and add resilient fallbacks (e.g., placeholder). Monitor image errors in logs/console and validate that critical images return 200 and cache correctly.
-
Use Original, Contextual Images (Limit Stock)
 Prefer real product shots, UI screenshots, data visuals, and custom illustrations. Stock is acceptable sparingly and only when clearly relevant. Optimize filenames/alt text, compress, and A/B test impact on engagement and conversions.
Prefer real product shots, UI screenshots, data visuals, and custom illustrations. Stock is acceptable sparingly and only when clearly relevant. Optimize filenames/alt text, compress, and A/B test impact on engagement and conversions.
-
Use Modern Formats & Responsive Images
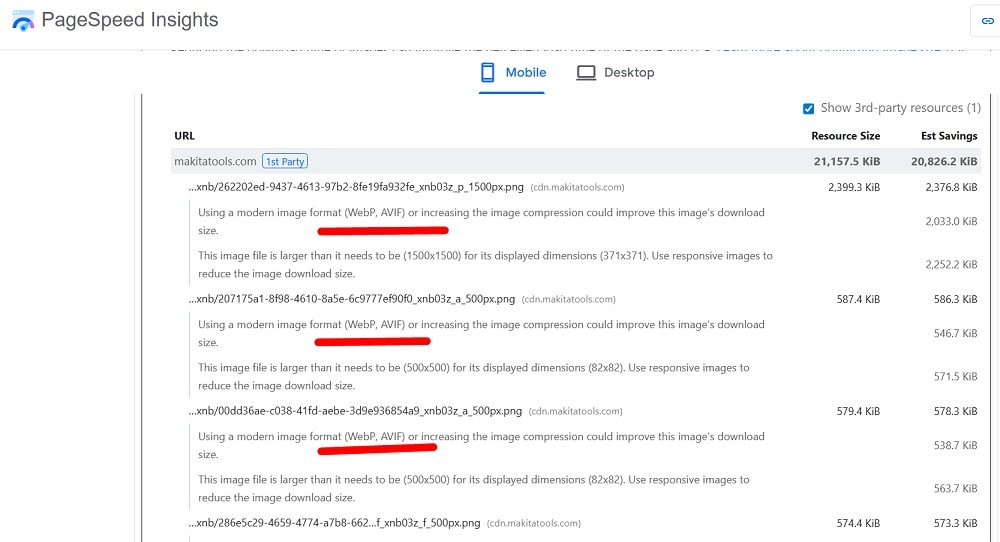 Implement <picture> with AVIF/WebP sources and fallback PNG/JPG. Provide srcset/sizes for responsive delivery, add intrinsic dimensions, and lazy-load non-critical images. Verify coverage in Search Console and watch CLS/LCP in field data.
Implement <picture> with AVIF/WebP sources and fallback PNG/JPG. Provide srcset/sizes for responsive delivery, add intrinsic dimensions, and lazy-load non-critical images. Verify coverage in Search Console and watch CLS/LCP in field data.
-
Implement Video SEO Essentials
 Add VideoObject schema, transcripts/captions, and a static poster image. Place the key video high on the page with supporting copy, ensure bots can fetch the file (no blocked CDN), and provide a video sitemap if video is core. Offer transcript sections for long videos and test playback/performance.
Add VideoObject schema, transcripts/captions, and a static poster image. Place the key video high on the page with supporting copy, ensure bots can fetch the file (no blocked CDN), and provide a video sitemap if video is core. Offer transcript sections for long videos and test playback/performance.
🔎 Competition analysis
-
Identify Top 3–5 Competitors
 Use SERP for your primary topics plus tools (Ahrefs/Semrush “Competitors”, Similarweb, G2 if B2B) to find true search competitors (not just business rivals). Prioritize by keyword overlap %, non-brand traffic, topical match, and region. Log domains, key sections, and notes in a sheet.
Use SERP for your primary topics plus tools (Ahrefs/Semrush “Competitors”, Similarweb, G2 if B2B) to find true search competitors (not just business rivals). Prioritize by keyword overlap %, non-brand traffic, topical match, and region. Log domains, key sections, and notes in a sheet.
-
Benchmark Competitors
 Build a benchmark table: organic traffic/visibility, #ranking keywords (non-brand), share of voice for target topics, linking root domains/DR, content cadence, SERP features held, CWV basics, and site speed. Capture baseline now; re-measure monthly to show delta and opportunities.
Build a benchmark table: organic traffic/visibility, #ranking keywords (non-brand), share of voice for target topics, linking root domains/DR, content cadence, SERP features held, CWV basics, and site speed. Capture baseline now; re-measure monthly to show delta and opportunities.
-
Document Each Competitor’s Top 10 Keywords
 Export each competitor’s top non-branded keywords (position, URL, volume, KD, intent). Keep it to their 10 most impactful terms per product/topic. Tag by funnel stage, cluster to themes, and mark pages you can beat (weaker content, thin links, outdated info).
Export each competitor’s top non-branded keywords (position, URL, volume, KD, intent). Keep it to their 10 most impactful terms per product/topic. Tag by funnel stage, cluster to themes, and mark pages you can beat (weaker content, thin links, outdated info).
-
Track Competitors’ Average Positions
 Create a shared keyword set (your target terms). Use Position Tracking (Semrush/Ahrefs) to monitor average position, visibility %, and winners/losers weekly. Segment by cluster (product, category, geo) to see where you’re losing and assign actions.
Create a shared keyword set (your target terms). Use Position Tracking (Semrush/Ahrefs) to monitor average position, visibility %, and winners/losers weekly. Segment by cluster (product, category, geo) to see where you’re losing and assign actions.
-
List Top-Ranking Keywords (All Players)
 Compile the current top-ranking keywords across your niche (who owns #1–3, which URL, and the intent). Note SERP features (snippets, FAQs, videos) and gaps where no one satisfies intent well. Feed this into your content plan and link-building targets.
Compile the current top-ranking keywords across your niche (who owns #1–3, which URL, and the intent). Note SERP features (snippets, FAQs, videos) and gaps where no one satisfies intent well. Feed this into your content plan and link-building targets.
🏠 Local SEO
-
Confirm Local Traffic Need
 Use GA4 (Reports → Acquisition) with City/Region dimensions to see how much traffic/conversions are local. Check SERPs for your queries—if you see map packs/“near me,” local intent exists. If the business serves a city/region or has physical locations, prioritize Local SEO (GBP, location pages, citations); if fully national/online-only with no local intent, de-prioritize.
Use GA4 (Reports → Acquisition) with City/Region dimensions to see how much traffic/conversions are local. Check SERPs for your queries—if you see map packs/“near me,” local intent exists. If the business serves a city/region or has physical locations, prioritize Local SEO (GBP, location pages, citations); if fully national/online-only with no local intent, de-prioritize.
-
Use Localized Title Tags
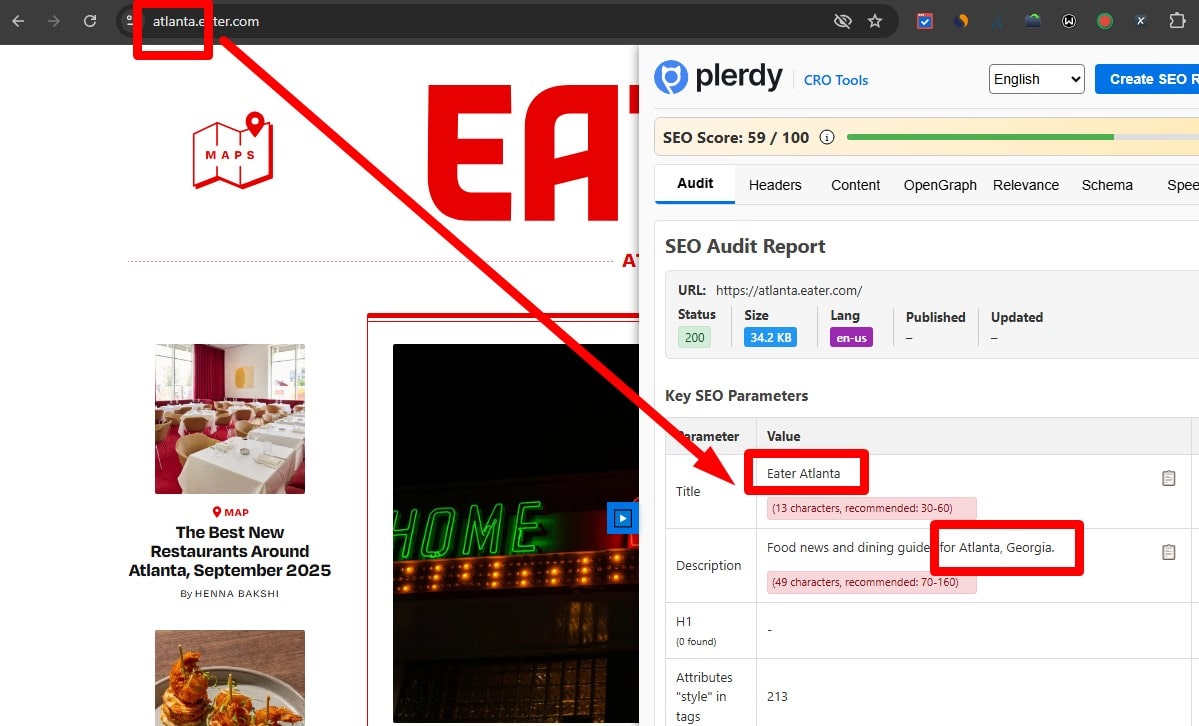 Include city/region in titles where local intent applies (e.g., “Plumber in Austin, TX | Brand”). Keep it natural, 50–60 chars, 1 location per page, and match on-page H1/URL. Avoid stuffing multiple cities in one title—use separate location/service pages.
Include city/region in titles where local intent applies (e.g., “Plumber in Austin, TX | Brand”). Keep it natural, 50–60 chars, 1 location per page, and match on-page H1/URL. Avoid stuffing multiple cities in one title—use separate location/service pages.
-
Implement Local Business Structured Data
 Add LocalBusiness (or a subtype) on each location page with @id, name, address, telephone, geo, openingHours, priceRange, and sameAs. Ensure NAP exactly matches GBP. Validate in Rich Results/Schema Markup Validator. Use Organization schema on global pages; LocalBusiness on location pages.
Add LocalBusiness (or a subtype) on each location page with @id, name, address, telephone, geo, openingHours, priceRange, and sameAs. Ensure NAP exactly matches GBP. Validate in Rich Results/Schema Markup Validator. Use Organization schema on global pages; LocalBusiness on location pages.
-
Set Up & Optimize Google Business Profile
 Verify GBP, select the best primary and relevant secondary categories, set accurate NAP, hours/holiday hours, service area, and UTM on website/menu links. Add quality photos, products/services, FAQs (Q&A), posts, and enable messaging/booking where relevant. Encourage and respond to reviews. Ensure on-site NAP/schema matches GBP.
Verify GBP, select the best primary and relevant secondary categories, set accurate NAP, hours/holiday hours, service area, and UTM on website/menu links. Add quality photos, products/services, FAQs (Q&A), posts, and enable messaging/booking where relevant. Encourage and respond to reviews. Ensure on-site NAP/schema matches GBP.
-
Apply Local SEO Fundamentals (NAP, GBP, Reviews)
 Keep NAP 100% consistent across your site, GBP, and top citations (Apple Business Connect, Bing Places, Yelp, industry/local directories). Build local links (sponsorships, chambers, events). Create unique city/service pages with helpful content and embedded map. Collect/respond to reviews; add internal links from relevant pages. Track performance with UTM tags and GBP Insights.
Keep NAP 100% consistent across your site, GBP, and top citations (Apple Business Connect, Bing Places, Yelp, industry/local directories). Build local links (sponsorships, chambers, events). Create unique city/service pages with helpful content and embedded map. Collect/respond to reviews; add internal links from relevant pages. Track performance with UTM tags and GBP Insights.